Type 2 diabetes, a condition affecting more than 36 million Americans, poses significant challenges due to its impact on blood sugar management and overall health. This metabolic disorder can lead to a variety of type 2 diabetes symptoms, including brain fog and mood swings, resulting from fluctuating blood sugar levels. Recent studies have drawn alarming connections between type 2 diabetes and cognitive decline, suggesting that individuals with this disorder may experience brain changes similar to those seen in Alzheimer’s disease. Understanding the relationship between diabetes and cognition is crucial, as unmanaged blood sugar can adversely affect brain health, exacerbating the risk of serious neurological issues. As we delve deeper into this topic, we will explore effective strategies for blood sugar control and their importance in preserving cognitive function.
Diabetes, specifically the type characterized by insulin resistance, is increasingly recognized for its detrimental effects on cognitive abilities. This pervasive disease not only disrupts normal blood glucose levels but also manifests in symptoms often indistinguishable from those of neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s. The interplay between blood sugar regulation and brain health highlights critical concerns regarding diabetes management and its implications on overall mental wellness. It is essential to examine how effective diabetic care can mitigate the cognitive risks associated with chronic high blood sugar and improve life quality for those affected. In this discussion, we will shed light on practical approaches that can help maintain a healthy brain amidst the challenges posed by this condition.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes Symptoms
Type 2 diabetes symptoms can vary significantly from person to person, but common indicators include frequent urination, excessive thirst, and an increased appetite. Additionally, many individuals may experience fatigue, blurry vision, and unintended weight loss. These symptoms arise due to elevated blood sugar levels that the body struggles to manage effectively. Alongside the physical manifestations, cognitive symptoms such as brain fog can also emerge, making it challenging for individuals to concentrate or recall information.
Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for effective management. Many people may overlook mild symptoms, attributing them to aging or stress. However, consistent monitoring of blood glucose levels and awareness of these signs can lead to timely intervention. Understanding how type 2 diabetes symptoms manifest can empower individuals to seek medical advice promptly, ultimately improving both physical health and cognitive function.
The Link Between Type 2 Diabetes and Alzheimer’s Disease
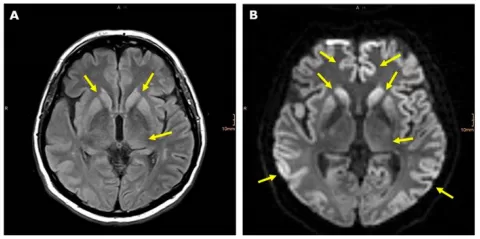
Recent studies have illuminated a concerning connection between type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. Research published in the Journal of Neuroscience has shown that high blood sugar levels can negatively impact brain functionality, specifically mimicking early symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease. Both conditions share similar deficits in cognitive function and memory processing, highlighting the importance of blood sugar management in maintaining overall brain health.
The correlation between insulin resistance and cognitive decline raises significant alarms for individuals with type 2 diabetes. It’s crucial to understand that not only does high blood sugar affect physical health, but it can also interfere with cognitive processes. Individuals diagnosed with type 2 diabetes might struggle with rewards and motivation due to impaired neural connections, particularly in brain regions associated with decision-making and emotional regulation.
Impact of Blood Sugar Management on Brain Health
Effectively managing blood sugar levels can play a pivotal role in preserving brain health among individuals with type 2 diabetes. Poorly controlled diabetes can lead to neurovascular damage, which in turn, affects cognition and overall brain function. Research indicates that patients who maintain their blood glucose within a healthy range exhibit better cognitive performance and lower risks of developing neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s.
Implementing strategies for blood sugar management, including dietary modifications, regular exercise, and medication adherence, significantly enhances the quality of life for diabetic patients. These lifestyle choices not only help in controlling blood sugar levels but also bolster cognitive resilience, thus mitigating the risks associated with cognitive decline and other symptoms associated with type 2 diabetes.
