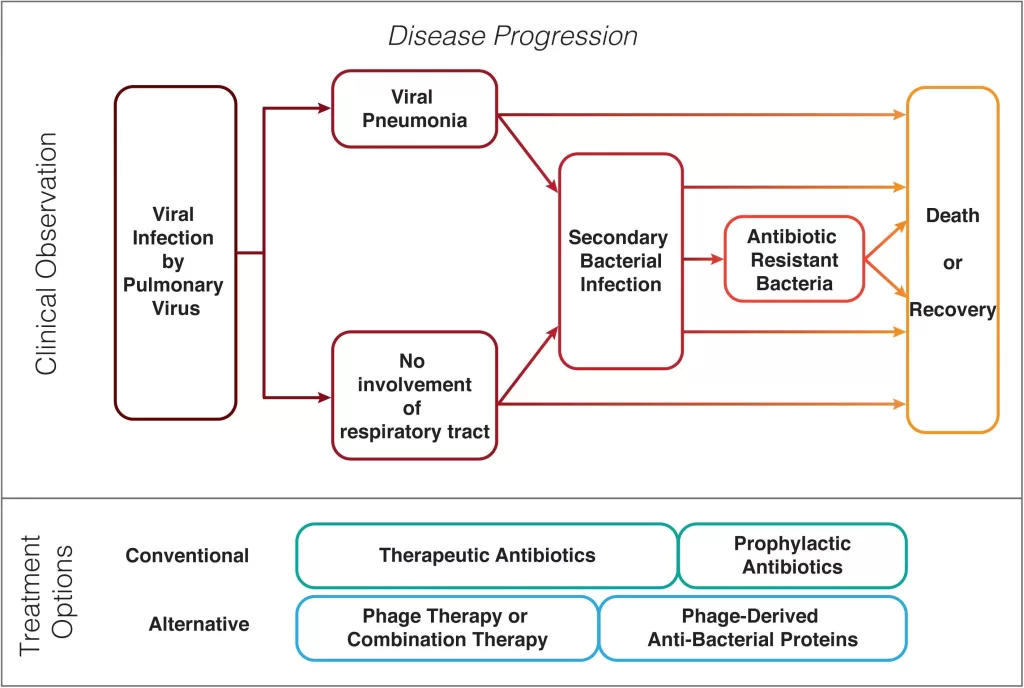
Secondary bacterial infections pose significant challenges in the treatment of patients suffering from viral pneumonia, a condition made even more complex by the ongoing pandemic. Especially in cases related to COVID-19, the interaction between viral pathogens and opportunistic bacteria, like *Klebsiella pneumoniae* and *Staphylococcus aureus*, has led to an alarming rise in complications for affected individuals. As the healthcare community grapples with the implications of these bacterial co-infections, antibiotic resistance remains a pressing concern that complicates effective treatment strategies. The dangers of these interlinked health issues are underscored by historical outbreaks such as SARS and MERS, where secondary infections contributed to notably high mortality rates. Understanding the dynamics of secondary bacterial infections is therefore crucial in enhancing patient management and developing effective therapeutic responses.
Infectious complications following primary viral infections have been recognized as a serious health issue, especially among hospitalized patients with respiratory illnesses. The phenomenon of superinfections, particularly in the context of viral pneumonia, is prevalent, as evidenced by the increasing rates of hospital-acquired bacterial infections. Terms such as bacterial co-infections and microbial superimposition have emerged in recent discussions about how viral diseases like COVID-19 exacerbate patient outcomes. With the rise of strains exhibiting antibiotic resistance, there is an urgency to rethink our treatment approaches for these dual-infection challenges. By exploring alternative therapies and preventive measures, healthcare professionals can better navigate the complexities of managing patients impacted by both viral and bacterial pathogens.
Understanding Secondary Bacterial Infections in Viral Pneumonia
Secondary bacterial infections are a significant complication arising from viral pneumonia, particularly in severe cases like COVID-19, SARS, and MERS. These infections often exacerbate the underlying conditions, leading to increased morbidity and mortality rates. For instance, bacterial co-infections can emerge during viral pneumonia, where pathogens such as *Klebsiella pneumoniae* and *Staphylococcus aureus* become opportunistic invaders. The body’s weakened immune response, due to the initial viral infection, fails to combat these bacterial pathogens effectively.
The interplay between viral and bacterial infections highlights the critical need to understand the mechanisms that promote secondary infections. Patients suffering from viral pneumonia are vulnerable due to an impaired immune response, which can allow for the growth of antibiotic-resistant bacterial strains. This phenomenon has become increasingly concerning amid the COVID-19 pandemic, where the prevalence of resistant infections complicates treatment options and outcomes.
