Rheumatoid arthritis flares are a daunting reality for those living with this chronic condition, turning everyday tasks into monumental challenges. Just as sailors rely on weather patterns to prepare for storms, individuals with rheumatoid arthritis may soon have a tool to predict these debilitating flare-ups thanks to groundbreaking research. Recent studies reveal that unique immune cells, known as PRIME cells, can signal an approaching flare up to a week in advance, potentially revolutionizing the management of rheumatoid arthritis. The ability to detect these cells through advanced RNA sequencing holds promise for the early detection of flares, allowing patients to take proactive measures to mitigate suffering. As researchers continue to explore the implications of predicting arthritis flares, the landscape of rheumatoid arthritis treatment may shift toward a future where patients can gain more control over their symptoms and overall well-being.
Flares of rheumatoid arthritis, often characterized by heightened pain and discomfort, present significant hurdles for patients. Understanding these episodes through innovative methods, such as RNA sequencing, enables researchers to identify pivotal biomarkers and cell types linked to symptom exacerbation. By examining blood samples, scientists have discovered novel cell signatures that could serve as early indicators of upcoming flare-ups. This research aims to not only improve the management of rheumatoid arthritis but also to enhance the quality of life for sufferers by promoting timely intervention. As we unravel the complexities of arthritis, leveraging insights into these flare-inducing cells could lead to promising therapeutic strategies tailored for individuals facing this chronic illness.
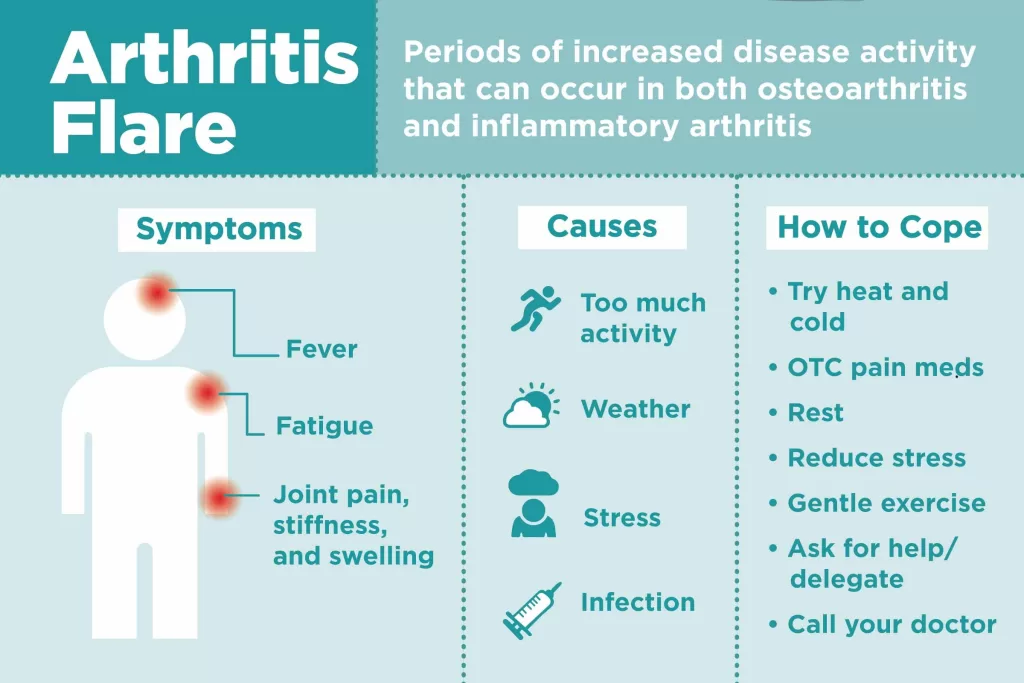
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Flares
Rheumatoid arthritis flares can wreak havoc on the lives of those affected, bringing sudden pain and discomfort that disrupt daily activities. Patients often experience periods of remission, where symptoms subside, followed by unforeseen flare-ups that can vary in intensity and duration. The unpredictability of these flares adds a layer of anxiety, as individuals attempt to navigate their daily routines without knowing when they might be affected again.
