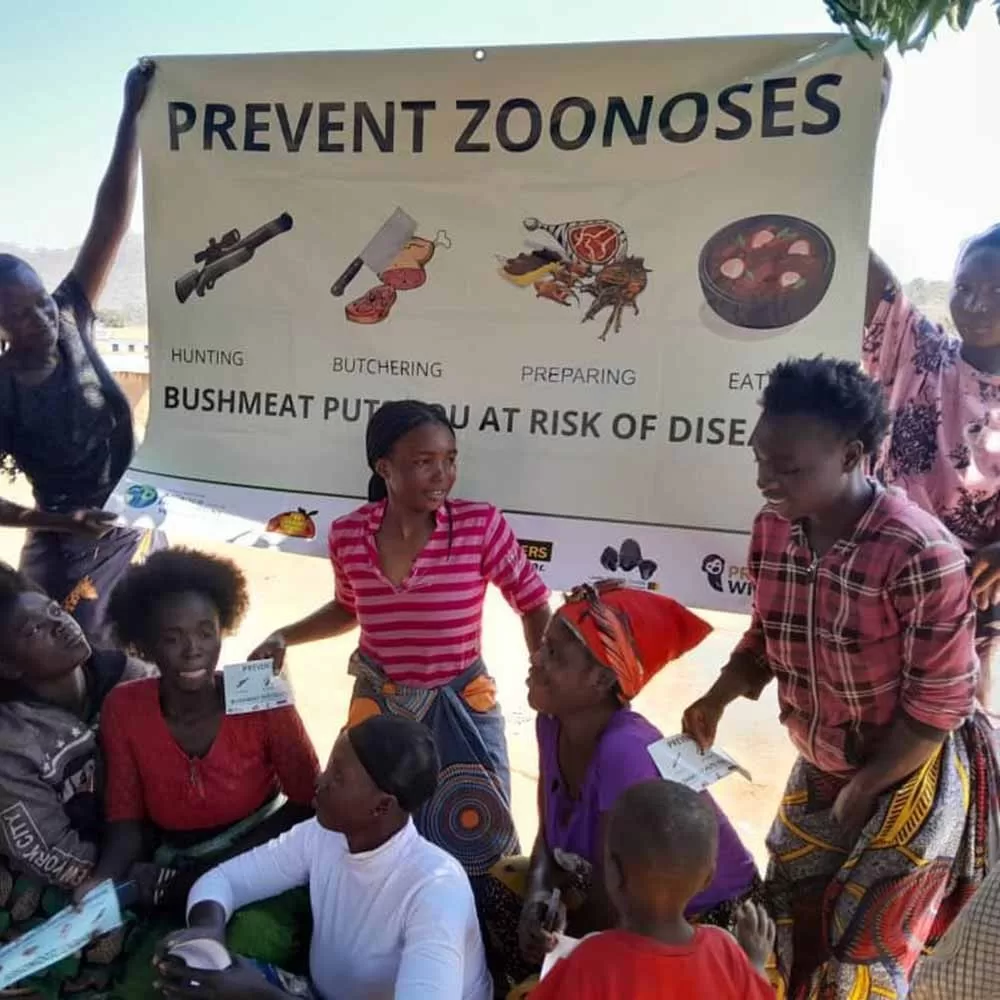
Zoonotic disease management in Zambia is becoming increasingly vital as the interconnections between humans, wildlife, and livestock intensify. In areas like the Nyawa Chiefdom, local communities are harnessing their unique understanding of Zambian zoonoses to address pressing health threats such as anthrax and heartwater. By implementing the One Health approach, these communities are fostering a holistic view that recognizes the importance of sustainable wildlife management alongside human and animal health. This community-driven strategy not only improves public health in Zambia but also leverages local knowledge for effective disease prevention, ultimately building healthier ecosystems. As the country navigates these complex relationships, the role of community health initiatives becomes more crucial than ever.