The Role of the Anterior Cingulate Cortex (ACC) in Diabetes
The anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) is integral to various cognitive and emotional functions, and recent research has revealed its susceptibility to the damaging effects of high blood sugar associated with type 2 diabetes. This brain region is responsible for processing rewards and regulating emotions, which can be adversely affected in individuals with uncontrolled diabetes. Disruption of this area can lead to diminished responses to rewards, further complicating adherence to lifestyle changes necessary for diabetes management.
Understanding the role of the ACC sheds light on the challenges many people with type 2 diabetes face in maintaining motivation for healthier behaviors. For example, difficulties in experiencing pleasure from food or physical activities can lead to a cycle of poor lifestyle choices, which complicates blood sugar management and exacerbates both diabetes and cognitive decline.
Lifestyle Changes to Combat Type 2 Diabetes Symptoms
Making lifestyle changes is crucial for managing type 2 diabetes symptoms effectively. Incorporating regular physical activity, following a balanced diet, and engaging in stress-reducing activities can significantly improve both physical and mental health. For instance, the Mediterranean diet, rich in whole grains, vegetables, and healthy fats, has been shown to enhance overall health and may help stabilize blood glucose levels.
Additionally, practicing mindfulness and ensuring adequate sleep can help regulate stress hormones that impact blood sugar levels. These changes not only assist in managing type 2 diabetes but also promote better cognitive function, thereby lowering the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease in those predisposed to both conditions.
Cognitive Function and Diabetes: Understanding the Overlap
There is increasing evidence that type 2 diabetes can impair cognitive function, leading to difficulties in areas such as memory, focus, and decision-making. The persistent presence of high blood sugar can cause inflammation and vascular damage within the brain, contributing to cognitive decline. This overlap between diabetes and neurological challenges emphasizes the importance of understanding how blood sugar management directly correlates with brain health.
Research suggests that individuals with type 2 diabetes often experience accelerated cognitive aging due to these detrimental effects. Therefore, maintaining optimal blood glucose levels isn’t just about physical health; it is also crucial for preserving cognitive integrity. This highlights the necessity for healthcare professionals to address both diabetes management and cognitive health in their treatment approaches.
Exploring Diabetes and Cognition: Research Insights
In the realm of diabetes research, the relationship between diabetes and cognition is an area of significant focus. Recent findings indicate that individuals with type 2 diabetes may experience cognitive impairment similar to that seen in neurodegenerative conditions. These insights support the hypothesis that diabetes may serve as a risk factor for cognitive decline, necessitating comprehensive management strategies.
Ongoing studies continue to explore the nuances of how blood glucose fluctuations affect cognitive performance. By understanding the mechanisms at play, researchers hope to develop targeted interventions that protect and enhance cognitive function among those living with type 2 diabetes. This multidimensional approach underscores the importance of integrating physical and mental health management in treating diabetic patients.
The Importance of Regular Check-Ups for Diabetic Patients
Regular medical check-ups are essential for individuals with type 2 diabetes to monitor blood sugar levels and assess overall health. These evaluations allow healthcare providers to adjust treatment plans as necessary, addressing any emerging symptoms related to both diabetes and cognitive function. Early detection and intervention are key factors in preventing complications that may arise from unmanaged blood glucose levels.
Additionally, these check-ups provide an opportunity to discuss lifestyle changes, medication adherence, and the psychological impact of living with diabetes. By prioritizing regular health assessments, diabetic individuals can enhance their quality of life, maintain better blood sugar control, and potentially protect their cognitive health.
Consulting Healthcare Professionals for Comprehensive Care
Seeking guidance from healthcare professionals is crucial for those managing type 2 diabetes, given the intricate relationship between blood sugar control and cognitive health. Doctors can prescribe individualized treatment plans that include medication, dietary recommendations, and lifestyle changes tailored to patients’ unique needs. This comprehensive approach is vital for optimizing health outcomes.
