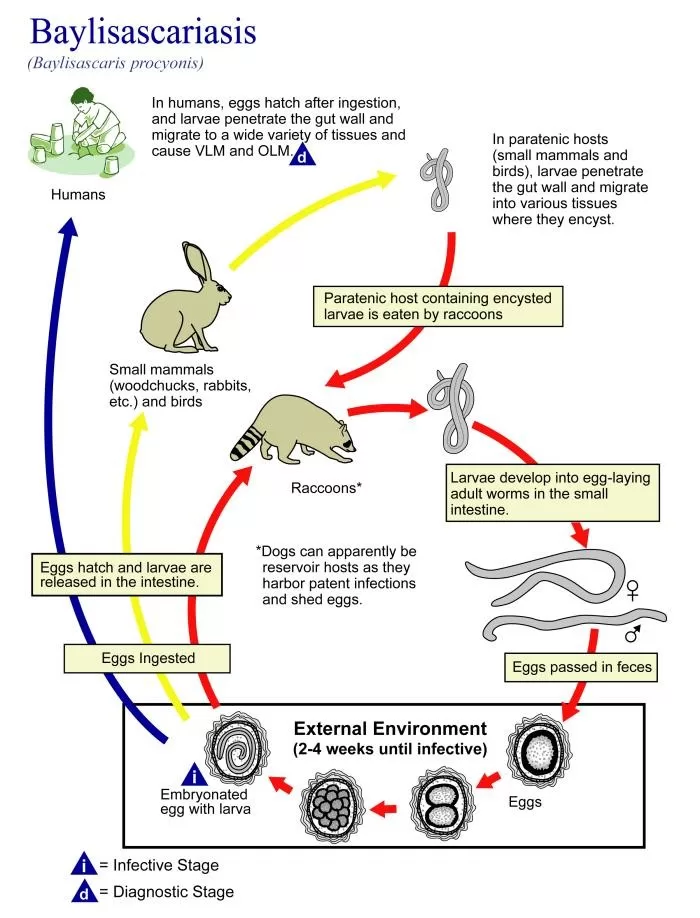
Raccoon roundworm infections, caused by the parasite Baylisascaris procyonis, pose significant health risks, especially to young children and individuals with developmental disabilities. This infection can lead to severe neurological complications, including eosinophilic meningoencephalitis, as recently reported in two California children. These cases involved symptoms such as roundworm larvae presence in the eye and elevated eosinophil levels, often resulting from exposure to contaminated soil or raccoon feces. Misdiagnoses can exacerbate the health impacts, leading to lasting motor, visual, and cognitive impairments. It is crucial to raise awareness about raccoon roundworm infections and educate the public on preventive measures to mitigate exposure to this dangerous parasite.
Raccoon roundworm, or Baylisascaris infection, is gaining attention due to its potential to inflict serious health challenges, especially in vulnerable populations such as children. The nematode larvae, when ingested, can lead to severe conditions, including neurological disorders like eosinophilic meningoencephalitis. Awareness of this parasite is essential since initial symptoms may mimic other illnesses, delaying proper treatment. The cases, particularly in young children with pica—a tendency to eat non-food items—highlight the importance of recognizing the signs and ensuring timely intervention. Ultimately, educating families about the risks associated with raccoon feces and effective prevention strategies is vital for reducing the occurrence of such infections.
Understanding Raccoon Roundworm Infections
Raccoon roundworm infections, caused by the parasite Baylisascaris procyonis, pose significant health risks, particularly to young children. These infections are contracted primarily through the ingestion of raccoon feces or contaminated soil where the roundworm larvae can reside. It is alarming that studies suggest up to 80% of raccoons in certain regions of the United States carry this parasite asymptomatically, making them a hidden yet potent source of infection. In the case reports from California, two children were severely affected after exposure to environments where raccoons frequently defecate, illustrating the importance of public awareness and preventive measures.
The infections can lead to a range of serious health issues, including eosinophilic meningoencephalitis, which is characterized by inflammation of the brain and protective membranes. Symptoms may vary but often include neurological complications such as difficulties in coordination, behavioral changes, and cognitive impairments. These conditions highlight the urgent need for healthcare providers to recognize and promptly treat potential raccoon roundworm infections, particularly in children who might engage in pica or other risk-taking behaviors related to environmental exposure.
Neurological Complications from Baylisascaris Procyonis Infections
Infections caused by Baylisascaris procyonis can lead to severe and sometimes irreversible neurological complications. The reports from Los Angeles County regarding two children illustrate the importance of early diagnosis and treatment. The first young patient, with pre-existing conditions, suffered from sustained cognitive and motor impairments due to a delay in recognizing the symptoms of roundworm infection. Neurological complications such as these emphasize the risks that raccoon roundworm infections pose, especially to those already vulnerable due to developmental disabilities.
