Young-onset dementia is a condition that affects individuals under the age of 65, and it remains alarmingly under-recognized in our society. While most people associate dementia with older adults, this misconception can lead to missed diagnoses and a lack of necessary support for younger individuals. Approximately 7 percent of the 57 million people worldwide diagnosed with dementia fall into this younger category, yet awareness remains low. Symptoms of dementia in younger individuals often differ from those typically seen in older adults, encompassing a range of cognitive decline issues that are easily misattributed to other conditions, such as mental health disorders. Raising dementia awareness is crucial, as early diagnosis not only improves the quality of life but also provides access to appropriate treatments and support for those grappling with Alzheimer’s disease in young people.
When discussing the challenges of cognitive decline within a younger demographic, it is essential to highlight the phenomenon often referred to as early-onset dementia. This condition manifests in individuals under 65 and can lead to a myriad of symptoms that are frequently mistaken for common mental health issues. The term “young-onset dementia” encapsulates various forms of neurodegenerative disorders that defy the traditional association of dementia with older age. The prevalence of early-onset Alzheimer’s provides a crucial lens through which we can understand the unique experiences of younger patients struggling with cognitive impairment. Increasing recognition of these conditions is vital for enacting change and ensuring that individuals receive timely support and care.
Understanding Young-Onset Dementia
Young-onset dementia is a term used to describe dementia that occurs in individuals under the age of 65. While it may be less common than dementia in older adults, the impact is just as profound. Approximately 7% of dementia cases are diagnosed in younger individuals, yet the condition remains largely under-recognized by both the public and healthcare providers. This lack of awareness means that many young people may not be diagnosed in a timely manner, potentially delaying access to much-needed support and resources.
Awareness campaigns focusing on young-onset dementia are crucial for informing the public about the symptoms and prevalence of this condition. Educational initiatives can help to debunk the myth that dementia only affects older individuals. By promoting understanding, we can encourage those experiencing cognitive decline to seek medical advice sooner, instead of dismissing their symptoms as typical age-related changes. Recognizing the distinctive signs of young-onset dementia is essential for ensuring individuals receive appropriate care and support.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is young-onset dementia and how does it differ from typical dementia?
Young-onset dementia refers to dementia that occurs in individuals under the age of 65. Unlike typical dementia, which is often associated with older adults, young-onset dementia can present different symptoms, including changes in personality and language difficulties, rather than just memory loss. It is often under-recognized, leading to delays in diagnosis and support.
What are the common symptoms of young-onset dementia?
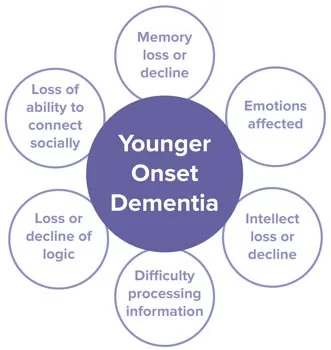
Symptoms of young-onset dementia can vary widely but may include cognitive decline, personality changes, language difficulties, problems with coordination, and in some cases, hallucinations or delusions. While memory loss is common in older adults with dementia, younger individuals may exhibit a broader range of cognitive and psychological symptoms.
Why is young-onset dementia often under-recognized by healthcare professionals?
Young-onset dementia is often under-recognized because many people and healthcare professionals associate dementia primarily with older age. Consequently, younger patients may not seek help for symptoms they experience, or those symptoms may be misattributed to mental health issues or normal aging, leading to a delay in proper diagnosis.
What are some ways to improve dementia awareness in relation to young-onset dementia?
Improving dementia awareness regarding young-onset dementia requires education and outreach initiatives. Advocacy groups can provide information about the symptoms and challenges of dementia in younger individuals, encouraging people to seek help if they experience cognitive decline. Awareness campaigns should also target healthcare providers to ensure they consider dementia in younger patients.
Is Alzheimer’s disease a common cause of young-onset dementia?
While Alzheimer’s disease is the most common form of dementia in older adults, it accounts for only about 40% of cases in individuals with young-onset dementia. Instead, younger patients are more likely to experience dementia caused by rarer neurodegenerative conditions, such as frontotemporal dementia.
How can caregivers support someone with young-onset dementia?
Caregivers of individuals with young-onset dementia can provide support by staying informed about the condition, seeking resources from dementia awareness organizations, and connecting with support groups. Establishing routines, promoting social engagement, and ensuring a safe environment are also vital in managing symptoms effectively.
What resources are available for individuals concerned about young-onset dementia?
Individuals concerned about signs of young-onset dementia can access resources from organizations like Alzheimer Scotland, Dementia UK, and the Alzheimer Society. These organizations provide information on symptoms, support groups, and guidance on how to obtain a diagnosis and care.
How can young-onset dementia affect the family dynamics of the affected individual?
Young-onset dementia can significantly impact family dynamics, as relatives may need to adjust to the changing needs of their loved ones. These adjustments can include increased caregiving responsibilities and emotional stress. Open communication and support from relevant organizations can help families navigate these challenges.
What steps should someone take if they notice symptoms of young-onset dementia?
If someone notices symptoms of young-onset dementia, they should document the changes they observe and consult a healthcare provider for an assessment. Early diagnosis is crucial for managing symptoms and accessing appropriate support and resources.
How does cognitive decline present differently in young-onset dementia versus late-onset dementia?
Cognitive decline in young-onset dementia can present with a wider range of symptoms compared to late-onset dementia. While older adults often exhibit memory loss as a primary symptom, younger individuals may experience significant changes in personality, social behaviors, and cognitive functions that affect day-to-day activities.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Dementia in Younger People | Dementia can occur in individuals under 65, with about 7 percent of cases diagnosed in this age group. |
| Common Misconceptions | Dementia is typically seen as a condition for older adults, leading to the underdiagnosis of younger individuals. |
| Variety of Symptoms | Symptoms of young-onset dementia can differ from those in older adults, including personality changes and cognitive challenges. |
| Causes of Dementia | In younger individuals, dementia is often caused by rarer conditions, such as frontotemporal dementias, rather than Alzheimer’s. |
| Overlap with Mental Health | Symptoms can overlap with mental health disorders like depression, leading to misdiagnosis. |
| Variability in Symptoms | The experience of dementia varies widely among individuals based on cognitive reserve and other factors. |
| Need for Awareness | Greater awareness is essential for the recognition, diagnosis, and support of young-onset dementia cases. |
Summary
Young-onset dementia is a crucial topic that often goes under-recognized in society due to common misconceptions about who can be affected by dementia. As awareness grows, it becomes ever more vital to understand that young-onset dementia can affect individuals as young as children, leading to a need for early recognition, diagnosis, and appropriate support systems. Awareness efforts can help ensure that those under 65 with symptoms receive the care and resources they need.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.