New research has emerged, highlighting the potential to understand and predict these arthritis flares. By analyzing blood samples through RNA sequencing, scientists have begun identifying specific cell types that may indicate an impending flare. This breakthrough provides hope for a more proactive approach in managing rheumatoid arthritis, potentially reducing the severity and impact of these disruptive episodes.
Incorporating the study of newly discovered PRIME cells could lead to significant advancements in predicting arthritis flares. By understanding how these cells function and increase in number prior to a flare, we may develop tests that allow patients and doctors to anticipate flare-ups. This could empower patients to adjust their activities and treatment plans, thus improving their quality of life.
Furthermore, the predictive ability of these cellular changes emphasizes the importance of regular monitoring and early detection of flares. As researchers continue to refine their methods through RNA sequencing and blood analysis, the future of arthritis management may see less reliance on reactive treatments and more focus on prevention.
The Role of RNA Sequencing in Predicting Flares
RNA sequencing represents a transformative approach in understanding rheumatoid arthritis, particularly in the context of predicting flares. This technique allows researchers to uncover the molecular changes that precede flare-ups by examining gene expression patterns over time. By collecting regular blood samples from patients, scientists can identify biomarkers that signal imminent flares, providing valuable insights into the body’s response before symptoms manifest.
The implications of RNA sequencing are profound—not only does it enhance our understanding of the biological mechanisms behind rheumatoid arthritis, but it also paves the way for developing innovative predictive models. Identifying specific gene expressions related to flares enables more tailored therapies to be designed, potentially enhancing the management of rheumatoid arthritis through personalized medicine.
By employing RNA sequencing in conjunction with the study of PRIME cells, researchers can deepen their understanding of the inflammatory processes of rheumatoid arthritis. This synergy could lead to new strategies for early detection of flares, allowing for timely interventions that mitigate flare severity and improve patient outcomes significantly.
Thus, the integration of RNA sequencing into arthritis research signals a shift towards a more data-driven, predictive approach in managing the condition. This evolving field holds the promise of empowering both patients and healthcare providers with the tools necessary for better management of rheumatoid arthritis.
PRIME Cells and Their Implications for Arthritis Management
The identification of PRIME cells marks a significant breakthrough in the understanding of rheumatoid arthritis and its unpredictable flares. These unique cells exhibit a peculiar increase in number prior to flare-ups, suggesting a critical role in the disease’s pathology. As researchers continue to investigate these cells, they may offer pivotal insights into the triggers of arthritis symptoms, helping to unveil the complexities of this autoimmune disorder.
The presence of PRIME cells prior to flares indicates potential windows for therapeutic intervention. If future studies confirm that these cells contribute to inflammation and flare development, they could become prime targets for new treatment strategies. Understanding their function may lead to innovative drugs that not only alleviate symptoms but also address the root causes of rheumatoid arthritis.
Moreover, the research surrounding PRIME cells provides a pathway for developing better management protocols for patients. By creating strategies tailored to predicting and managing flares based on PRIME cell activity, healthcare providers can offer more effective, personalized care. This could ultimately lead to improved patient adherence to treatment plans and better overall outcomes.
In conclusion, the exploration of PRIME cells is set to revolutionize the field of rheumatoid arthritis management, emphasizing the importance of predictive models and early interventions. Continued research in this area could mean a future where patients are better prepared to handle their condition and enjoy a higher quality of life.
Managing Flares: Proactive Approaches to Treatment
Effective management of rheumatoid arthritis hinges on the ability to anticipate and respond to flares proactively. The emerging research on PRIME cells and RNA sequencing presents new opportunities for achieving this goal. By utilizing information gained from these studies, healthcare providers can develop formulations and treatment plans that preemptively address the signs of a flare.
One practical approach might include establishing regular monitoring for patients at risk of experiencing frequent flares. Implementing regular RNA testing to track PRIME cell levels could provide the necessary data for timely interventions. This proactive management approach hopes to minimize the impact of flare-ups, allowing individuals to maintain their daily routines with less disruption.
Moreover, education plays a crucial role in managing rheumatoid arthritis effectively. Patients must be informed about the significance of recognizing the early signs of flares and understanding their treatment options. Workshops or sessions with rheumatologists about recent research findings can empower patients to take an active role in their health management.
