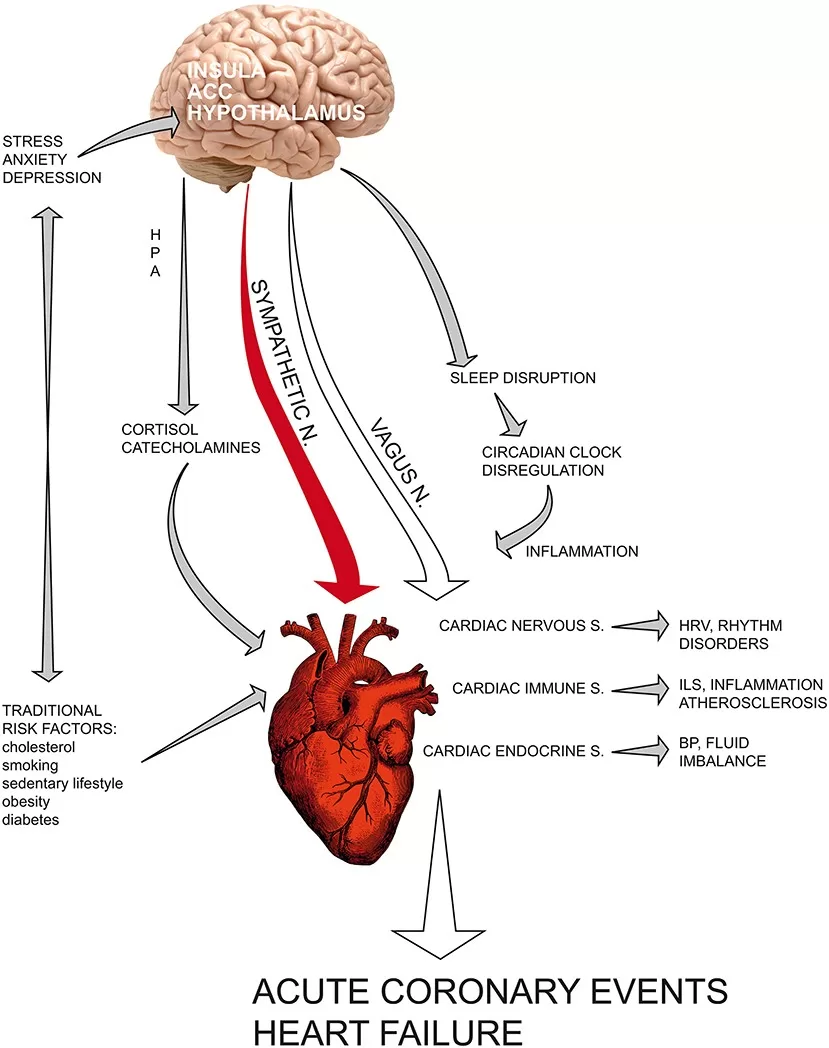
In today’s high-pressure environment, understanding the interplay between stress and coronary heart disease (CHD) has become increasingly important. Chronic stress not only affects our mental health but also poses a significant risk for developing cardiovascular conditions like heart disease. As modern life inundates us with pressures from work, family, and health issues, the impact of stress on heart health demands immediate attention. This article explores the vital connection between stress management strategies and the prevention of coronary heart disease, underlining the necessity of integrating mental well-being into our overall health approach. By recognizing the implications of stress on psychological health, we can take proactive steps toward heart disease prevention.
The rising concern regarding emotional strain and its effect on cardiovascular fitness highlights a crucial dialogue about the relationship between anxiety and heart conditions. The mental burden borne from everyday life situations can escalate into significant health risks, particularly when it comes to conditions like coronary artery disease. Research indicates that effective mental health management, including tailored stress reduction techniques, plays a fundamental role in maintaining cardiac health. Furthermore, fostering psychological resilience not only enhances individual well-being but also protects against the escalation of heart disease risk factors. Therefore, delving into innovative strategies for managing stress is essential for preserving both psychological health and long-term cardiovascular fitness.
Understanding the Impact of Stress on Heart Health
The physiological effects of stress on the heart are more profound than many might realize. When faced with stressful situations, the body produces an array of stress hormones, such as cortisol and adrenaline, which can lead to increased heart rate and blood pressure. Prolonged exposure to these heightened levels not only strains the cardiovascular system but can also trigger inflammatory responses, further predisposing individuals to coronary heart disease. This biological reaction illustrates why it’s crucial to recognize stress as a legitimate risk factor for heart-related ailments.
Moreover, chronic stress often leads to behavioral changes that can negatively impact heart health. Individuals under stress may indulge in unhealthy coping mechanisms such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, or poor dietary choices, all of which can escalate the risk of coronary heart disease. Clearly, understanding this connection can inspire individuals to seek stress management techniques, thus aiming at reducing both psychological distress and promoting heart disease prevention.
Effective Stress Management Strategies for Heart Disease Prevention
Adopting effective stress management strategies plays an essential role in heart disease prevention. Techniques such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) have been shown to significantly reduce the symptoms of anxiety and depression, which are closely linked to an increased risk of coronary heart disease. By restructuring negative thought patterns, individuals can improve their mental health and, consequently, their cardiovascular health.