The challenge of managing diseases that can be transmitted between animals and humans—often referred to in the context of zoonoses—has gained significant attention in Zambia. This issue has sparked a proactive response from local populations, particularly in regions like the Nyawa Chiefdom, where there’s a rich tapestry of traditional knowledge regarding disease management. By integrating sustainable wildlife practices with a focus on community health, these initiatives aim to protect both people and wildlife from the threats posed by zoonotic infections. Engaging in collaborative efforts such as the One Health strategy emphasizes not only veterinary and medical care but also ecological balance and the significance of local expertise in disease prevention. Ultimately, these multifaceted approaches strive to cultivate resilience within communities while safeguarding public health.
Understanding Zoonotic Diseases in Zambia
Zambia experiences a range of zoonotic diseases that pose significant risks to community health. Among the most concerning are anthrax, heartwater, and Newcastle disease, which affect both livestock and wildlife. The interactions between humans, animals, and ecosystems create a complex landscape whereby disease transmission can occur. Understanding the epidemiology of these zoonoses is crucial to creating effective management strategies that protect both public health and biodiversity.
Local knowledge plays a significant role in the identification and management of these diseases in Zambia. Communities in regions like Nyawa Chiefdom actively engage in disease mapping and prioritization workshops, which are essential in recognizing the risks posed by zoonotic diseases. By combining scientific research with indigenous wisdom regarding animal health and environmental stewardship, communities can develop localized strategies for effective disease prevention.
The Role of Local Knowledge in Disease Prevention
In Nyawa Chiefdom, local communities have demonstrated a robust understanding of the zoonotic threats they face. This understanding often stems from generations of observation and experience interacting with wildlife and livestock. Local practices and knowledge about preventing disease transmission have become invaluable assets in the fight against zoonoses. Community members recognize when animals exhibit signs of illness and understand the importance of early intervention.
Training and empowering community members in disease surveillance and prevention strategies create a proactive approach to health management. Such initiatives elevate local voices, ensuring their insights inform public health policies and initiatives. As these communities collaborate with researchers and public health officials, the result is a synergistic effort that enhances the effectiveness of disease control and prevention measures.
Zoonotic Disease Management in Zambia
Effective zoonotic disease management in Zambia requires a multi-faceted approach that encompasses public health, wildlife management, and local community engagement. The One Health framework, which recognizes the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental health, is instrumental in addressing zoonotic risks. By implementing strategies that integrate veterinary services, wildlife conservation, and community health education, Zambia can work toward a holistic solution.
Efforts to establish programs like the Mize Community Conservancy are vital in this regard. These initiatives not only provide a structured environment for managing human-wildlife interactions but also emphasize the importance of sustainable wildlife management. By reducing the risk of zoonotic disease transmission, these conservancies ensure that both human health and ecosystem stability are prioritized.
Community Health Initiatives in Zambia
Community health initiatives in Zambia take on new importance in light of rising zoonotic diseases. Programs focused on educating local populations about the diseases that affect both humans and animals can lead to more effective prevention strategies. Workshops and training sessions designed to enhance understanding of disease transmission dynamics empower local farmers and livestock owners to adopt safer practices.
Additionally, these initiatives foster a sense of ownership among community members regarding their health and the health of their ecosystem. By working collaboratively through participatory methods, locals can identify specific health challenges and work towards tailored solutions, ensuring that health improvement initiatives are relevant and effective.
The One Health Approach in Zoonotic Disease Management
The One Health approach emphasizes a collaborative, multi-disciplinary strategy to understand and manage zoonotic diseases. In Zambia, this framework has gained traction, as it enables a comprehensive understanding of how environmental changes, wildlife trafficking, and human encroachment on habitats increase the risk of diseases like COVID-19. By addressing the factors that contribute to zoonotic transmission, this integrated approach enhances the effectiveness of public health interventions.
