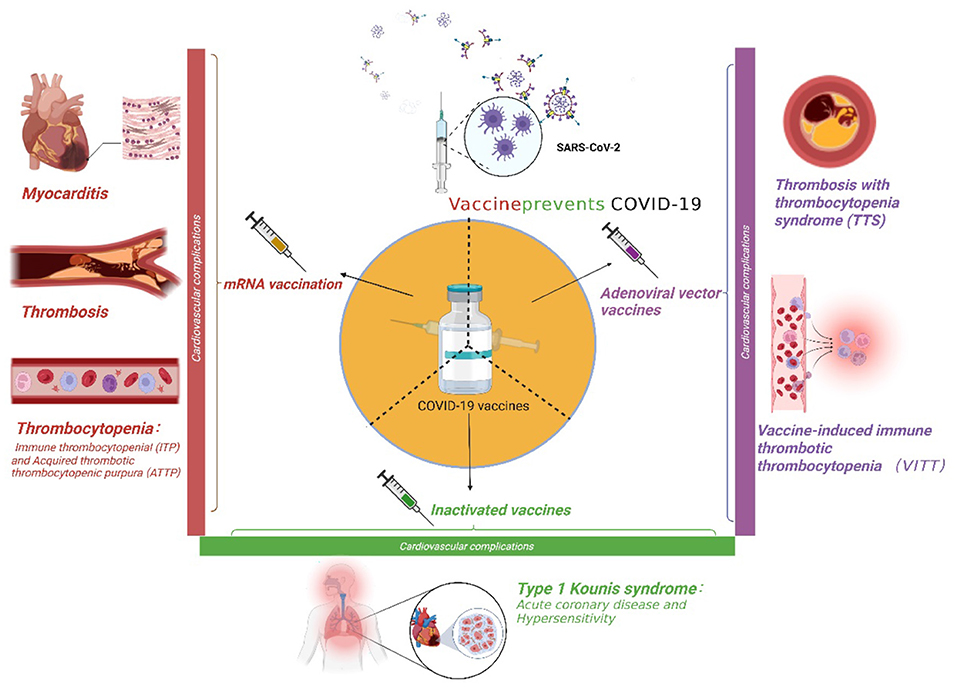
Myocarditis and Covid-19 vaccines have become critical topics of discussion as health authorities assess the safety of mRNA vaccines. Myocarditis, which is the inflammation of the heart muscle, has been observed in rare cases following vaccination, particularly among young males under the age of 25. While myocarditis symptoms can range from mild to severe, the overall incidence remains low compared to the risks associated with Covid-19 itself. Studies indicate that the risk of heart inflammation from the virus far exceeds that from the vaccines, leading health experts to affirm the benefits of vaccination. Understanding Covid-19 vaccine risks, including the potential for myocarditis and pericarditis, is essential for informed health decisions.
When discussing heart inflammation in the context of vaccination, myocarditis and its related conditions, such as pericarditis, are often highlighted. These conditions can arise from various sources, including viral infections and, in rare cases, mRNA vaccines like those used for Covid-19. It is crucial to differentiate between the risks associated with the disease itself and the side effects of vaccination. The conversation around mRNA vaccine side effects has gained traction, particularly in light of recent studies revealing that myocarditis symptoms, while concerning, are substantially less frequent than complications arising from Covid-19. By examining these aspects, individuals can make better health choices regarding their vaccination status.
Understanding Myocarditis Symptoms After Vaccination
After receiving a Covid-19 vaccine, particularly mRNA vaccines like Pfizer and Moderna, some individuals may experience myocarditis symptoms. Common signs include chest pain, shortness of breath, and palpitations. These symptoms typically manifest within a week of vaccination and can vary in intensity. While these reactions are rare, they are important for individuals to recognize, especially among young males who are at a higher risk of developing heart inflammation post-vaccination.
It’s crucial for individuals to monitor their health following vaccination. If someone experiences chest discomfort or difficulty breathing, they should seek immediate medical attention. Although the occurrence of myocarditis symptoms is low, being aware of the potential side effects can help in timely diagnosis and treatment. Medical professionals emphasize that while symptoms can be alarming, the overall risk of myocarditis remains significantly lower than the risks associated with Covid-19 itself.
The Risks of Covid-19 Vaccine-Induced Myocarditis
The association between Covid-19 vaccines and myocarditis has raised concerns about vaccine risks. Studies have shown that while there is an increased incidence of heart inflammation following mRNA vaccinations, the overall occurrence remains very low. For instance, the risk of developing myocarditis is about 1 in 10,000 doses for both the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines. This risk is notably higher after the second dose, particularly in younger males. Such statistics are essential for individuals weighing the benefits and risks of vaccination.
