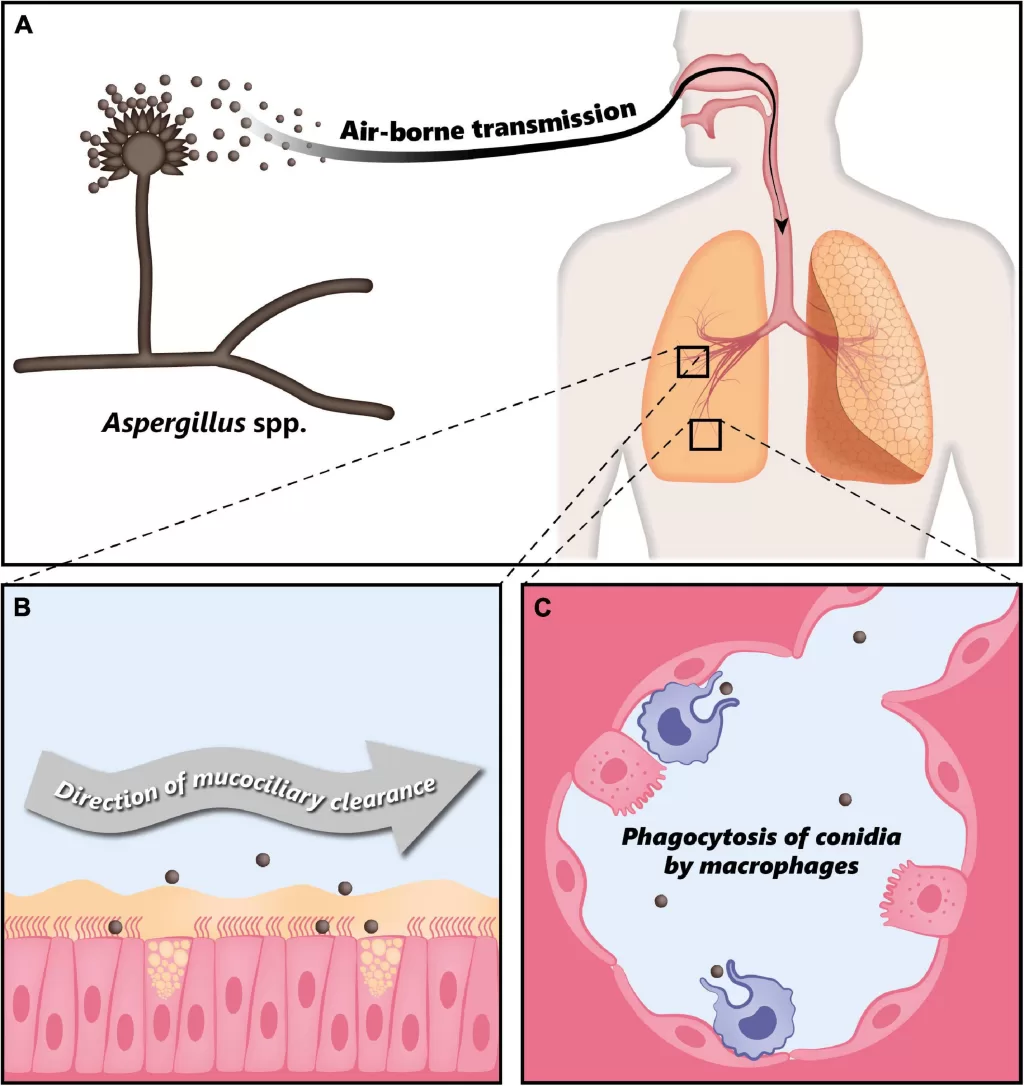
Fungal spores and respiratory illness have emerged as critical topics in public health discussions, particularly in light of recent research linking increased airborne fungal spores to heightened cases of influenza and COVID-19. This connection underscores the importance of understanding how environmental factors can influence respiratory infections, especially in densely populated areas where spores are prevalent. Researchers from the American Society for Microbiology found that spikes in fungal spore counts aligned closely with surges in respiratory illnesses, providing significant insights into managing viral outbreaks. Furthermore, these findings highlight the need for public health alerts to be updated and informed by environmental data. By monitoring these airborne fungal spores, health officials can potentially predict and mitigate the impact of respiratory illnesses on vulnerable populations, including the elderly and those with preexisting conditions.
The relationship between airborne particulates and respiratory health issues has garnered increasing attention in the field of epidemiology. Environmental factors, such as levels of fungal microorganisms in the atmosphere, may significantly contribute to the rise in respiratory infections, including those caused by viruses like COVID-19 and influenza. Current findings suggest that fluctuations in the concentration of these microscopic spores can serve as precursors to viral outbreaks, warranting the development of targeted health advisories. As researchers delve deeper into the interplay between environmental factors and infectious disease patterns, the potential for proactive public health measures becomes increasingly apparent. Such strategies could not only improve early detection but also protect at-risk groups in our communities.
