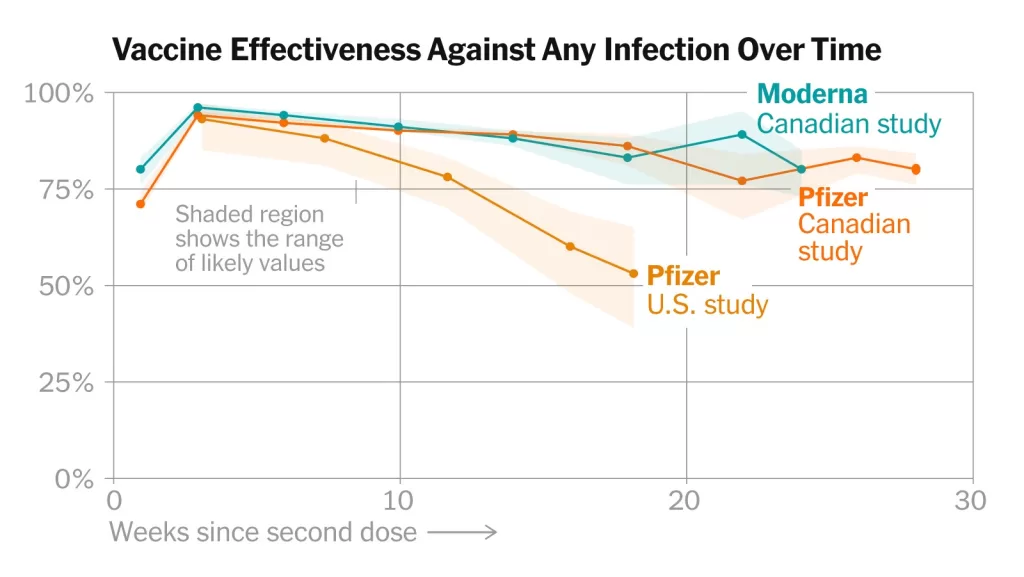
Vaccine effectiveness is a critical aspect of public health, particularly in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic. Evaluated through extensive COVID-19 vaccine studies, this measure provides insight into how well a vaccine protects individuals from severe illness, hospitalization, and mortality. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) continually conducts rigorous vaccine efficacy assessments using observational studies, leveraging data from surveillance platforms and electronic health records. As new variants emerge and vaccination rates fluctuate, understanding vaccine policy implications becomes essential not only for protecting vulnerable populations but also for shaping future vaccination strategies. By collecting and analyzing data on various factors influencing vaccine performance, stakeholders can make informed decisions to enhance public health outcomes.
Evaluating the protective benefits of vaccinations against illnesses is essential, especially during health crises. The effectiveness of vaccines, particularly in preventing severe disease outcomes, is firmly rooted in comprehensive research and data analysis. Observational studies form the backbone of this inquiry, providing real-world insights necessary for understanding vaccine efficacy across diverse demographics. With the evolving landscape of infectious diseases, including the emergence of new variants, ongoing research into these vaccinations’ effectiveness is crucial to inform health policies. Recognizing the factors that contribute to vaccination outcomes is vital in ensuring optimal public health protection and addressing the nuances within different population groups.
Understanding Vaccine Effectiveness: Key Factors at Play
Vaccine effectiveness is influenced by a myriad of factors that interconnect host attributes, characteristics of the pathogen, and specific properties of the vaccine itself. Host-related considerations include age, existing medical conditions like diabetes or heart disease, and any prior COVID-19 infections. Such variables can critically impact how well a vaccine performs in protecting individuals against the virus. As CDC vaccine research highlights, the interaction between these host factors and vaccine outcomes is essential for understanding the granular insights regarding efficacy in different demographics.
Moreover, pathogen-related factors play a significant role, particularly with the emergence of new COVID-19 variants. The variant circulating in the community can substantially alter vaccine effectiveness. For example, vaccines may show lower efficacy against variants that exhibit increased transmissibility or resistance to immune response. This underscores the importance of continuous observational studies in generating data that informs vaccine policy decisions.
The Role of Observational Studies in Vaccine Research
Observational studies are pivotal in assessing the real-world effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines. The CDC employs diverse methodologies across various observational frameworks to gather crucial data that reflect the vaccine performance in everyday situations. These studies use electronic health records, surveillance information, and direct observations to evaluate how vaccines are functioning among different populations, particularly those at heightened risk for severe disease outcomes.
By focusing on real-world data, the findings from these observational studies help paint a comprehensive picture of vaccine efficacy. For instance, understanding rates of hospitalization and severe illness among vaccinated versus unvaccinated populations provides direct insights that are essential for crafting informed vaccine policy implications. As the landscape of the pandemic evolves, so too will the insights drawn from these studies, necessitating ongoing assessment and adaptation.