In addition to psychological interventions, lifestyle changes are vital in stress management. Regular exercise serves as a natural stress reliever, releasing endorphins that enhance mood and promote heart health. Furthermore, practices such as yoga and meditation can mitigate stress responses, fostering both psychological and physiological balance, thus lowering the risk of heart disease.
The Role of Mindfulness in Promoting Psychological Health
Mindfulness practices have gained traction as effective tools for managing stress and enhancing psychological health. Research has demonstrated that mindfulness meditation can lower blood pressure, reduce the frequency of anxiety attacks, and improve overall mood. This practice encourages individuals to focus on the present, reduce rumination on stressors, and cultivate a more resilient mindset towards challenges, which in turn fosters a healthier heart.
Moreover, mindfulness can enhance emotional regulation, allowing individuals to approach stressors with a more balanced perspective instead of resorting to unhealthy coping strategies. Engaging regularly in mindfulness exercises can assist in maintaining emotional stability, further contributing to cardiovascular health and preventing stress-related heart conditions.
Building Support Systems for Mental and Heart Health
Establishing strong support systems is crucial for managing stress and maintaining both mental and cardiovascular health. Social connections provide individuals with emotional support during challenging times, reducing feelings of isolation and loneliness, which are linked to higher stress levels. Groups or online communities focused on health and wellness can foster shared experiences and coping strategies, enhancing psychological well-being.
Encouraging supportive relationships among family and friends contributes significantly to heart disease prevention. These relationships create a nurturing environment where individuals can discuss their struggles and seek help when needed. Integrated care models involving mental health professionals in cardiovascular care can strengthen this support system, facilitating better heart health outcomes while addressing psychological needs.
The Interconnection of Mental Health and Cardiovascular Well-being
The intricate relationship between mental health and cardiovascular well-being is clear in contemporary research. Studies consistently reveal that mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety significantly increase the likelihood of coronary heart disease. It suggests that mental wellness is not just a qualitative issue but a critical parameter that should be monitored as part of cardiovascular health assessments.
Moreover, addressing psychological health provides an opportunity for comprehensive heart disease prevention. Mental health management should become a routine component of cardiovascular care to effectively decrease the prevalence of stress-induced heart conditions. Implementing screening for mental health as part of heart disease risk assessments can elevate patient care and promote a proactive approach toward cardiovascular health.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does stress contribute to coronary heart disease?
Stress is a significant risk factor for coronary heart disease (CHD) as it can lead to physiological changes such as increased blood pressure and inflammation. Chronic stress often results from work demands or personal challenges, which can foster unhealthy lifestyle choices that further elevate the risk of heart disease. Studies indicate that individuals experiencing high levels of stress have a 30% increased risk of developing cardiovascular diseases like CHD.
What are effective stress management strategies to prevent coronary heart disease?
Effective stress management strategies are crucial for coronary heart disease prevention. Techniques like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) can help individuals address negative thought patterns, while mindfulness practices reduce stress levels. Regular physical exercise serves dual purposes by relieving stress and promoting heart health. Incorporating healthy routines such as adequate sleep, balanced nutrition, and relaxation activities like yoga or meditation further enhances overall cardiovascular wellness.
What role does mental health management play in reducing the risk of coronary heart disease?
Mental health management plays a vital role in reducing the risk of coronary heart disease by addressing underlying psychological factors such as anxiety and depression. Chronic mental health issues are closely linked to an elevated risk of heart disease; thus, interventions focused on improving mental well-being can mitigate these risks. By using therapeutic methods and promoting a healthy lifestyle, individuals can effectively enhance their heart health.
Can mindfulness practices help mitigate stress related to coronary heart disease?
Yes, mindfulness practices can significantly help mitigate stress related to coronary heart disease. Research indicates that engaging in mindfulness activities reduces stress levels and promotes better cardiovascular health outcomes. Techniques such as meditation and yoga not only promote relaxation but also foster mental clarity, which contributes to overall heart health.
What lifestyle changes can support psychological health and prevent coronary heart disease?
Lifestyle changes that support psychological health and help prevent coronary heart disease include maintaining a balanced diet, ensuring adequate sleep, and engaging in regular physical exercise. Incorporating self-care practices such as relaxation techniques and building strong social connections can also reduce stress. These actions collectively enhance mental health and lower the physiological risk factors associated with coronary heart disease.
| Aspect | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Connection between Stress and CHD | Chronic stress significantly increases the risk of coronary heart disease (CHD), with studies showing a 30% increased risk among highly stressed individuals. |
| Psychological Impact | Mental health issues like anxiety and depression are strongly linked to a higher risk of heart disease. |
| Management Strategies | Effective management of stress includes Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), mindfulness practices, and regular physical exercise. |
| Self-Care Practices | Incorporating adequate sleep, healthy eating, and relaxation techniques can help lower stress and improve heart health. |
| Community Support | Strong social connections foster mental well-being and assist in managing stress that can negatively impact heart health. |
Summary
The connection between stress and coronary heart disease is a crucial topic that highlights the need for effective stress management to reduce cardiovascular risks. As modern life continues to present various stressors, it is essential to recognize how chronic stress can lead to detrimental health outcomes, including an increased likelihood of coronary heart disease. By implementing mental health management strategies such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, mindfulness, regular exercise, and maintaining a supportive social network, individuals can proactively reduce their stress levels and enhance their overall heart health. Prioritizing both mental and physical well-being is key to mitigating the risks associated with stress and coronary heart disease, leading to a healthier future.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.