The Link Between Fungal Spores and Respiratory Illness
Research has shown a significant connection between airborne fungal spores and respiratory illness outbreaks, particularly influenza and COVID-19. A thorough study conducted in Puerto Rico revealed that surges in fungal spores correlate directly with increases in respiratory infections. This correlation underscores how environmental factors can significantly influence public health concerns. Thus, understanding the dynamics of fungal spores in the environment is crucial for developing effective health management strategies.
The presence of airborne fungal spores acts as an indicator for potential health risks, particularly for vulnerable populations. The analysis conducted between 2022 and 2024 highlighted that as fungal spore levels rise, so does the incidence of respiratory diseases. This revelatory information suggests that public health alerts can be effectively enhanced by monitoring fungal spore activity, offering a proactive approach to controlling respiratory infections.
Impact of Airborne Fungal Spores on COVID-19 and Influenza Cases
The findings from the annual meeting of the American Society for Microbiology have spotlighted the often-overlooked impact that airborne fungal spores can have on respiratory diseases like COVID-19 and influenza. During times of increased fungal spore activity, public health officials observed significant spikes in flu and COVID-19 cases. This indicates that, in controlling outbreaks of these respiratory illnesses, monitoring of fungal spores might be as crucial as tracking human-to-human transmission rates.
Incorporating fungal spore data into public health strategies can potentially revolutionize how we respond to respiratory virus outbreaks. By regularly monitoring fungal spore levels, health authorities could detect patterns and predict spikes in illnesses, prompting timely public health responses, particularly in regions where these spores are prevalent. Educating the public about the relationship between airborne fungal spores and respiratory infections could be an essential step in reinforcing community health.
Public Health Alerts and Environmental Factors
The study reveals that environmental factors should not be underestimated when considering outbreaks of respiratory diseases. Traditional models have focused primarily on transmission dynamics; however, the increasing recognition of fungal spores as key players shifts the focus towards more comprehensive public health strategies. With the data suggesting a robust link between spore levels and illness rates, crafting public health alerts based on spore counts could be vital in informing at-risk populations.
Furthermore, integrating environmental monitoring into public health systems has the potential to create new avenues for community health safety. Alerts could be tailored specifically to areas experiencing high spore counts, thus enabling targeted preventive measures for vulnerable individuals, such as the elderly or those with chronic asthma. This dual approach, combining epidemiological data with environmental monitoring, promises to enhance public health initiatives.
Understanding the Role of Fungal Spores in Public Health
As the recent findings emphasize, airborne fungal spores are more than mere airborne particulates; they play a significant role in respiratory health. The evidence gathered over the years reflects a growing need for public health officials to revisit existing models of disease tracking by incorporating fungal spore data. This shift could lead to timely interventions and potentially reduced transmission rates for respiratory illnesses such as COVID-19 and influenza.
In light of these findings, enhancing awareness about the link between environmental conditions and public health becomes imperative. Communities can be educated about the importance of monitoring their surroundings for factors such as fungal spore levels which could serve as an early warning system. Ultimately, this leads to smarter public health interventions that are rooted not just in pathogens but also in the environment.
Mitigating Risks During High Fungal Spore Seasons
Recognizing the cyclical nature of fungal spore emissions can be crucial for public health preparedness. Researchers suggest that in certain regions, particularly tropical climates like Puerto Rico, seasonal patterns of fungal spores are predictable. By anticipating these spikes, health authorities can implement proactive measures such as public announcements, recommendations for vulnerable populations to stay indoors, and the distribution of protective equipment.
Additionally, increased surveillance during these high-risk periods can help in identifying abrupt changes in respiratory disease incidences, allowing for a more effective response to potential outbreaks. Communities and healthcare providers must collaborate to develop strategies that mitigate the risks associated with high fungal spore levels, thus safeguarding public health.
Potential Interventions for Vulnerable Populations
To enhance public safety amidst rising spore counts, tailored interventions for high-risk groups must be prioritized. Elderly individuals and people with preexisting respiratory conditions, such as asthma, need specific guidance and resources to reduce exposure to fungal spores. These interventions could include disseminating information regarding the times of elevated spore counts, suggesting indoor activities during those periods, and providing resources such as air filters.
Moreover, creating a robust database that tracks spore levels and correlates them with respiratory illness incidence could serve as a valuable tool for healthcare providers. Making this information readily accessible to the public can empower individuals to take personal responsibility for their health, leading to broader community engagement in health initiatives.
Research Innovations in Fungal Spore Monitoring
Advancements in technology now allow for more sophisticated monitoring of airborne fungal spores, which can significantly enhance our understanding of their impact on respiratory illnesses. Studies utilizing real-time data collection methods have shown that integrating technology into public health surveillance can provide comprehensive insights into environmental health threats. This innovation holds promise for early detection of spikes in respiratory infections.