In summary, the continuous advancements in arthritis research, particularly regarding rheumatoid arthritis flares, foster an optimistic perspective for future management strategies. A focus on proactive approaches can drastically improve life quality for those living with rheumatoid arthritis.
Future Directions in Rheumatoid Arthritis Research
The landscape of rheumatoid arthritis research is rapidly evolving, spurred on by groundbreaking studies that explore the underlying mechanisms of the disease. Researchers are encouraged by the discovery of new indicators, such as PRIME cells, that hold promise for flagging impending flares. The implications of such findings reach far beyond immediate symptom management; they pave the way for revolutionary advancements in preventative care.
Future directions in this field will likely focus on refining methods for detecting these predictive cells and developing protocols that incorporate their findings into routine care. Innovations in home testing and patient monitoring can expand access to this advanced level of care, allowing for more personalized and effective strategies in managing rheumatoid arthritis.
As scientific understanding deepens, it may result in novel therapeutic interventions that target the core biological processes leading to flares. This could fundamentally change how clinicians prescribe treatments, transitioning from reactive to proactive management strategies that prioritize long-term health outcomes.
Overall, the persistent exploration of new research avenues promises to lead to enhanced quality of life for those battling rheumatoid arthritis. As we look to the future, the collaborative efforts of researchers, healthcare providers, and patients are essential in transforming the management of this complex condition.
The Importance of Early Detection in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Early detection of rheumatoid arthritis flare-ups can significantly affect the management and overall health outcomes of patients. Recognizing the signs that precede a flare allows both patients and medical professionals to intervene early, reducing the severity and duration of symptoms. Understanding how cellular markers, such as those identified in recent studies, can indicate impending flares reflects an advance toward more informed patient care.
Advancements in research—including RNA sequencing that highlights changes in gene expression and the discovery of PRIME cells—are invaluable for formulating effective early detection strategies. By implementing simple testing methods that monitor these biological indicators, individuals with rheumatoid arthritis could be better positioned to navigate daily life significantly.
Incorporating early detection protocols into routine care may also empower patients to communicate more effectively with their healthcare providers. It enhances engagement and responsibility, encouraging patients to monitor their symptoms proactively and seek help at the first signs of potential flare-ups.
Ultimately, the commitment to early detection illustrates a broader shift toward prioritizing quality of life for individuals managing rheumatoid arthritis. The fusion of research and clinical practice has the potential to create a more sustainable and efficient approach to managing this chronic condition.
Living with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Coping Strategies
Coping with the challenges of rheumatoid arthritis involves not just medical treatment but also adopting holistic strategies that enhance overall well-being. Patients often have to navigate physical limitations and emotional stress from unpredictable flare-ups. Developing practical coping mechanisms—such as maintaining a healthy lifestyle, effective communication with healthcare providers, and seeking support from community resources—is crucial.
Mindfulness and stress management techniques can also play a pivotal role in helping individuals manage their arthritis symptoms. Engaging in activities such as yoga, meditation, or tai chi can promote physical comfort and emotional resilience. These approaches can contribute to minimizing stress, which can, in turn, help reduce the frequency and severity of flares.
Moreover, it’s essential for patients to stay informed about their condition. Understanding their disease and the research surrounding it can empower individuals to take charge of their health. With new advancements in predicting flare-ups through the monitoring of PRIME cells, patients can set realistic goals and expectations for their day-to-day life.
Support groups and counseling can provide additional resources and emotional connections, allowing patients to share experiences and coping strategies. This community aspect can create a sense of solidarity and resilience, making it easier to manage the ups and downs of living with rheumatoid arthritis.
Impact of Lifestyle Choices on Rheumatoid Arthritis Management
The management of rheumatoid arthritis greatly benefits from mindful lifestyle choices. Diet, exercise, and stress levels play significant roles in influencing the frequency and intensity of flare-ups. Research suggests that certain dietary components can either exacerbate or alleviate symptoms. For instance, anti-inflammatory foods such as omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and whole grains may help in reducing inflammation and potentially mitigate flare-ups.
Regular physical activity is essential for maintaining joint mobility and overall health. Patients are encouraged to engage in low-impact exercises that respect their limits while promoting joint strength and flexibility. A well-designed exercise regimen can enhance physical endurance, thus diminishing the impact of rheumatoid arthritis flares.
