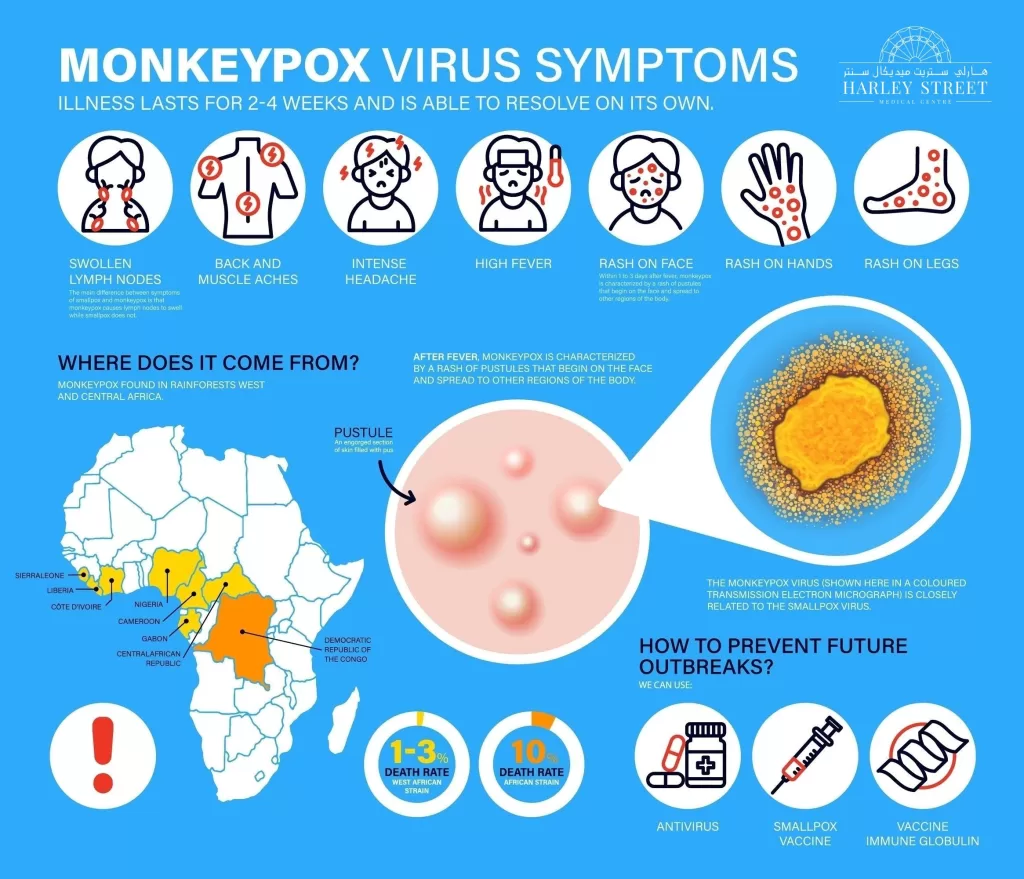
Monkeypox Virus Infection has captured global attention due to its recent resurgence and implications for public health. In late 2023, the identification of a novel clade Ib MPXV strain in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) sparked concerns, especially following earlier mpox outbreaks connected to international travel. A case linked to Thai travel, involving a patient returning from DRC, brings to light critical issues surrounding the prevention and management of monkeypox infections. The World Health Organization (WHO) has underscored the urgent need for enhanced public health responses to combat mpox, particularly as symptoms such as lesions and fever become apparent in infected individuals. As we delve deeper into this topic, it is essential to discuss potential measures including pre-exposure vaccination to safeguard at-risk communities in the face of the Mpox outbreak in Thailand.
The monkeypox disease, an emerging viral infection, has recently drawn significant attention in discussions surrounding infectious diseases. This illness, primarily carried by the monkeypox virus (MPXV), has been linked to cases from Africa, sparking international concern regarding its spread and effective management. Recent findings surrounding the clade Ib variant highlight its serious implications, especially in the context of travel-related infections. The Thai public health response has grown increasingly pivotal in addressing these challenges, particularly in light of confirmed monkeypox travel linked cases. Awareness of MPXV symptoms and proactive measures is crucial in combating the potential fallout from ongoing outbreaks.