The application of such technologies not only aids public health professionals in issuing timely advisories but also potentially influences the development of new treatment protocols that address environmental triggers for respiratory conditions. By continuing to invest in this area of research, we can bolster our public health infrastructure against respiratory outbreaks, thereby establishing more robust mechanisms for managing health crises.
Public Awareness and Education on Respiratory Health
Raising public awareness about the risks associated with airborne fungal spores is vital for fostering a proactive health-conscious society. Educational campaigns can inform communities about the potential dangers posed by increased spore levels, particularly during certain seasons or weather conditions. This type of public health effort empowers individuals to take informed actions, such as minimizing outdoor activity during high spore counts or ensuring adequate ventilation indoors.
Moreover, educational initiatives can effectively demystify the connection between fungi and respiratory illnesses, breaking down barriers of misinformation. By enhancing public understanding and providing practical guidance on mitigating risks, we can promote healthier communities capable of navigating fluctuations in environmental health challenges.
Future Directions in Fungal Research and Public Health
The link between fungal spores and respiratory diseases opens up numerous avenues for future research. Investigating the mechanisms through which spores influence respiratory health could lead to significant breakthroughs in public health policy and intervention strategies. Understanding the biology of these fungi and their relationship with viral pathogens could illuminate novel pathways for preventing respiratory infections.
Furthermore, funding and resources should be allocated to interdisciplinary studies that bridge mycology with epidemiology. By fostering collaboration across various fields of study, we can enhance our understanding and develop comprehensive strategies to address the challenges posed by environmental health threats. As we move forward, the integration of fungal research into public health considerations will be essential for safeguarding community health.
Frequently Asked Questions
How are fungal spores related to respiratory illness like COVID-19 and influenza?
Recent research indicates a strong correlation between increased levels of airborne fungal spores and the surges in respiratory illnesses, specifically COVID-19 and influenza. The study showed that elevated fungal spore counts matched spikes in flu and COVID cases, suggesting that monitoring these spores may help predict outbreaks of respiratory infections.
Can monitoring airborne fungal spores help public health efforts for respiratory infections?
Yes, monitoring airborne fungal spores could assist public health systems in predicting short-term spikes in respiratory infections like COVID-19 and influenza. The data collected on spore counts can provide early warning signals, enabling targeted public health alerts, especially in regions with higher levels of airborne fungi.
What pollutants should be monitored alongside fungal spores for respiratory health?
While the study primarily focuses on fungal spores, it highlights the importance of air quality monitoring in general, which includes pollutants like pollen and other allergens. However, the researchers found no correlation between pollen levels and respiratory illness, making fungal spores a crucial factor for public health surveillance.
Who is most at risk from increased airborne fungal spores and respiratory illnesses?
Vulnerable populations, such as the elderly and individuals with pre-existing conditions like asthma, are at heightened risk from increased airborne fungal spores and their association with respiratory infections, including COVID-19 and influenza. Public health measures may need to focus on these groups during high fungal spore activity.
What environmental conditions contribute to increased levels of fungal spores?
Environmental factors such as humidity, temperature, and seasonal changes significantly contribute to the prevalence of airborne fungal spores. Areas with endemic fungi, like Puerto Rico, often see consistent spore presence year-round, which may relate to incident rates of respiratory infections like influenza and COVID-19.
Are fungal spores a major factor in respiratory infections compared to viral transmission?
The findings suggest that fungal spores could be a significant environmental factor in the incidence of respiratory infections, aside from traditional person-to-person transmission. This highlights the need for a multifaceted approach to tackling respiratory illnesses, considering both environmental and viral factors.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Increased fungal spores linked to illness spikes | Study shows a strong correlation between high airborne fungal spore levels and surges in flu and COVID-19 cases based on data from San Juan and Caguas, Puerto Rico. |
| Fungal spores vs pollen | No correlation was found between pollen levels and respiratory illness; only fungal spores were linked to illness spikes. |
| Monitoring spores for health alerts | Researchers suggest that tracking airborne fungal spore levels could provide an early warning for outbreaks of flu and COVID-19. |
| Public health implications | Findings could lead to environmental risk alerts, targeting vulnerable populations like the elderly or individuals with asthma. |
Summary
Fungal spores and respiratory illness are intricately linked, as recent research indicates that heightened levels of fungal spores in the atmosphere correlate strongly with increased cases of influenza and COVID-19. Conducted in Puerto Rico, the study presents a significant step toward understanding the role of environmental factors in viral infections. This new data suggests that monitoring fungal spore levels may not only help predict short-term illness outbreaks but also enhance public health responses, particularly for at-risk groups. Addressing this connection could open doors for innovative approaches to managing respiratory illnesses tied to airborne pathogens.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.