Maternal syphilis is emerging as a significant public health crisis, with alarming statistics revealing a 28% increase in maternal syphilis rates in the United States from 2022 to 2024. The National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) reports that this rise is part of a much larger trend, with rates climbing over 200% in the past decade. Congenital syphilis, which can result from an untreated maternal syphilis infection, poses severe risks to newborns, including low birth weight and even fetal death. The urgency for effective syphilis treatment and comprehensive prenatal care has never been more critical, as these conditions are largely preventable through routine screenings and early intervention. Addressing the rising rates of maternal syphilis is essential to combat the surge in congenital syphilis cases and ensure healthier outcomes for mothers and their babies.
The term “maternal syphilis” encompasses instances of syphilis infections that occur during pregnancy, affecting both the health of the mother and child. This public health concern is intricately linked to issues surrounding prenatal care and the alarming rise in congenital syphilis cases. As syphilis treatment efforts falter due to systemic gaps in healthcare access, vulnerable populations face heightened risks. The consequences extend beyond individual cases, indicating a broader health crisis exacerbated by socio-economic disparities. Effective interventions are crucial to reverse this troubling trend and safeguard future generations from the devastating effects of untreated maternal infections.
Increasing Maternal Syphilis Rates: A Growing Concern
Maternal syphilis rates have skyrocketed over the last decade, with a staggering increase of over 200% since 2012. This alarming trend not only raises concerns about the health of mothers but also has dire implications for newborns, as maternal syphilis is directly linked to congenital infections. The National Center for Health Statistics reported a 28% hike from 2022 to 2024, marking an unprecedented period in which maternal health outcomes have dramatically deteriorated. As these figures climb, so does the urgency for public health initiatives focused on preventive measures and education surrounding prenatal care.
Increased maternal syphilis rates necessitate a comprehensive approach to combat this public health crisis. This includes enhanced screening during early prenatal visits, which can significantly reduce transmission rates to the fetus. Moreover, raising awareness about syphilis prevention and treatment options is crucial, particularly in populations at higher risk. The rise in cases demonstrates an urgent need for healthcare systems to adapt and address these urgent needs, ensuring that all expectant mothers receive the necessary support and medical care.
Impact of Maternal Syphilis on Congenital Syphilis Rates
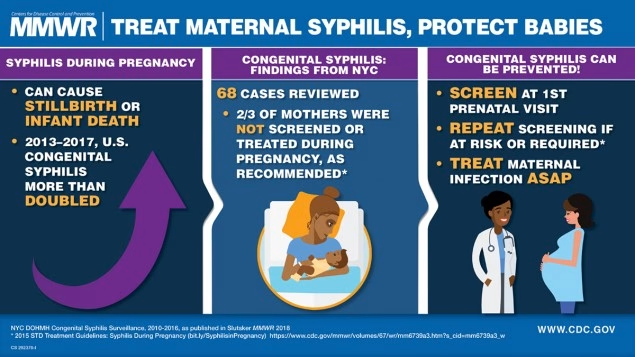
The alarming rise in maternal syphilis rates directly correlates with a surge in congenital syphilis cases. With more mothers contracting syphilis, the risk of transmitting the infection to their infants increases, leading to severe health outcomes. In 2023, the U.S. recorded its highest congenital syphilis cases since 1992, a statistic that underscores the devastating consequences of untreated maternal infections. These infections can result in significant complications for newborns, including fetal and neonatal death, low birth weights, and various long-term cognitive and physical disabilities.
Preventing congenital syphilis relies heavily on proper treatment and care of maternal syphilis cases. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention emphasize that timely treatment with penicillin during pregnancy can almost entirely prevent congenital syphilis. As public health systems continue to grapple with rising rates, the focus must shift to ensuring that all pregnant women have access to adequate screening and treatment options. Without these measures, the cycle of maternal infection and its transmission to infants will only perpetuate.
Addressing Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Maternal Syphilis
Racial and ethnic disparities substantially impact maternal syphilis rates, revealing a critical public health issue that requires targeted intervention. For instance, American Indian and Alaska Native mothers have experienced a staggering increase of 52% in maternal syphilis rates from 2022 to 2024. This highlights an alarming trend of increased vulnerability among specific demographic groups, underscoring the need for culturally competent healthcare and targeted public health strategies to address these disparities.
