The prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 symptoms has been a focal point of research since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, revealing a wide array of manifestations that vary by variant and individual. Recent meta-analysis of COVID-19 studies highlights how symptom progression can differ significantly, with some variants like Omicron presenting with distinct symptoms. This analysis spans data collected from over 430,100 patients in East and Southeast Asia, shedding light on common symptoms such as cough, fever, and fatigue. Understanding these patterns is essential for developing effective public health interventions and managing the ongoing challenges posed by SARS-CoV-2 variants. As researchers continue to explore COVID-19 symptom analysis, recognizing the evolving landscape of symptom prevalence will aid in preparedness for future outbreaks.
Exploring the symptom landscape associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection reveals critical insights into the COVID-19 experience that patients undergo. This ongoing investigation into the variety of symptoms, often referred to as COVID-19 symptomatology, provides a deeper understanding of how different SARS-CoV-2 variants, including the notorious Omicron strain, impact individuals. By examining the sequential onset of symptoms, it becomes clear that some manifestations, like respiratory issues and fatigue, are more prevalent during certain phases of infection. The use of advanced statistical models to analyze these trends enhances our grasp of symptom progression, which is vital for clinical management and public health strategies. As the pandemic continues, keeping abreast of these developments in symptom prevalence remains crucial for effective response and treatment.
Understanding SARS-CoV-2 Symptom Prevalence Across Variants
The symptom prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 has evolved significantly from 2020 to 2022, influenced heavily by emerging variants of the virus. Studies indicate that while fever and cough have been traditionally associated with COVID-19, the manifestation of symptoms varies considerably among the different SARS-CoV-2 variants. For example, data from our meta-analysis highlighted that the Alpha variant prominently featured fever in 78.18% of cases, while the Omicron variant is characterized by milder respiratory symptoms, often presenting as upper respiratory tract infections. This shifting symptom profile underscores the necessity for ongoing symptom prevalence evaluations to inform public health strategies.
Moreover, symptom prevalence is not just about identifying the most common symptoms; it involves understanding how these symptoms progress over time. The sequential onset of symptoms during SARS-CoV-2 infection can provide insight into the overall trajectory of the disease. Our use of stochastic models revealed that initial symptoms like dry cough and fever often precede more debilitating conditions such as sleep disorders and fatigue. This information is crucial for healthcare providers to anticipate potential complications and tailor their interventions accordingly.
The Role of COVID-19 Symptom Analysis in Variant Tracking
COVID-19 symptom analysis plays a pivotal role in tracking the spread and impact of various SARS-CoV-2 variants. By monitoring symptom progression and prevalence, researchers can establish patterns that may indicate how a variant behaves and how it might affect different populations. For instance, the emergence of the Omicron variant has been linked to a distinct set of symptoms that diverge from those associated with earlier variants. Understanding these differences through rigorous symptom analysis allows public health officials to adapt their response strategies effectively.
Furthermore, the meta-analysis of COVID-19 symptoms provides a comprehensive overview of how symptoms can inform our understanding of the virus’s evolution. The findings from our research, which included data from over 430,000 patients, reveal that while classic symptoms like fever remain prevalent, newer variants exhibit a range of symptoms that can complicate diagnosis and treatment. This evolution in symptomatology highlights the importance of continuous research and data collection to keep pace with the dynamic nature of the virus and its variants.
Symptom Progression: Insights from Advanced Analytical Models
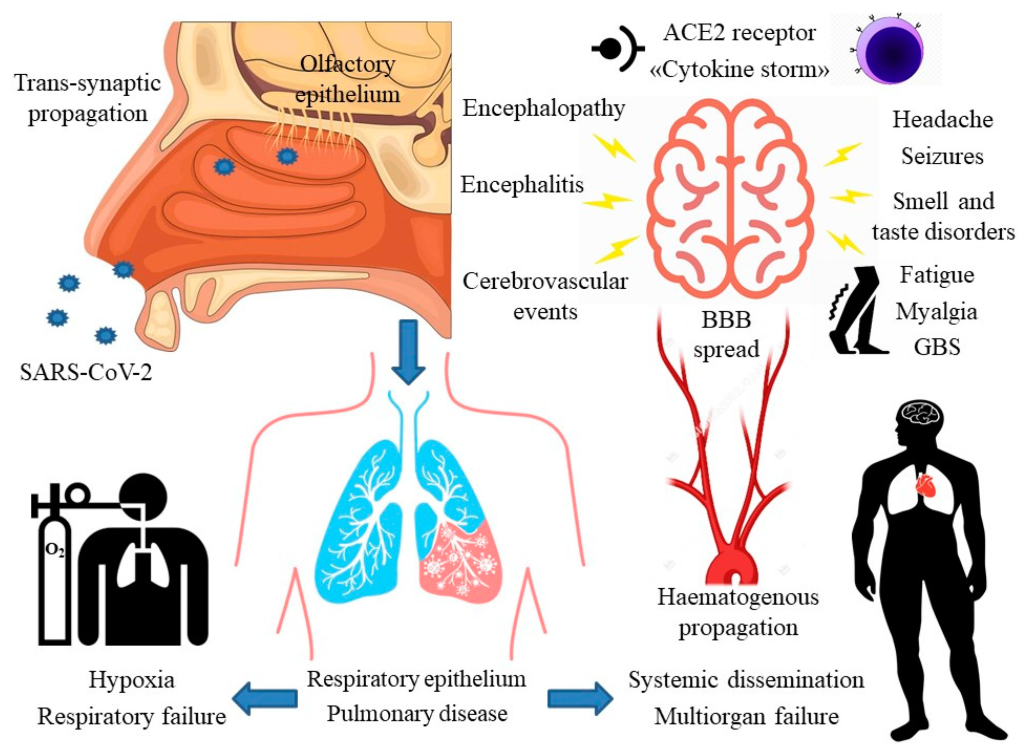