Moreover, healthcare providers can facilitate referrals to specialists, such as dietitians or mental health professionals, addressing the multifaceted challenges that arise from type 2 diabetes. By maintaining open communication with their medical team, patients can better navigate their condition, proactively manage symptoms, and support their cognitive function effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of type 2 diabetes that affect mental health?
Common symptoms of type 2 diabetes that influence mental health include brain fog, mood swings, and difficulty concentrating. These symptoms are often exacerbated by fluctuations in blood sugar levels and can significantly affect cognitive function, making management of blood sugar crucial for mental clarity.
How does type 2 diabetes mimic Alzheimer’s disease in the brain?
Recent studies suggest that unmanaged high blood sugar in individuals with type 2 diabetes can lead to symptoms that resemble early Alzheimer’s disease. This occurs due to changes in brain structure and function, particularly affecting areas like the anterior cingulate cortex, impacting memory and reward processing.
What role does blood sugar management play in supporting brain health for those with type 2 diabetes?
Effective blood sugar management is vital for preserving brain health in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Controlling blood sugar levels can help prevent cognitive decline and reduce the risk of developing symptoms similar to Alzheimer’s disease by minimizing brain inflammation and improving nutrient delivery to brain cells.
Can high blood sugar levels lead to cognitive issues in people with type 2 diabetes?
Yes, high blood sugar levels can potentially lead to cognitive issues in individuals with type 2 diabetes. These issues stem from inflammation, vascular damage, and neural changes caused by prolonged hyperglycemia, which can affect decision-making, memory, and emotional regulation.
What lifestyle changes can help manage blood sugar and possibly improve brain health in type 2 diabetes?
Lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, adhering to a balanced diet (like the Mediterranean diet), managing stress, and ensuring adequate sleep can significantly help in managing blood sugar levels. These changes not only aid in diabetes management but may also improve overall brain health and cognitive function.
Is it possible to reverse brain changes caused by type 2 diabetes?
While it is unclear if brain changes due to unmanaged type 2 diabetes can be completely reversed, significant improvements can often be achieved through lifestyle modifications and effective blood glucose management, including possible medications prescribed by healthcare professionals.
What is the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) and its significance in type 2 diabetes?
The anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) is a critical brain region involved in motivation, emotion, and reward processing. In type 2 diabetes, high blood sugar levels can disrupt ACC function, impacting cognitive abilities and creating parallels with early symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease.
Why is it important for individuals with type 2 diabetes to be aware of their blood sugar levels?
Awareness of blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with type 2 diabetes, as fluctuations can lead to severe symptoms, including cognitive issues like brain fog and mood swings. Regular monitoring helps in implementing timely interventions to minimize potential complications affecting both physical and mental health.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes | Affects more than 36 million Americans, causing constant concern over blood sugar levels. |
| Impacts on Mental Health | Low or high blood sugar can result in brain fog and mood swings, potentially leading to severe health issues. |
| Alzheimer’s Mimicry | High blood sugar in type 2 diabetes may imitate early Alzheimer’s symptoms due to brain changes. |
| Study Findings | Rodent studies show that high blood sugar disrupts reward processing in the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC). |
| Significance of ACC | Essential for cognitive functions like motivation and decision-making and linked to Alzheimer’s disease. |
| Effects of High Blood Sugar | Can lead to vascular disease, nerve damage, and inflammation, affecting brain functionality. |
| Reversibility of Changes | Uncertain if changes in the brain from diabetes can be fully reversed, but significant improvement is possible. |
| Natural Blood Sugar Management | Consult healthcare for a tailored plan; lifestyle changes like exercise, diet, and good sleep are key. |
Summary
Type 2 diabetes can have significant effects on brain health and may mimic symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease. This condition, experienced by millions of Americans, leads to harmful fluctuations in blood sugar that can impair cognitive functions. Effective management of type 2 diabetes through lifestyle changes and proper medical intervention is crucial in preventing potential brain damage and maintaining overall health.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.