The need for equitable access to prenatal care and syphilis screening is essential in reversing these troubling trends. By focusing on the social determinants of health that contribute to these disparities, such as access to healthcare resources and education, public health authorities can implement programs tailored to at-risk populations. Reducing these racial and ethnic disparities is not only a matter of fairness but also a public health necessity in order to combat the escalating rates of maternal and congenital syphilis.
The Importance of Prenatal Care in Syphilis Prevention
Prenatal care plays a pivotal role in preventing maternal syphilis and its associated complications. Regular screenings and timely interventions can significantly diminish the risks associated with untreated syphilis during pregnancy. Routine testing for sexually transmitted infections, including syphilis, allows for early diagnosis and treatment, which are crucial for both maternal and fetal health. When effectively integrated into prenatal care protocols, these screenings can drastically reduce the incidence of congenital syphilis.
Enhancing prenatal care access is vital in addressing rising syphilis rates. Public health policies that promote inclusivity and accessibility in maternal healthcare must be prioritized to ensure that all pregnant women receive comprehensive care. Increased focus on health education, emphasizing the importance of regular check-ups and screenings, can empower women to seek necessary medical assistance, ultimately aiding in the reduction of maternal and congenital syphilis rates.
Understanding the Public Health Crisis of Maternal Syphilis
The surge in maternal syphilis cases in the U.S. is a glaring indicator of a wider public health crisis that has developed over the past few years. Once nearing eradication, syphilis has re-emerged as a significant health threat, affecting vulnerable populations disproportionately. The rise in maternal syphilis is inextricably linked to systemic issues within public health infrastructure, including inadequate screening capabilities and lack of access to necessary treatment for pregnant women.
Addressing this crisis requires a multi-faceted response, integrating policy reforms, enhanced educational efforts, and targeted interventions to improve treatment access, especially for underserved communities. As health authorities work to combat these rising rates, it becomes increasingly clear that investing in public health initiatives will be essential in reversing this trend, safeguarding both maternal and infant health during this critical period.
The Role of Syphilis Treatment in Maternal Health
Effective treatment of maternal syphilis is essential in preventing adverse health outcomes for both mothers and infants. Penicillin remains the recommended and effective treatment for pregnant women diagnosed with syphilis, and timely administration can prevent the transmission of the disease to the fetus. As the rates of maternal syphilis surge, ensuring that healthcare systems can provide adequate treatment becomes paramount in mitigating the public health implications of this rising crisis.
However, the nation currently faces a concerning shortage of injectable penicillin G benzathine, the only approved medication for treating syphilis in pregnant women, which poses an additional barrier to effective intervention. Addressing this shortage, while simultaneously ensuring that pregnant women are informed about their treatment options, is vital for assisting in the prevention of congenital syphilis and improving overall maternal health outcomes.
Impact of Maternal Syphilis on Long-term Child Health Outcomes
Maternal syphilis not only jeopardizes the immediate health of newborns but can also have lasting effects on child development and health. Children exposed to maternal syphilis in utero are at an elevated risk for hospitalization and may face prolonged health complications, which can strain both family and healthcare resources. Evidence indicates that such children may experience a myriad of health issues that could compromise their quality of life and development, necessitating proactive healthcare strategies.
To counter these potential long-term outcomes, public health officials must ensure pregnant women receive appropriate care and treatment for syphilis. Implementing effective screening protocols combined with accessible healthcare services can mitigate these negative impacts. Moreover, supporting families affected by maternal syphilis with ongoing medical care and resources is essential to improve health trajectories for these children.
The Role of Public Health Interventions in Combating Maternal Syphilis
Public health interventions play a crucial role in tackling the rising rates of maternal syphilis. Innovative programs focusing on education, outreach, and accessibility can significantly reduce the incidence of untreated syphilis among pregnant women. These interventions should prioritize areas with the highest rates of infection and ensure that comprehensive prenatal care, including syphilis screening, is integrated into standard healthcare practices.
Additionally, ongoing collaboration between health departments, community organizations, and healthcare providers can foster trust and ensure that expectant mothers receive necessary treatments. The implementation of policies that support access to care and improve health literacy about maternal syphilis can create a more informed public and lead to better health outcomes for mothers and their babies.
Looking Toward the Future: Strategies to Reduce Maternal Syphilis Rates
As the rates of maternal syphilis continue to rise, it is imperative for stakeholders to develop effective strategies aimed at reversing this trend. Future initiatives should encompass a holistic approach that integrates community health education, enhanced access to screening, and streamlined treatment protocols for syphilis among pregnant women. By focusing on prevention and early intervention, we can aim to reduce the vast impact of maternal syphilis on public health.