The second patient, a 15-month-old child who was previously healthy, faced significant challenges after misdiagnosis. His case underlines the necessity for swift intervention, including empirical treatment with antiparasitic medications like albendazole. Neurological recovery can occur in some cases, but delays result in profound complications, emphasizing a crucial message for healthcare professionals to maintain a high index of suspicion for Baylisascaris procyonis in patients presenting with characteristic symptoms.
Pica in Children and its Connection to Raccoon Roundworm
Pica, a condition characterized by the consumption of non-food items, can significantly heighten the risk of raccoon roundworm infections among children. The 14-year-old reported from Los Angeles had a known history of pica, which may have led to his exposure to contaminated environments or materials. This behavior can predispose children to ingest contaminants, including eggs from Baylisascaris procyonis, thus illustrating a direct correlation between pica and the likelihood of infection.
Health professionals emphasize the need for vigilance in assessing children exhibiting pica behaviors, particularly in areas known to harbor raccoon populations. Educational programs and public health campaigns focused on raising awareness about the risks associated with pica and measures to mitigate exposure to raccoon feces can significantly reduce infection rates. By informing parents and caregivers about the dangers of pica in conjunction with raccoon-related hazards, we can strive to prevent such severe infections and protect vulnerable children.
Preventive Measures Against Raccoon Roundworm
Preventing raccoon roundworm infections requires a collaborative approach combining individual awareness, community education, and effective wildlife management. Families living in areas where raccoons are prevalent should implement strategies to deter these animals from encroaching on their properties, such as securing trash bins, removing potential food sources, and sealing entry points into homes. Additionally, community outreach programs can guide residents on appropriate disposal of raccoon feces and safe gardening practices to avoid soil contamination.
Local health departments play a vital role in educating residents about the risks of raccoon roundworm and the importance of prompt medical consultation for symptoms aligned with B. procyonis infections. By fostering community engagement and sharing facts on the significance of reporting unusual wildlife behavior, public health officials can drive proactive measures, thereby reducing potential exposure to raccoon roundworm infections and protecting children’s health.
The Role of Healthcare Providers in Diagnosis and Treatment
Healthcare providers are on the frontline when it comes to recognizing and treating complications from raccoon roundworm infections. A comprehensive understanding of the presenting symptoms, particularly in young children, is essential. Given the diverse symptoms that B. procyonis infections can manifest, from eosinophilic meningoencephalitis to neurological impairments, providers must remain informed about recent cases and combine clinical evaluation with patient history, especially concerning environmental exposures.
Further, providers should be proactive in initiating treatment protocols when signs suggestive of raccoon roundworm infections arise. Empirical usage of medications like albendazole, alongside appropriate supportive care, can significantly improve patient outcomes. Engagement in continued education regarding zoonotic diseases and collaboration with public health entities will enhance recognition and management of infections, ultimately contributing to community health and safety.
Emerging Trends in Raccoon Roundworm Infections
With the rise in urban raccoon populations, there has been a notable increase in reported cases of raccoon roundworm infections. Urbanization has driven these wild animals closer to human habitats, leading to more opportunities for transmission of Baylisascaris procyonis through contaminated environments. Public health officials are observing trends that reflect changing infection patterns, raising concerns over heightened exposure risks for children and vulnerable populations.
The emergence of these trends calls for robust epidemiological studies to better understand the relationship between raccoon populations and transmission dynamics of the roundworm. In particular, monitoring environmental factors and human interactions with raccoon habitats will be paramount to developing effective public health strategies aimed at mitigating risks associated with these infections. As research continues, communities must remain vigilant and responsive to the evolving landscape of raccoon roundworm infections.
The Importance of Public Awareness Campaigns
Public awareness campaigns are vital in combatting the risks associated with raccoon roundworm infections. Educating families about safe practices, such as avoiding contact with raccoon feces, can dramatically reduce the incidence of infection. Campaigns can also emphasize the significance of reporting any encounters with raccoons in residential neighborhoods, ensuring communities take proactive measures to control wildlife populations.
Moreover, integrating information on the potential health consequences of Baylisascaris procyonis and related neurological issues into educational initiatives can prepare communities for identification and management of symptoms. By fostering a culture of awareness, public health leaders can empower individuals to contribute to disease prevention efforts, thus promoting a safer living environment for all.
Developing Effective Treatment Protocols
As highlighted in the recent reports, developing effective treatment protocols for raccoon roundworm infections is imperative for improving patient outcomes. Prompt diagnosis and management strategies, particularly for pediatric patients, need to evolve in accordance with the evolving landscape of these infections. Treatments should be standardized to include antiparasitic medications like albendazole and corticosteroids to mitigate inflammation and address the severe symptoms associated with B. procyonis.