Advanced analytical models, such as the Stochastic Progression Model and SPADE algorithm, have revolutionized our understanding of symptom progression in COVID-19. These models utilize complex statistical techniques to uncover patterns in how symptoms develop over time, offering insights that traditional analyses may overlook. For instance, our study revealed that patients infected with the Omicron variant often experience an initial phase of mild respiratory symptoms, which may quickly transition to more severe neuropsychiatric symptoms. This understanding is crucial for early intervention and management of COVID-19.
Additionally, the implementation of these models allows researchers to simulate various scenarios of symptom progression across different variants. This capability is essential for anticipating healthcare needs and planning resource allocation effectively. By leveraging these advanced methodologies, we can gain a deeper understanding of the implications of SARS-CoV-2 variants on public health, ultimately leading to better outcomes for affected populations.
Comparative Analysis of Omicron Symptoms vs. Previous Variants
The Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 has introduced a new dimension to COVID-19 symptomatology, particularly when compared to earlier variants like Alpha and Delta. Our analysis found that while fever and cough were prominent in previous variants, Omicron symptoms are often milder and predominantly affect the upper respiratory tract. This shift in symptom profile may lead to underreporting or misdiagnosis, as individuals may not associate mild symptoms with COVID-19, highlighting the need for increased awareness and testing.
Furthermore, the comparative analysis also underscores the unique neuropsychological challenges posed by the Omicron variant. Patients have reported increased instances of fatigue, sleep disturbances, and cognitive difficulties, which were less prevalent in earlier variants. This emerging symptomatology necessitates targeted public health interventions and support systems to address the comprehensive impact of COVID-19 on mental health, particularly as the pandemic continues to evolve.
Meta-Analysis of COVID-19 Symptoms: Key Findings
Conducting a meta-analysis of COVID-19 symptoms provides a holistic view of how the disease manifests across different populations and variants. In our study, we synthesized data from multiple sources, involving over 430,100 patients, to derive key insights into symptom prevalence and progression. The findings revealed consistent patterns, such as the dominance of cough and fever across most variants, while also highlighting variant-specific symptoms that require tailored responses.
The meta-analysis approach is instrumental for identifying not only the frequency of symptoms but also their interrelations and progression pathways. For instance, understanding that dry cough often precedes fatigue can inform healthcare providers regarding patient management strategies, enabling them to anticipate complications and prioritize care effectively. This level of insight is crucial for adapting public health initiatives in response to the evolving landscape of COVID-19.
Emerging Trends in COVID-19 Symptomatology
As the COVID-19 pandemic continues, emerging trends in symptomatology warrant close attention from healthcare professionals and researchers alike. The evolution of SARS-CoV-2 variants has led to noticeable shifts in how symptoms present, with newer variants such as Omicron exhibiting a milder overall clinical picture but also introducing new challenges like neuropsychiatric symptoms. These trends not only affect individual patient care but also have broader implications for public health strategies and resource allocation.
Tracking these emerging trends involves continuous data collection and analysis, particularly through robust meta-analyses that can capture variations across demographics and regions. By staying informed of these developments, healthcare systems can better prepare for potential surges in cases and adapt their response protocols to meet the needs of affected populations, ensuring that interventions remain relevant and effective.
The Importance of Continuous Research in COVID-19 Symptom Tracking
Continuous research is vital in the context of COVID-19 symptom tracking as it allows for the identification of changing patterns in symptomatology over time. Given the rapid evolution of SARS-CoV-2 variants, ongoing studies are necessary to keep healthcare professionals informed about the latest findings regarding symptom prevalence and progression. Our comprehensive meta-analysis serves as a reminder of the importance of integrating new data into public health frameworks, ensuring that strategies remain effective against emerging variants.