Moreover, fostering collaborations between healthcare providers and public health authorities can promote the sharing of best practices and resources, creating a more robust framework for tackling maternal syphilis. Continuous monitoring of syphilis rates and healthcare access will also be necessary to ensure that we remain proactive in our efforts, ultimately safeguarding maternal and fetal health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current state of maternal syphilis rates in the United States?
Maternal syphilis rates in the United States have seen a dramatic increase, rising by 28% from 2022 to 2024. As reported by the National Center for Health Statistics, the rates went from 280.4 to 357.9 cases per 100,000 births, highlighting the ongoing public health crisis surrounding maternal syphilis.
How does maternal syphilis contribute to congenital syphilis?
Maternal syphilis directly contributes to congenital syphilis when untreated infections in pregnant women lead to the transmission of syphilis to their fetuses. This can result in severe health complications for the newborn, including low birth weight, preterm birth, and even fetal death.
Why is prenatal care crucial in preventing maternal syphilis?
Prenatal care is essential in preventing maternal syphilis as routine early screening and adequate treatment with penicillin can almost entirely prevent congenital syphilis. Increased access to comprehensive prenatal services ensures that pregnant women are tested and treated promptly.
What are the effects of increasing maternal syphilis rates on public health?
Increasing maternal syphilis rates pose a significant public health crisis, contributing to a surge in congenital syphilis cases and adverse birth outcomes. High rates, especially among certain demographics and regions, signal urgent needs for improved public health interventions and prenatal care.
How are racial and ethnic disparities reflected in maternal syphilis rates?
Maternal syphilis rates display significant racial and ethnic disparities. For instance, from 2022 to 2024, American Indian and Alaska Native mothers experienced a 52% increase, while Hispanic and Black mothers saw increases of 31% and 30%, respectively, indicating a need for targeted public health responses.
What are the implications of untreated syphilis during pregnancy?
Untreated syphilis during pregnancy can result in severe implications for both the mother and child, including fetal and neonatal death, low birth weight, and developmental disorders in infants. Timely prenatal care and treatment are vital to mitigate these risks.
What role does penicillin play in syphilis treatment?
Penicillin is the only recommended treatment for syphilis in pregnant women and is crucial in preventing transmission to the fetus. A nationwide shortage of injectable penicillin G benzathine is currently exacerbating the rise in maternal syphilis rates and associated congenital outcomes.
What are the trends in maternal syphilis rates across different age groups?
Maternal syphilis rates have increased across all maternal age groups, with 36% rises among mothers aged 35 to 39 and 30% among those aged 30 to 34. Younger mothers also saw significant increases, highlighting the widespread nature of this public health issue.
How have regional disparities affected maternal syphilis rates?
Regional disparities are pronounced in maternal syphilis rates, with states like Mississippi experiencing over a 1,000% increase from 2013 to 2023. Such regional spikes reflect systemic healthcare gaps and necessitate urgent public health responses.
What measures can be taken to address the rising rates of maternal syphilis?
To address rising rates of maternal syphilis, public health initiatives should focus on enhancing prenatal screening, ensuring access to treatment, particularly penicillin, and implementing policies that increase access to obstetrical care for all pregnant women.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Increase in Maternal Syphilis Rate | 28% increase from 2022 to 2024, with rates escalating from 280.4 to 357.9 cases per 100,000 births. |
| Surge in Congenital Syphilis | Highest number of congenital syphilis cases reported in the US since 1992, linked to untreated maternal syphilis. |
| Racial and Ethnic Disparities | 52% increase in American Indian and Alaska Native mothers, 31% among Hispanic, 30% among Black, and 23% among White mothers (2022-2024). |
| Age Disparities | 36% increase in rates among mothers aged 35-39; 31% in those aged 40+; lower but significant increases in younger mothers. |
| Geographic Disparities | Mississippi’s maternal syphilis rates surged over 1,000% from 2013-2023, prompting a public health emergency declaration in 2025. |
| Gaps in Screening and Treatment | Over one-third of pregnant women with syphilis in Mississippi lacked treatment; nationwide shortage of penicillin worsening the crisis. |
Summary
Maternal syphilis is a serious and escalating public health issue in the United States, with the rate increasing significantly over the past few years. This alarming trend necessitates immediate action in the form of enhanced screening and treatment protocols to protect mothers and their newborns from the devastating effects of this preventable infection.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.