In Nyawa Chiefdom, researchers are employing the One Health framework to better understand disease patterns and engage local knowledge. By integrating veterinary science and public health initiatives, communities can develop preventative measures that consider the health of both people and wildlife, identifying specific zoonoses that pose the highest risks and creating targeted responses.
Sustainable Wildlife Management and Public Health
Sustainable wildlife management in Zambia is not only crucial for conserving biodiversity but also plays a pivotal role in safeguarding public health from zoonotic diseases. As communities engage in sustainable practices, such as establishing conservancies that carefully manage human-wildlife interaction, they enhance both ecological resilience and community health. These conservation efforts reduce habitat destruction and the risks associated with wildlife trafficking, ultimately curbing zoonotic disease outbreaks.
Furthermore, local economies benefit from sustainable wildlife management through initiatives like ecotourism and permissible natural resource use. These income-generating activities provide communities with alternatives to practices like illegal hunting, which can facilitate zoonotic transmission. By emphasizing the value of wildlife and promoting sustainable livelihoods, Zambia can effectively address the root causes of zoonotic diseases while improving public health outcomes.
Empowering Communities for Disease Surveillance
Empowering local communities to engage in disease surveillance is a critical component of effective zoonotic disease management. In areas like Nyawa, community members possess invaluable knowledge regarding local diseases and their transmission pathways. By establishing community-led surveillance systems, they can quickly identify and respond to disease outbreaks, reducing their impact on both human health and livestock.
Training community members in disease detection and reporting encourages proactive health management. Collaborations with research institutions allow for the integration of scientific knowledge with local insights, creating a more robust approach to zoonotic disease prevention. This empowerment fosters resilience, enabling communities to better protect their health and the health of local wildlife.
Challenges in Zoonotic Disease Management
Despite ongoing efforts, challenges persist in managing zoonotic diseases in Zambia. Limited access to veterinary services, economic barriers, and varying levels of community engagement can hinder effective disease prevention strategies. Addressing these challenges requires multi-stakeholder collaboration, where government agencies, non-governmental organizations, and local communities work together to alleviate the socio-economic factors that contribute to disease spread.
Moreover, increasing awareness about zoonotic diseases among stakeholders is crucial. By educating communities and fostering collaborations, health officials can create a supportive environment that encourages participation in disease management initiatives. Comprehensive strategies that combine health education, access to resources, and awareness campaigns can empower communities and ultimately lead to better health outcomes.
Future Directions in Zoonotic Disease Research
The future of zoonotic disease research in Zambia hinges upon innovative, community-centric approaches. Continuous investment in participatory research allows for the identification of emerging zoonoses and insights into effective management strategies. By adapting research efforts to local contexts, such initiatives can yield sustainable solutions tailored to the unique socio-economic and environmental landscapes.
Emphasizing local knowledge in scientific inquiry also strengthens the bridge between researchers and communities. Future research will benefit from integrating local practices into health protocols, ensuring that communities are not just subjects of study but active participants in the health management process. This approach acknowledges the value of indigenous knowledge systems in combating zoonotic diseases.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role does local knowledge play in managing zoonotic diseases in Zambia?
Local knowledge is critical in managing zoonotic diseases in Zambia, especially within communities like Nyawa Chiefdom. Residents actively participate in identifying zoonotic threats, such as anthrax and heartwater, thereby enhancing community health and disease prevention efforts through culturally relevant practices. This community-driven approach enriches the One Health perspective by integrating local insights with scientific research.
How does the One Health approach influence zoonotic disease management in Zambia?
The One Health approach significantly influences zoonotic disease management in Zambia by promoting the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental health. In Nyawa Chiefdom, for instance, this integrated framework helps communities understand and manage the risks associated with wildlife interactions, emphasizing sustainable wildlife management and community health initiatives.
What are some challenges faced in zoonotic disease management in Zambia’s communities?
