Understanding achalasia is crucial for anyone experiencing difficulties with swallowing or related digestive issues. This rare esophageal disorder affects the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), preventing it from relaxing and allowing food to pass into the stomach. As a result, those with achalasia often endure frustrating symptoms such as regurgitation, chest pain, and significant weight loss. Recognizing achalasia symptoms early can facilitate timely achalasia treatment, which may include medications, surgery, or innovative procedures like peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM). By raising awareness about achalasia causes and treatment options, we can support individuals suffering from this condition and improve their quality of life.
Esophageal motility disorders, particularly achalasia, present significant challenges for those affected. Characterized by the failure of the lower esophageal sphincter to relax, this condition leads to various complications, including severe dysphagia and regurgitation. Understanding the underlying factors contributing to achalasia can enhance patient awareness and encourage timely intervention. Treatment approaches range from surgical options to medication, emphasizing the importance of tailored care. By exploring the nuances of achalasia and similar esophageal disorders, we can foster a deeper understanding of the impact on individuals’ lives and the necessity for comprehensive support.
Understanding Achalasia: An Overview of Symptoms and Diagnosis
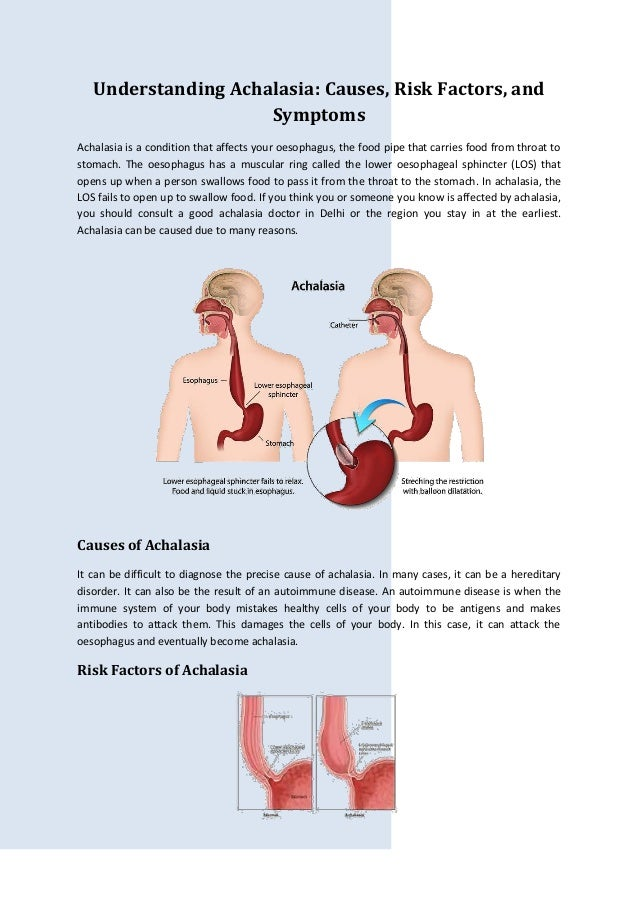
Achalasia is a chronic condition that primarily affects the esophagus, leading to significant difficulties in swallowing, known as dysphagia. Patients often report a sensation of food being stuck in their throat or chest, which can be both distressing and frustrating. In addition to dysphagia, regurgitation of undigested food, chest pain after meals, and unintentional weight loss are common complaints. Notably, these symptoms can overlap with other gastrointestinal disorders, making timely diagnosis challenging. It is crucial for individuals experiencing these symptoms to seek medical attention promptly, as early diagnosis can lead to better management of the condition.
Diagnosis of achalasia typically involves a combination of patient history, symptom evaluation, and diagnostic tests such as esophageal manometry, which measures the pressure in the esophagus, and barium swallow studies, which visualize the swallowing process. Understanding achalasia symptoms is essential for both patients and healthcare providers, and educating oneself can lead to more informed discussions about treatment options.
Exploring the Causes of Achalasia
The etiology of achalasia remains complex and not fully understood, but several potential causes have been identified. Research indicates that degeneration of nerve cells within the esophagus plays a critical role in the development of achalasia. This nerve damage disrupts the normal function of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), preventing it from relaxing appropriately during swallowing. Additionally, there may be an autoimmune component, where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the esophageal nerves, further exacerbating the condition.
Genetic factors may also influence the likelihood of developing achalasia, with some studies suggesting a familial link among affected individuals. Furthermore, underlying conditions such as Chagas disease, which is caused by a parasitic infection, have been associated with the onset of achalasia, particularly in certain regions. Understanding these causes helps to delineate the complexity of achalasia and underscores the need for ongoing research into its pathophysiology.