Understanding Monkeypox Virus Infection
Monkeypox virus infection, caused by the monkeypox virus (MPXV), presents a unique challenge to global health due to its zoonotic nature and transmission dynamics. Initially identified in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the clade Ib MPXV variant has highlighted the ongoing risk of transmission, especially through travel. Understanding how monkeypox spreads—primarily through close contact with infected individuals or contaminated materials—is crucial for developing appropriate public health measures and for personal safety, especially for travelers to endemic regions.
In recent years, particularly during global outbreaks, cases of monkeypox have surged, prompting health agencies worldwide to reconsider their readiness and response strategies. Symptoms typical of MPXV infection include fever, rash, and lymphadenopathy, yet the clinical presentation can vary significantly. It is vital for healthcare professionals and travelers alike to be aware of these symptoms and remain vigilant, especially in light of recent travel-linked cases. This vigilance is essential to ensure timely diagnosis and treatment, which can prevent further spread.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Monkeypox virus infection and how is it transmitted?
Monkeypox virus infection (mpox) is an infectious disease caused by the monkeypox virus (MPXV). It is primarily transmitted through close contact with infected individuals, bodily fluids, or contaminated surfaces. In recent outbreaks, including the mpox outbreak in Thailand linked to travel, understanding transmission is crucial for effective prevention.
What are the symptoms of Clade Ib MPXV associated with Monkeypox virus infection?
Symptoms of Clade Ib MPXV associated with monkeypox virus infection typically include fever, body aches, fatigue, and the development of lesions on the skin. These lesions may start as maculopapular rashes and can progress to vesicular and necrotic lesions, as seen in cases reported after travel to high-risk areas like the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
How did the Monkeypox travel linked case in Thailand occur?
The Monkeypox travel linked case in Thailand involved a 66-year-old man who traveled from the Democratic Republic of the Congo, where he may have been exposed to Clade Ib MPXV. After developing symptoms upon his return, he was diagnosed with monkeypox infection. This case highlights the importance of monitoring travelers returning from areas with known mpox outbreaks.
What is the public health response to Monkeypox virus infection in Thailand?
The public health response to monkeypox virus infection in Thailand includes enhanced surveillance, contact tracing, and improved diagnostic testing. Following the importation of Clade Ib MPXV cases, authorities are considering pre-exposure vaccination for high-risk groups and developing better screening measures at points of entry to prevent future outbreaks.
How can one prevent the spread of Monkeypox virus infection?
To prevent the spread of monkeypox virus infection, individuals should avoid close contact with infected persons, practice good hygiene, and consider vaccination if they fall into high-risk groups. Public health initiatives, especially in areas with recent mpox outbreaks, are vital for controlling transmission and improving community awareness.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Case Background | A 66-year-old German man traveled from the DRC to Thailand, developing symptoms after returning. |
| Symptoms noted | Genital itching, followed by erythematous maculopapular lesions. |
| Diagnosis | Confirmed through real-time PCR tests. |
| Treatment | Patient treated with tecovirimat and discharged without complications. |
| Public Health Response | Contact tracing identified 89 individuals; no secondary cases reported. |
| Challenges Identified | Lack of mpox screening at entry points; missing cases due to symptom presentation. |
| Recommendations | Improve diagnostics, surveillance, and consider mpox vaccination for high-risk groups. |
Summary
Monkeypox Virus Infection is a significant public health concern, particularly highlighted by the recent case in Thailand linked to travel from the Democratic Republic of the Congo. This incident underscores the urgency for enhanced diagnostic measures, better public health responses, and vaccination initiatives for at-risk populations to effectively manage and prevent the spread of the monkeypox virus. Strengthening the response strategies will be critical in addressing the challenges posed by this infectious disease, especially amid rising global cases.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.