Additionally, stress management is critical in the life of someone diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis. High-stress levels can catalyze inflammation responses, leading to potential flare-ups. Techniques such as cognitive behavioral therapy, relaxation practices, and hobbies can positively influence stress levels and promote a healthier outlook on life.
In summary, the choices individuals make in their daily lives have a profound impact on their experience with rheumatoid arthritis. By focusing on positive habits, patients can significantly improve their physical health and emotional well-being, helping to curtail the unpredictability of arithmetic flares.
Collaborative Healthcare Approaches in Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis
Navigating the complexities of rheumatoid arthritis often requires a collaborative and multidisciplinary healthcare approach. It’s essential for patients to engage not only with rheumatologists but also with physiotherapists, dietitians, and mental health professionals. This teamwork can lead to a more comprehensive understanding of the disease and develop targeted strategies tailored to individual needs.
For example, a rheumatologist can provide the necessary medical regimen while a physiotherapist can assist in creating an exercise plan that accommodates joint limitations. A dietitian can offer dietary adjustments that help reduce inflammation, and a mental health professional can address the emotional aspects of living with a chronic illness. Together, this collaborative approach can enhance overall treatment efficacy.
Moreover, the integration of technology comes into play within this collaborative model. Utilizing telehealth services can facilitate better communication among team members and patients, ensuring that everyone stays updated on progress, setbacks, and flare predictions through cell markers like PRIME cells.
Overall, a team-centric model in managing rheumatoid arthritis exemplifies the importance of comprehensive care. This holistic perspective can ultimately lead to better health outcomes and empower patients to take an active role in their journey, reducing the impact of unpredictable rheumatoid arthritis flares.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can predicting arthritis flares improve the management of rheumatoid arthritis?
Predicting arthritis flares allows patients and healthcare providers to prepare in advance for increased symptoms. By identifying specific biomarkers, such as the newly discovered PRIME cells, interventions can be implemented before flares occur, potentially reducing pain and enhancing the quality of life for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis.
What are PRIME cells and their role in rheumatoid arthritis flares?
PRIME cells are a new type of cell identified in recent research that show increased levels in blood up to a week before an arthritis flare. Their presence may indicate an impending flare, providing a crucial opportunity for early intervention and potentially reducing the severity of symptoms associated with rheumatoid arthritis.
What is RNA sequencing in arthritis research and its significance in detecting flares?
RNA sequencing in arthritis research involves analyzing gene expression over time to identify molecular changes leading up to rheumatoid arthritis flares. This technique has led to the discovery of PRIME cells, which may help predict flares and improve patient management by allowing for timely treatments.
How does early detection of flares contribute to better outcomes for patients with rheumatoid arthritis?
Early detection of flares, facilitated by identifying biomarkers like PRIME cells, contributes to better outcomes by enabling proactive treatment strategies. This can minimize the impact of flares on daily life and potentially prevent long-term joint damage associated with uncontrolled rheumatoid arthritis.
What are the implications of the new findings on PRIME cells for the future treatment of rheumatoid arthritis?
The discovery of PRIME cells has significant implications for future rheumatoid arthritis treatments. If these cells are confirmed to be precursors to inflammatory processes, they could serve as targets for new therapies aimed at preventing flares, ultimately leading to more effective management of rheumatoid arthritis symptoms.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose of Study | To identify cellular changes in blood samples that can predict rheumatoid arthritis flares. |
| Methodology | Patients used a finger-prick kit for weekly blood samples, which were analyzed using RNA sequencing. |
| New Cell Discovery | Researchers found a new cell type called PRIME cells that increase in number before a flare. |
| Implications | Identifying PRIME cells could help predict flares, allowing patients to manage their symptoms better. |
| Future Directions | Focus on understanding PRIME cells and developing therapies to prevent flares effectively. |
Summary
Rheumatoid arthritis flares can severely disrupt daily life, but new research offers hope for better predictability. By studying blood samples, scientists have identified a new cell type that may signal impending flares, providing patients with a valuable tool for managing their condition. This discovery could lead to innovative ways to anticipate and mitigate the pain associated with rheumatoid arthritis, making flares less disruptive and enhancing overall quality of life.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.