Vaccine Effectiveness Evaluations: Hospitalizations and Critical Outcomes
Measuring the effectiveness of vaccines in preventing severe outcomes, such as hospitalization and critical illness, is a cornerstone of CDC’s research strategy. Various platforms, including VISION and IVY, illustrate how different health facilities track COVID-19-related hospitalizations across diverse populations. These evaluations are crucial not only for establishing the protective benefits of vaccinations but also for informing healthcare capacity planning and public health responses in real-time.
The findings from these evaluations are paramount for healthcare policymakers and practitioners, as they align vaccine utilization with observed outcomes. Assessments of emergency department visits and severe illness rates help analyze the correlation between vaccination status and health-facing incidents related to COVID-19. This data directly informs the adjustments needed in vaccination strategies and public health messaging, ensuring that vulnerable populations receive adequate protection against severe disease.
Vaccine Efficacy: Absolute, Relative, and Incremental Measures
Understanding the different dimensions of vaccine efficacy is fundamental for interpreting research findings. Absolute vaccine effectiveness compares health outcomes like infection rates and hospitalization between fully vaccinated and unvaccinated individuals. Relative vaccine effectiveness, on the other hand, sheds light on comparisons between different vaccine regimens, helping determine which formulations may offer superior protection or safety profiles.
Incremental vaccine effectiveness specifically addresses the benefits of receiving additional doses beyond the primary series. This measurement is critical in the context of booster recommendations and helps policymakers assess if populations with prior vaccinations still gain added protection from subsequent doses. Collectively, these metrics offer a nuanced understanding of vaccine effectiveness that is vital for ongoing public health strategies against COVID-19.
Communicating Vaccine Findings to the Public
A crucial aspect of the CDC’s vaccine effectiveness program is the clear communication of findings to the public and policymakers. The ability to relay complex epidemiological data in an understandable manner is essential for fostering trust in vaccine recommendations and encouraging participation in vaccination programs. This involves tailoring messages not only to healthcare professionals but also to community members who may have varying degrees of health literacy and access to information.
Engaging with the public through informative campaigns that summarize study findings, emphasize the importance of vaccination, and address common concerns can significantly enhance vaccine uptake. As real-world data emerges and the landscape of COVID-19 evolves, consistent communication becomes even more critical for adapting public health responses to reflect new evidence and ensure community protection against severe outcomes.
The Impact of Vaccine Policy on Community Health
Vaccine policy implications are critical in shaping community health outcomes during the pandemic. Effective vaccine policies based on rigorous studies can lead to increased vaccination rates, especially in high-risk populations. Policies such as mandates in healthcare settings or educational institutions create environments where vaccination is prioritized, thus protecting those at greatest risk of severe outcomes from COVID-19.
Furthermore, aligning vaccine policy with emerging findings from observational studies allows for timely adjustments and more effective public health interventions. As new variants of concern emerge or as vaccine effectiveness wanes over time, adaptive policies can be implemented to manage outbreaks and maintain community immunity. In this way, informed vaccine policymaking remains integral to bolstering public health responses against COVID-19.
Monitoring Vaccine Effectiveness Amidst Variants
Ongoing surveillance of vaccine effectiveness is vital in the face of emerging COVID-19 variants. The evaluation of how vaccines perform against these evolving strains allows health authorities to make informed decisions about booster doses and updates to vaccine formulations. CDC’s commitment to monitoring vaccine effectiveness through dedicated programs ensures that data on emerging variants is continuously integrated into public health strategies.
The role of continuous monitoring cannot be understated, as it helps in alerting the public health community to potential declines in mRNA-based vaccine protection or the necessity for updated immune responses. By capturing this data effectively, the CDC can communicate actionable insights that support vaccination efforts and adapt strategies as necessary, fostering a resilient public health approach.
Vaccine Surveillance: Data Collection and Analysis Methods
The methods used for data collection and analysis in vaccine effectiveness studies are pivotal for generating reliable findings. The CDC utilizes multiple platforms that foster rigorous data analysis, such as VISION and IVY, enabling comprehensive evaluations across different demographics and geographic regions. Such methodologies not only allow for robust direct comparisons but also help in accounting for confounders that may impact the effectiveness metrics.
These advanced analytical methodologies are crucial to isolating the impact of vaccination from other variables influencing COVID-19 outcomes. By employing diverse statistical techniques and study designs, the CDC gathers meaningful data that informs both vaccine strategies and public health policies moving forward. Such an evidence-based approach ensures that the right protective measures are directed where they are most needed, optimizing health benefits across populations.