Despite the potential for myocarditis, it’s important to highlight that the risk of myocarditis from Covid-19 infection itself is much higher. Research indicates that unvaccinated individuals face a greater chance of developing myocarditis and other serious complications like heart attacks. Thus, health authorities recommend vaccination as a preventive measure against severe illness and complications. The benefits of vaccination, including protection from Covid-19 and related heart issues, substantially outweigh the risks of vaccine-induced myocarditis.
Covid-19 Vaccines vs. Covid-19: A Risk Comparison
When comparing the risks associated with Covid-19 vaccines versus the risks of contracting Covid-19, the data is compelling. Covid-19 poses a significantly higher risk of myocarditis and other serious cardiovascular issues than the vaccines themselves. Studies suggest that vaccinated individuals enjoy a lower risk of heart inflammation, heart attacks, and strokes compared to those who are unvaccinated. This critical insight drives the recommendation for vaccines as a safe and effective way to mitigate the risks of severe Covid-19 complications.
The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) supports the conclusion that the benefits of vaccination outweigh the risks, particularly for high-risk populations. Vaccines not only help reduce the severity of Covid-19 symptoms but also protect the heart by decreasing the likelihood of myocarditis and other related conditions. For those considering vaccination, understanding these risk comparisons is vital to making an informed decision.
What You Need to Know About Myocarditis and Covid-19 Vaccines
Myocarditis, an inflammatory condition of the heart muscle, has been linked to Covid-19 vaccines, particularly in younger males. However, it’s essential to recognize that myocarditis itself can be caused by various factors, including viral infections like influenza and Covid-19. This highlights the importance of understanding the context of myocarditis cases following vaccination. The overall incidence remains low, and most individuals recover well without long-term effects.
Vaccines, especially mRNA vaccines, have been shown to provide significant protection against severe Covid-19, which can lead to myocarditis. The risk of heart inflammation post-vaccination is far outweighed by the benefits of vaccination. Health experts continue to stress that while being informed about myocarditis is important, the priority should be on vaccination to prevent severe illness from Covid-19.
Pericarditis: A Related Condition to Consider
Pericarditis, the inflammation of the lining surrounding the heart, is often discussed alongside myocarditis, especially in the context of Covid-19 vaccinations. Similar to myocarditis, pericarditis can occur after receiving an mRNA vaccine, but the overall incidence remains low. Symptoms may overlap with those of myocarditis, including chest pain and discomfort. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Most individuals with pericarditis recover fully within weeks, but some may require longer recovery times. It is important for vaccinated individuals to be aware of these potential side effects and seek medical attention if they experience symptoms. Healthcare professionals are prepared to manage these conditions effectively, ensuring the best outcomes for patients.
The Importance of Monitoring Heart Health Post-Vaccination
Post-vaccination heart health monitoring is crucial, especially for those who may be at higher risk of myocarditis and pericarditis. Individuals should remain vigilant for symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or palpitations in the days following their Covid-19 vaccine. While the risk of these side effects is low, early detection and treatment can prevent more serious complications.
Healthcare providers encourage open communication with patients regarding any concerns following vaccination. By fostering an environment where individuals feel comfortable reporting symptoms, the healthcare system can better manage and understand the rare occurrences of myocarditis and other heart conditions post-vaccination. Awareness and education about these potential risks are vital for promoting overall health and safety.
Understanding the Mechanism of Vaccine-Induced Myocarditis
The mechanism behind vaccine-induced myocarditis is still being studied, but it is thought to involve an immune response triggered by the mRNA vaccines. This response may lead to inflammation of the heart muscle in susceptible individuals. Research is ongoing to identify specific risk factors that contribute to this rare side effect, including genetic predispositions and underlying health conditions.
Understanding how the immune system reacts to mRNA vaccines can help healthcare professionals better predict and manage potential myocarditis cases. Education about the immune response and its implications can empower individuals to make informed decisions about vaccination. Continued research is essential to fully understand the relationship between Covid-19 vaccines and myocarditis, ensuring that safety measures and guidelines are based on the latest scientific evidence.
Long-Term Outlook for Myocarditis Patients
For most individuals who experience myocarditis, the long-term outlook is positive. Many recover completely without enduring heart damage or complications. However, some may develop scarring or other issues that require ongoing monitoring. It is crucial for healthcare providers to offer follow-up care and support to those affected by myocarditis, ensuring they receive appropriate treatment and lifestyle guidance.