Impact of COVID-19 on Bacterial Co-Infections
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly highlighted the risks associated with secondary bacterial infections. Studies have reported that up to 15% of hospitalized COVID-19 patients experience these co-infections, leading to severe complications. As healthcare providers employed antibiotic treatments, the effectiveness of broad-spectrum antibiotics like quinolones appeared limited against resistant strains. This predicament necessitates a more nuanced approach to antibiotic prescribing, where stewardship is critical to preserving the effectiveness of these essential drugs.
The increasing incidence of antibiotic resistance among bacterial co-infections emphasizes the urgent need for research into novel treatment strategies. Traditional antibiotics may not suffice; hence, alternative therapies, such as phage therapy, are coming into the spotlight. These innovative approaches could potentially offer new avenues for treatment, significantly enhancing recovery outcomes for patients battling the dual challenge of viral pneumonia and bacterial infections like those observed in COVID-19.
The Role of Antibiotic Resistance in Treatment Challenges
Antibiotic resistance presents a formidable challenge in the management of secondary bacterial infections. As resistance rates climb, healthcare providers find themselves in a precarious situation where standard antibiotic regimens fail to provide adequate coverage against resistant strains. The rise of multi-drug resistant bacteria, increasingly documented in viral pneumonia cases, notably complicates recovery and raises mortality risks, making it crucial to rethink treatment protocols and infection control measures.
Addressing antibiotic resistance requires a multidisciplinary approach involving microbiologists, clinicians, and epidemiologists to devise effective strategies. Public health initiatives aimed at educating the healthcare community and the public about responsible antibiotic use are paramount. Furthermore, investing in research to develop new antimicrobial agents and alternative therapies will be essential in combatting the dashboard of antibiotic resistance observed with viral pneumonia and bacterial co-infections.
Historical Perspectives: SARS and MERS Co-Infections
History has shown us that viral outbreaks such as SARS and MERS were not only marked by viral pathogenesis but also by the challenges posed by secondary bacterial infections. During the SARS epidemic, many patients experienced bacterial pneumonia, leading to significant complications and deaths. This historical data serves as a learning point, underlining the necessity for heightened surveillance and analysis of co-infections in any ongoing viral outbreak.
The patterns observed in SARS and MERS highlight the need for proactive measures in managing secondary bacterial infections during viral pandemics. Understanding the dynamics of these concurrent infections can inform better clinical practices and enhance preparedness for future outbreaks. As we continue to face new viral challenges, the lessons learned from past events can guide effective treatment strategies and intervention policies.
Exploring Novel Therapeutic Approaches
In the wake of rising antibiotic resistance, exploring novel therapeutic approaches is becoming increasingly critical. Traditional antibiotics are no longer a reliable first-line defense against the bacterial co-infections that follow viral infections. Research into phage therapy, antimicrobial peptides, and other alternatives shows promise in effectively targeting resistant pathogens. These innovative treatment modalities could redefine the approach to managing secondary bacterial infections in viral pneumonia cases, offering a glimmer of hope amidst the escalating resistance crisis.
Moreover, advancements in personalized medicine may provide tailored treatment options for patients based on their specific microbiological profiles. This could lead to more effective and targeted therapies, increasing the chance of recovery while minimizing the risk of developing further resistance. As we look forward, integrating these innovative strategies into clinical practice will be paramount in improving patient outcomes and controlling the rise of antibiotic resistance.
Viral Pneumonia and Public Health Implications
The intersection of viral pneumonia and secondary bacterial infections poses significant public health implications. The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has served as a stark reminder of how viral respiratory infections can lead to widespread complications and health crises. The rapid transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and its severe impact on respiratory health have necessitated a reassessment of public health policies regarding infection prevention and control measures.
Public health agencies must focus on enhancing surveillance systems to monitor antibiotic resistance patterns closely. Additionally, promoting vaccination against common respiratory viruses can play a vital role in mitigating the incidence of viral pneumonia. By reducing the initial viral load within populations, we may ultimately lower the risk of secondary bacterial infections, thereby preventing further strain on healthcare systems.
The Importance of Vigilant Microbial Stewardship
Vigilant microbial stewardship is crucial in managing complications arising from secondary bacterial infections associated with viral pneumonia. Given the alarming rates of antibiotic resistance, healthcare providers must prioritize responsible antibiotic prescribing practices. This requires a comprehensive understanding of local resistance patterns and the impact of over-prescription on the efficacy of antibiotics, especially in the context of co-infections.
Engaging healthcare professionals in continuing education about the risks of antibiotic misuse and the importance of appropriate antibiotic selection can significantly affect patient outcomes. By fostering a culture of stewardship, healthcare settings can help curb the rise of resistant pathogens, ensuring that effective treatment options remain available for future generations.