Vaccine Effectiveness Research: Future Directions
Looking to the future, the field of vaccine effectiveness research holds immense potential for contributing to our understanding of pandemic management. As emerging data sheds light on the long-term effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines and the implications of boosters, researchers will need to maintain flexibility and adapt to rapidly changing landscapes. The integration of new technologies, such as advanced data analytics and genomics, will be vital in shaping future studies.
Additionally, continued focus on diverse populations, particularly those with heightened vulnerabilities, will enhance the comprehensiveness of vaccine effectiveness research. As more data becomes available, the insights derived from this research can guide robust vaccine policy initiatives that aim to protect the most at-risk groups and promote overall public health resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is vaccine effectiveness in the context of COVID-19 vaccine studies?
Vaccine effectiveness refers to how well COVID-19 vaccinations protect individuals from health outcomes such as infection, hospitalization, and death. This measure is typically determined by comparing adverse outcomes in vaccinated versus unvaccinated populations through observational studies and surveillance data.
How does the CDC conduct vaccine effectiveness research?
The CDC conducts vaccine effectiveness research by collaborating with public health partners to perform observational studies. These studies employ diverse methodologies and utilize data from health records, surveillance platforms, and other sources to assess the effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines in real-world settings.
What factors influence vaccine efficacy according to observational studies?
Vaccine efficacy can be influenced by several factors including demographic variables (like age and underlying health conditions), characteristics of the virus (such as circulating variants), and the specific type of vaccine and timeline of administration. Understanding these factors helps the CDC provide accurate effectiveness estimates.
What outcomes are monitored to inform vaccine policy implications?
The CDC monitors key outcomes such as critical illness or death, hospitalization, medically attended COVID-19 cases, and symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. These evaluations are essential for guiding COVID-19 vaccine policies and assessing the overall impact of vaccination programs.
What is the difference between absolute and relative vaccine effectiveness?
Absolute vaccine effectiveness compares health outcomes between vaccinated and unvaccinated individuals, while relative vaccine effectiveness assesses the comparative effectiveness of different vaccine types or regimens within vaccinated populations. Both metrics provide valuable insights for policymakers.
How does vaccine effectiveness vary among high-risk populations?
Vaccine effectiveness can differ significantly among high-risk populations, such as older adults and those with immunocompromising conditions. The CDC adjusts effectiveness estimates based on these demographics to ensure accurate assessments and effective public health responses.
What platforms does the CDC use for evaluating COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness?
The CDC utilizes several platforms such as VISION, IVY, and Overcoming COVID-19 to evaluate vaccine effectiveness. These platforms track hospitalization rates, emergency department visits, and other patient-important outcomes to provide insights into how well vaccines protect against severe disease.
What role do observational studies play in understanding vaccine effectiveness?
Observational studies are crucial for generating real-world evidence regarding vaccine effectiveness. They help identify how well vaccines work in diverse populations and under varying conditions, facilitating informed decisions about vaccination strategies and public health policies.
How does the CDC inform the public about vaccine effectiveness findings?
The CDC communicates vaccine effectiveness findings to policymakers, the scientific community, and the general public through reports, data trackers, and publications, ensuring transparency and fostering public trust in vaccination efforts.
What are the implications of waning vaccine effectiveness over time?
Waning vaccine effectiveness refers to the gradual reduction in protection provided by vaccines as time passes. Monitoring this decline allows the CDC to recommend booster doses and adapt vaccination policies according to emerging data on immunity and variants.
| Key Points | Description |
|---|---|
| Vaccine Effectiveness Overview | The CDC monitors how effective COVID-19 vaccines are in real-world scenarios to guide public health policy. |
| Factors Influencing Vaccine Effectiveness | Host factors (age, underlying conditions), pathogen factors (virus variants), and vaccine factors (type and timing) influence effectiveness. |
| Goals of CDC’s Program | To evaluate vaccine effectiveness in key populations and against important outcomes, and to provide data for policy decisions. |
| Outcomes of Interest | Critical illness, hospitalization, medically attended COVID-19, and symptomatic infections are monitored for effectiveness. |
| Types of Vaccine Effectiveness | Absolute, relative, and incremental effectiveness measures inform decisions on vaccination strategies. |
| Evaluation Platforms | CDC uses platforms like VISION, IVY, and Overcoming COVID to assess effectiveness in various settings and populations. |
Summary
Vaccine effectiveness is critical in understanding how well vaccines protect against COVID-19. The ongoing studies led by the CDC focus on generating reliable data regarding vaccine performance under actual conditions. By analyzing a range of factors impacting vaccine efficacy, including host and pathogen variables, the CDC effectively informs vaccine policy decisions. Continued monitoring enables public health officials to adapt recommendations and ensure the optimal protection of at-risk populations.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.