Longitudinal studies are essential to understanding the long-term effects of myocarditis, especially in the context of Covid-19 vaccination. As more data becomes available, healthcare professionals can better guide patients in managing their health post-vaccination. Awareness of potential complications and the importance of regular check-ups will contribute to improved outcomes for those who have experienced myocarditis.
The Role of Public Health in Vaccine Education
Public health initiatives play a critical role in educating communities about the risks and benefits of Covid-19 vaccination, including the potential for myocarditis. Clear communication about the rarity of these side effects compared to the benefits of vaccination is essential for building public trust. Campaigns aimed at dispelling myths and providing accurate information help individuals make informed choices about their health.
Healthcare authorities are working to ensure that patients understand the safety profile of Covid-19 vaccines. By disseminating information through various channels, public health agencies can reach diverse audiences. Education about the connections between Covid-19 and heart inflammation is crucial for encouraging vaccine uptake and protecting community health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do Covid-19 vaccines increase the risk of myocarditis?
Yes, there is evidence suggesting a link between mRNA Covid-19 vaccines and an increased risk of myocarditis, particularly in young males under 25 years old. This inflammation of the heart muscle is more frequently reported after the second dose of these vaccines.
How common are myocarditis symptoms after Covid-19 vaccination?
Myocarditis symptoms following Covid-19 vaccination are rare. Reports indicate that myocarditis or pericarditis occurs in up to 1 in 10,000 individuals vaccinated with Pfizer’s or Moderna’s mRNA vaccines.
What are the typical myocarditis symptoms to watch for after receiving a Covid-19 vaccine?
Myocarditis symptoms that may arise after Covid-19 vaccination include chest pain, shortness of breath, and palpitations. If you experience these symptoms within a week of vaccination, seek medical attention.
Can Covid-19 itself cause myocarditis, and how does it compare to vaccine risks?
Yes, Covid-19 can cause myocarditis, and the risk is significantly higher than that associated with the Covid-19 vaccines. Vaccination reduces the overall risk of severe heart complications from the virus.
What distinguishes myocarditis from pericarditis in relation to Covid-19 vaccines?
Myocarditis refers to inflammation of the heart muscle, while pericarditis involves inflammation of the lining around the heart. Both conditions can occur together and may present similar symptoms following Covid-19 vaccination.
What should I do if I experience myocarditis symptoms after a Covid-19 vaccine?
If you experience myocarditis symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or palpitations after receiving a Covid-19 vaccine, it is important to seek medical help immediately to rule out any serious conditions.
Are the side effects of myocarditis related to Covid-19 vaccines severe?
Most cases of myocarditis linked to Covid-19 vaccines are mild and recover well, but in severe cases, they can lead to long-term complications such as heart rhythm disturbances and heart failure.
What is the recommended action regarding Covid-19 vaccines for individuals at risk of myocarditis?
For individuals at higher risk of severe illness from Covid-19, the benefits of vaccination outweigh the risks of myocarditis. It’s important to consult healthcare providers for personalized advice.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Association with Myocarditis | There is a recognized link between mRNA Covid-19 vaccines and a slight increase in myocarditis and pericarditis, especially in young males under 25. |
| Risk Factors | The risk of myocarditis is higher after the second dose of the vaccine compared to the first or booster doses. |
| Rarity of Side Effects | The occurrence of myocarditis or pericarditis is very low, estimated at up to 1 in 10,000 for both Pfizer’s and Moderna’s vaccines. |
| Covid-19 vs Vaccines | Covid-19 infection carries a significantly higher risk of myocarditis compared to vaccination. |
| Understanding Myocarditis | Myocarditis is inflammation of the heart muscle caused by various factors, including viral infections. Most recover well, but severe cases can lead to lasting damage. |
| Understanding Pericarditis | Pericarditis is inflammation of the heart lining, often occurring alongside myocarditis, with most patients recovering within weeks. |
| Symptoms to Watch For | Symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and palpitations should prompt medical attention. |
Summary
Myocarditis and Covid-19 vaccines have been the subject of extensive research, highlighting a potential association primarily among young males after mRNA vaccinations. Although these cases are rare, understanding the risks is crucial. Importantly, the risks associated with Covid-19 itself are significantly greater than those associated with vaccination, making the benefits of getting vaccinated outweigh the risks for the majority of individuals. Awareness of symptoms and prompt medical attention can ensure better health outcomes for those affected.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.