Moreover, consistent updates to clinical guidelines can ensure healthcare providers are equipped with current knowledge on managing eosinophilic meningoencephalitis and related manifestations of infection. Collaborative efforts between healthcare facilities and public health agencies will facilitate the dissemination of best practices and encourage a unified approach to treatment, ultimately aiming to minimize the long-term impacts on affected individuals.
Research Advances in Raccoon Roundworm Infection Management
Ongoing research into raccoon roundworm infections is crucial for developing improved management strategies. Investigative studies focused on understanding the life cycle of Baylisascaris procyonis and its transmission patterns can yield significant insights into prevention methodologies. Enhanced knowledge regarding the environmental factors that enable the parasite’s persistence will be instrumental in formulating community guidelines aimed at reducing infection rates.
Additionally, further exploration into the neurotoxicity of roundworm larvae and their impacts on cognitive and motor functions will contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of treatment needs. Collaborative research efforts between epidemiologists, parasitologists, and public health officials will be key to advancing strategies aimed at controlling raccoon populations and minimizing public health risks associated with roundworm infections.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are raccoon roundworm infections and how does Baylisascaris procyonis affect humans?
Raccoon roundworm infections are caused by the parasite Baylisascaris procyonis, which primarily infects raccoons. Humans can become infected through the ingestion of raccoon feces or contaminated soil, leading to a condition called baylisascariasis. This can result in severe neurological complications, including encephalitis and visual impairments, particularly in young children or individuals with developmental issues.
What symptoms should I look for in cases of Baylisascaris procyonis infection?
Symptoms of Baylisascaris procyonis infection can include encephalopathy, elevated eosinophils in the cerebrospinal fluid, behavioral changes, and unsteady gait. In severe cases, infection can lead to eosinophilic meningoencephalitis, neurological complications, and even vision problems caused by roundworm larvae affecting the eye.
How can children be at risk for raccoon roundworm infections?
Children, especially those with a history of pica (eating non-food items), are at higher risk for raccoon roundworm infections. They may inadvertently ingest roundworm larvae from contaminated soil or raccoon feces while playing outdoors. Public health recommendations emphasize the importance of preventing raccoon access to human environments to reduce risk.
What are the potential long-term effects of raccoon roundworm infections in children?
Children infected with raccoon roundworm (Baylisascaris procyonis) may experience long-term neurological complications and cognitive deficits. In the reported cases, one child faced significant health challenges like cognitive and motor impairments due to delays in diagnosis and treatment, highlighting the need for timely medical intervention.
How can raccoon roundworm infections be prevented?
Preventing raccoon roundworm infections involves discouraging raccoon activity near homes by securing food sources and trash, avoiding contact with raccoon feces, and safely removing raccoon latrines. Education about exposure risks is vital in community health efforts, especially in areas where raccoons are prevalent.
What treatment options are available for raccoon roundworm infections?
Treatment for raccoon roundworm infections typically includes antiparasitic medications like albendazole and corticosteroids to address symptoms. Prompt treatment is critical, especially in individuals presenting with eosinophilic meningoencephalitis, to mitigate the risk of severe neurological complications.
Are there any specific guidelines for healthcare providers regarding raccoon roundworm infections?
Healthcare providers are advised to suspect Baylisascaris procyonis infection in patients, particularly young children or those with developmental disabilities presenting gastrointestinal or neurological symptoms. Rapid initiation of treatment with albendazole, along with a thorough examination of medical history for potential exposure, is crucial for improved outcomes.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Reported Cases | Two children in Los Angeles County, California, were reported with raccoon roundworm infections in 2024. |
| Symptoms | Symptoms included encephalopathy, roundworm larvae in the eye, elevated eosinophils, behavioral changes, and unsteady gait. |
| Diagnosis and Treatment | Both patients tested positive for Baylisascaris procyonis and were treated with albendazole and corticosteroids. |
| Impacted Patients | The first patient (14 years old) had autism and a history of pica; the second patient (15 months old) faced severe complications. |
| Source of Infection | Raccoon feces from a rooftop latrine was identified as the likely source for the older child; younger child’s source unknown. |
| Preventive Measures | Prevent exposure to raccoon feces, discourage raccoon presence near homes, and safely clean up raccoon latrines. |
Summary
Raccoon roundworm infections can lead to serious health issues, as seen in recent cases involving two children in California. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are critical to mitigate severe complications associated with Baylisascaris procyonis infections. Increased awareness and preventive measures are essential to protect vulnerable populations from these rare but potentially devastating infections.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.