Moreover, by focusing on symptom tracking, researchers can identify potential public health threats early, facilitating timely interventions. The ability to discern trends in symptom presentation not only aids in clinical decision-making but also enhances the effectiveness of public health messaging. As we continue to navigate the complexities of the COVID-19 pandemic, the commitment to continuous research will be essential in mitigating the disease’s impact on communities worldwide.
Neuropsychological Impacts of COVID-19: A Growing Concern
The neuropsychological impacts of COVID-19 have garnered increasing attention, particularly in light of findings related to the Omicron variant. Our study highlights that many patients experience cognitive difficulties, fatigue, and sleep disturbances, which are significant concerns for long-term recovery and mental health. These symptoms, while often overlooked in earlier discussions about COVID-19, have become crucial in understanding the full scope of the virus’s impact on individuals.
Understanding these neuropsychological effects is essential for developing comprehensive treatment plans that address both physical and mental health. As healthcare providers become more aware of the prevalence of these symptoms, there is an urgent need for integrated care approaches that consider the psychological well-being of patients. Future research should prioritize exploring these dimensions to provide better support and resources for those affected by COVID-19.
Implications for Public Health Interventions and Policies
The evolving landscape of COVID-19 symptomatology has significant implications for public health interventions and policies. As new variants emerge and symptoms continue to diversify, health officials must adapt their strategies to ensure effective management of COVID-19 cases. This includes enhancing surveillance systems to capture data on symptom prevalence, which can inform resource allocation and targeted interventions.
Additionally, public health messaging must evolve to educate the public on the changing nature of COVID-19 symptoms. By raising awareness of atypical presentations, particularly those associated with variants like Omicron, health authorities can encourage timely testing and isolation measures, thereby reducing transmission rates. Well-informed policies that reflect the latest research will be critical in managing the ongoing pandemic and protecting vulnerable populations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the prevalence of symptoms associated with SARS-CoV-2 variants during the acute phase of COVID-19?
The prevalence of symptoms associated with SARS-CoV-2 variants varies significantly. A meta-analysis of 430,100 patients indicated that fever was most prevalent in Alpha variant cases, while cough was consistently reported across wild-type, Delta, and Omicron variants. Understanding symptom prevalence across these variants is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment.
How do COVID-19 symptom analysis and symptom progression differ among SARS-CoV-2 variants?
COVID-19 symptom analysis reveals distinct patterns of symptom progression among SARS-CoV-2 variants. For instance, the Omicron variant primarily affects the upper respiratory system, while the Delta variant shows a broader range of systemic symptoms. Sequential onset often begins with fever and cough, followed by fatigue and neuropsychiatric symptoms, highlighting the importance of variant-specific approaches in treatment.
What are the common symptoms reported in patients infected with the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2?
Common symptoms reported in patients infected with the Omicron variant include upper respiratory issues such as a runny nose and sore throat, along with dry cough and fatigue. Although Omicron symptoms tend to be milder compared to previous variants, there is an increased prevalence of neuropsychological challenges, necessitating targeted interventions.
How does the symptom prevalence of COVID-19 change over time and with different SARS-CoV-2 variants?
Symptom prevalence of COVID-19 changes over time and varies with different SARS-CoV-2 variants. For example, early symptoms typically include fever and cough, but as the infection progresses, symptoms like fatigue and sleep disorders may emerge. The study’s use of advanced stochastic models provides insights into these evolving patterns, which are essential for understanding disease trajectory.
What implications does the meta-analysis of COVID-19 symptoms have for public health interventions?
The meta-analysis of COVID-19 symptoms highlights the need for public health interventions to be tailored to the symptomatology associated with specific SARS-CoV-2 variants. Recognizing the predominance of certain symptoms can guide healthcare providers in diagnosis and treatment, improving patient outcomes and resource allocation during the pandemic.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Background | The COVID-19 pandemic’s diverse symptoms necessitate understanding due to variant-driven changes. |
| Methods | Meta-analysis of literature before December 9, 2022, using various databases to evaluate symptom prevalence. |
| Results | Among 430,100 patients, cough was prevalent across variants; fever most common in Alpha (78.18%). Omicron linked to upper respiratory, cardiovascular, and neuropsychiatric symptoms. |
| Conclusion | Evolving symptoms noted across variants, with Omicron showing milder symptoms but increased neuropsychological issues. |
| Contributions | Identified neuropsychological challenges of Omicron; utilized advanced models for symptom progression analysis. |
Summary
SARS-CoV-2 symptom prevalence has been deeply analyzed, revealing significant trends and patterns across different variants from 2020 to 2022. This study indicates that while symptoms such as fever, cough, and fatigue remain common across the Alpha, Delta, and Omicron variants, the manifestation and severity of these symptoms can vary. Notably, the Omicron variant is associated with milder respiratory symptoms but poses greater neuropsychological challenges. The findings emphasize the importance of continuous monitoring and targeted interventions to address the evolving symptom landscape of SARS-CoV-2.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.