Future Directions in Research and Treatment
The pressing challenges posed by secondary bacterial infections in viral pneumonia highlight a critical need for directed research efforts. Future studies should focus on understanding the mechanisms of bacterial co-infections, especially in the context of viral infections like COVID-19. Investigating the genetic and phenotypic traits of bacteria responsible for co-infections could provide insights into their resilience against antibiotics, paving the way for the development of more effective therapeutic strategies.
Furthermore, collaborative research across disciplines will be essential in harnessing innovative solutions to address the complexities of viral pneumonia and its bacterial complications. Emphasizing interdisciplinary studies can link virology, microbiology, and clinical research to form comprehensive treatment protocols that can better serve patients suffering from dual infections, ultimately leading to improved healthcare outcomes.
Conclusion: Addressing the Dual Threat
In conclusion, the dual threat of viral pneumonia and secondary bacterial infections underscores the necessity for integrated management strategies. As we navigate through pandemics and respiratory infections, understanding the implications of bacterial co-infections is vital. The interconnectedness of viral and bacterial pathogens calls for a holistic approach that encompasses prevention, timely intervention, and innovative treatment options.
Future efforts must prioritize research on antibiotic resistance while fostering a culture of microbial stewardship within healthcare settings. Developing comprehensive treatment protocols that include both antiviral and antibiotic measures will be essential for improving patient outcomes. By learning from past outbreaks and enhancing our preparedness, we can ensure better management of secondary infections amidst the challenges posed by viral pneumonia.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are secondary bacterial infections and how are they related to COVID-19?
Secondary bacterial infections occur when bacteria infect a person already suffering from a viral infection, like COVID-19. These infections complicate recovery and can lead to serious health issues, as seen in hospitalized patients, where antibiotic-resistant strains often emerge.
How do secondary bacterial infections impact the prognosis of patients with viral pneumonia?
In patients with viral pneumonia, such as those caused by SARS-CoV-2, secondary bacterial infections significantly worsen prognosis. Studies show that these infections can lead to increased mortality rates, highlighting the need for effective management of such co-infections.
What role does antibiotic resistance play in treating secondary bacterial infections after viral pneumonia?
Antibiotic resistance complicates the treatment of secondary bacterial infections that occur following viral pneumonia. Traditional antibiotics often fail against resistant strains, necessitating alternative treatment strategies to effectively combat these infections and improve patient outcomes.
Can you explain the link between bacterial co-infections and respiratory viruses like SARS and MERS?
Bacterial co-infections frequently arise during viral infections, such as SARS and MERS, exacerbating lung damage and increasing mortality risks. The co-existence of these pathogens makes vigilant monitoring and tailored treatment essential in affected patients.
What should healthcare professionals consider when treating patients with COVID-19 and secondary bacterial infections?
Healthcare professionals must consider the high prevalence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria when treating patients with COVID-19 and secondary bacterial infections. Employing broad-spectrum antibiotics may not be sufficient, and exploring alternatives like phage therapy could be critical.
Are there new strategies to manage antibiotic-resistant secondary bacterial infections in viral pneumonia patients?
New strategies include incorporating phage therapy and antimicrobial peptides as alternatives to traditional antibiotics. These emerging treatments show promise in managing antibiotic-resistant secondary bacterial infections, potentially improving outcomes for patients with viral pneumonia.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Impact of Secondary Bacterial Infections | Secondary bacterial infections in patients with viral pneumonia, especially COVID-19, complicate clinical outcomes and increase mortality rates. |
| Common Pathogens | Pathogens like *Klebsiella pneumoniae* and *Staphylococcus aureus* are frequently involved in secondary infections following viral pneumonia. |
| Antibiotic Resistance | There is a growing prevalence of antibiotic-resistant bacterial strains, which complicates treatment and patient management. |
| Mortality Rates | Clinical studies reported a 15.2% mortality rate in COVID-19 patients due to secondary bacterial infections. |
| Treatment Strategies | Broad-spectrum antibiotics are commonly used, but they have shown limited effectiveness against resistant strains. |
| Need for Research | Ongoing research is needed to develop alternative treatments, including phage therapy and antimicrobial peptides. |
Summary
Secondary bacterial infections pose a significant risk in the management of viral pneumonia cases, particularly in the context of infections like COVID-19. The prevalence of antibiotic-resistant pathogens not only complicates the treatment process but also increases mortality rates, highlighting the urgent need for innovative therapeutic strategies. Comprehensive understanding and management of these infections are crucial to improving patient outcomes in the face of ongoing viral outbreaks.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.