Advances in Achalasia Treatment: Options and Innovations
Recent advancements in the treatment of achalasia have provided patients with more effective options than ever before. One of the most promising procedures is Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM), a minimally invasive surgical technique that has shown significant success in alleviating symptoms. The procedure involves making an incision in the esophageal muscle to allow for easier passage of food. Patient satisfaction rates following POEM have been encouraging, and it represents a modern solution for those struggling with debilitating symptoms of achalasia.
In addition to POEM, traditional surgical options like laparoscopic Heller myotomy remain viable alternatives. This procedure has been a staple in achalasia treatment for years and involves cutting the tight sphincter muscle to improve swallowing capabilities. For patients who may not be candidates for surgery, medications such as nitrates and calcium channel blockers can provide temporary relief. Understanding the variety of treatment options allows patients to make informed decisions tailored to their individual needs.
Botulinum toxin injections have also emerged as a less invasive option for those with milder symptoms. This treatment involves injecting the toxin directly into the LES to temporarily alleviate pressure, making swallowing easier. Such diverse treatment strategies highlight the importance of personalized care plans in managing achalasia.
The Role of Awareness in Achalasia Management
Increased awareness of achalasia is essential for both patients and healthcare providers. Many individuals with this condition report feeling isolated due to the rarity of achalasia, which can lead to misunderstandings about their symptoms. Public education efforts, such as campaigns and informational resources, can help demystify the condition and encourage those who experience symptoms to seek medical assistance promptly. Advocacy for greater awareness can improve the quality of life for patients and foster a more supportive environment.
Personal narratives, like that of Elise Baynard, serve as powerful reminders of the daily challenges faced by those with achalasia. Sharing these stories can help to bridge the gap between patients and the broader community, promoting empathy and understanding. By highlighting individual experiences, we can cultivate a culture of support and encourage more proactive discussions about diagnosis and treatment options for achalasia.
Understanding Achalasia ICD 10 Classification and Its Implications
The ICD-10 classification for achalasia, specifically K22.0, plays a crucial role in the diagnosis and management of this condition. Understanding this classification not only aids healthcare professionals in identifying and coding the disease accurately but also facilitates appropriate treatment planning and insurance reimbursement processes. Accurate coding ensures that patients receive the necessary care while also contributing to broader healthcare data that can inform future research and treatment advancements.
Furthermore, awareness of the ICD-10 classification empowers patients to engage in informed discussions with their healthcare providers. It provides a framework for understanding the complexities of their diagnosis and navigating the healthcare system effectively. As patients become more knowledgeable about their condition and its classification, they can advocate for themselves and seek appropriate treatments, leading to improved health outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of Achalasia?
Understanding achalasia symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis. Common symptoms include dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), regurgitation of undigested food, chest pain, weight loss, and occasional heartburn. If you experience these symptoms, seek medical advice.
What are the main causes of Achalasia?
The causes of achalasia are not fully understood, but potential factors include degeneration of nerve cells in the esophagus, autoimmune responses, genetic predispositions, and underlying conditions like Chagas disease. Identifying achalasia causes is key to understanding treatment options.
What treatment options are available for Achalasia?
Understanding achalasia treatment options includes several approaches: Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM) is a minimally invasive surgery, while laparoscopic Heller myotomy is a traditional surgical method. Medications can temporarily relieve symptoms, and botulinum toxin injections may help some patients.
Is surgery necessary for Achalasia treatment?
Surgery is often a recommended treatment for achalasia, especially when symptoms are severe. Understanding achalasia surgery options, like POEM or laparoscopic Heller myotomy, can significantly improve swallowing and quality of life for affected individuals.
What is the ICD 10 code for Achalasia?
The ICD 10 code for achalasia is K22.0. Understanding achalasia ICD 10 coding is important for accurate medical billing and record-keeping, ensuring patients receive appropriate care and treatment.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Understanding Achalasia | Achalasia is a rare esophageal disorder that affects swallowing due to the inability of the LES to relax. |
| Symptoms | Dysphagia, regurgitation, chest pain, weight loss, and heartburn. |
| Causes | Degeneration of nerve cells, immune response, genetic factors, and underlying conditions like Chagas disease. |
| Treatment Options | 1. Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM) 2. Laparoscopic Heller myotomy 3. Medications (nitrates, calcium channel blockers) 4. Botulinum toxin injection. |
| Awareness | Limited public understanding; personal stories emphasize the need for awareness and education. |
Summary
Understanding achalasia is crucial as it is a rare but significant esophageal disorder that impacts individuals’ ability to swallow. This condition leads to various distressing symptoms such as dysphagia and chest pain, which can severely affect a person’s quality of life. The exact causes of achalasia are not fully understood, but factors like nerve degeneration and autoimmune responses may contribute. Fortunately, advancements in treatment options, including minimally invasive surgical techniques like POEM and other therapeutic measures, provide hope for those affected. Increased awareness and education about achalasia are essential, as they can lead to earlier diagnosis and better management of the condition, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.