Communities in Zambia face several challenges in zoonotic disease management, including limited access to veterinary services, financial burdens associated with livestock treatment, and skepticism towards certain preventative measures. Addressing these challenges is essential for effective management and requires a combination of local knowledge, improved infrastructure, and community engagement.
How does sustainable wildlife management contribute to community health in Zambia?
Sustainable wildlife management contributes to community health in Zambia by creating protected areas like the Mize Community Conservancy in Nyawa Chiefdom. These initiatives help manage human-wildlife interactions, reduce the incidence of zoonotic disease transmission, and provide economic opportunities, thereby improving the overall health and livelihood of local populations.
What are the key zoonotic diseases prioritized in Zambia’s Nyawa Chiefdom?
In Zambia’s Nyawa Chiefdom, key zoonotic diseases prioritized by the local community include corridor disease, blackleg, heartwater, hemorrhagic septicemia, Newcastle disease, and anthrax. Recognizing these threats enables targeted interventions and community training on disease prevention practices.
How does community participation enhance disease surveillance in Zambia?
Community participation enhances disease surveillance in Zambia by empowering local members to engage in identifying and reporting zoonotic disease outbreaks. In Nyawa Chiefdom, participatory methodologies encourage locals to share their experiences, leading to more effective disease management strategies that are culturally appropriate and rooted in local knowledge.
What initiatives are in place in Zambia to promote health security against zoonotic diseases?
In Zambia, initiatives like the establishment of the Mize Community Conservancy aim to promote health security against zoonotic diseases. Supported by the Sustainable Wildlife Management Programme, these initiatives involve community-led research, disease mapping, and prevention workshops to build resilience and improve public health outcomes.
Why is collaboration between different sectors important for managing zoonotic diseases in Zambia?
Collaboration between different sectors—such as communities, government agencies, NGOs, and wildlife management organizations—is vital for managing zoonotic diseases in Zambia. This coordinated approach fosters comprehensive responses to disease challenges, integrating diverse expertise and resources to improve community health and sustainable wildlife management.
What impact does informal hunting have on zoonotic disease transmission in Zambia?
Informal hunting can significantly increase the risk of zoonotic disease transmission in Zambia by introducing pathogens from wildlife into human and livestock populations. By promoting legal and sustainable practices within the wildlife sector, communities can reduce these risks while supporting both public health and conservation efforts.
How are recommendations from community engagement shaping zoonotic disease management in Zambia?
Recommendations from community engagement shape zoonotic disease management in Zambia by highlighting the importance of local knowledge in creating effective interventions. Enhancing engagement, improving veterinary services, and promoting sustainable livelihoods are all strategies informed by community input, ensuring that management approaches are tailored to the specific needs and conditions of each community.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Community Involvement | Local communities are actively participating in identifying and managing zoonotic diseases. |
| Key Zoonotic Diseases | Diseases like anthrax, heartwater, and blackleg have been prioritized by the community as major threats. |
| One Health Approach | The integrated ‘One Health’ framework promotes the interconnectivity of human, animal, and environmental health to address zoonotic threats. |
| Research Goals | The research aims to identify diseases, explore local prevention practices, assess disease prevalence, and develop an integrated disease management plan. |
| Community Conservancy | The establishment of the Mize Community Conservancy promotes sustainable land use and helps manage human-wildlife interactions. |
| Challenges | Key challenges include limited access to veterinary services and skepticism regarding prevention methods. |
| Recommendations | Strengthening community engagement, improving access to veterinary care, and promoting sustainable livelihoods are critical for effective zoonotic disease management. |
Summary
Zoonotic disease management in Zambia is increasingly shaped by the involvement of local communities, particularly in regions like Nyawa Chiefdom. By prioritizing local knowledge and fostering collaboration between researchers and community members, Zambia is making strides towards a comprehensive approach to managing zoonotic diseases. This initiative not only safeguards public health but also strengthens ecosystem resilience, ensuring both wildlife and human communities can thrive together.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.