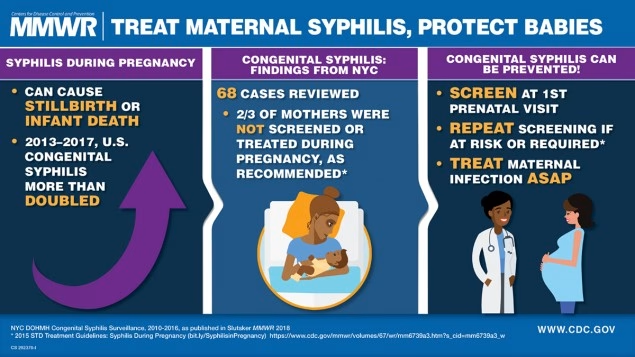
Maternal syphilis is an alarming public health issue that has seen a significant resurgence, particularly in states like Mississippi. Recent data shows that infection rates have skyrocketed, reflecting a worrying trend in maternal health that poses severe risks to newborns. Congenital syphilis, transmitted during pregnancy or childbirth, can lead to devastating health complications if left untreated. In response, public health authorities are focusing on preventing maternal syphilis by implementing widespread STI testing and treatment programs, essential for safeguarding both mothers and their infants. Addressing the high rates of syphilis infections in pregnancy is vital for protecting future generations and reversing the troubling increase in STI rates.
Maternal syphilis, or syphilis in pregnant women, is increasingly recognized as a critical public health concern, particularly evident in regions facing rising infection rates, such as Mississippi. The resurgence of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) during pregnancy highlights the urgent need for effective strategies aimed at screening and treating expectant mothers. This condition poses serious threats not only to maternal health but also dramatically affects infant well-being through congenital syphilis transmission. Efforts to control this preventable disease include widespread public health initiatives aimed at educating communities about the importance of prenatal screenings and access to care. As syphilis becomes a focal point in discussions surrounding reproductive health, it’s vital to acknowledge the broader implications on society and the system’s capacity to manage this ongoing challenge.
The Rising Challenge of Maternal Syphilis in Mississippi
In recent years, Mississippi has witnessed an alarming increase in maternal syphilis cases, showcasing a significant public health crisis. This rise in syphilis infection rates jeopardizes both maternal and child health, emphasizing the need for urgent intervention. Maternal syphilis, which can lead to congenital syphilis and severe health complications for infants, represents a glaring public health challenge in the state. With the increasing prevalence of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) during pregnancy, Mississippi’s situation serves as a warning for other states that might face similar surges in syphilis rates.
Public health experts are alarmed that the challenge of maternal syphilis rates in Mississippi reflects broader national trends. Stakeholders are concerned that if these infection rates continue to rise, they may precipitate a larger public health crisis across the country. The increasing prevalence of syphilis among pregnant women raises red flags, especially since effective prevention strategies, such as regular screenings and education, can significantly mitigate these rates. Addressing these issues will require a concerted effort from public health agencies, healthcare providers, and policymakers.
Effective Strategies for Preventing Maternal Syphilis
Preventing maternal syphilis requires a multi-faceted approach centered on education, testing, and timely treatments. Regular prenatal care is crucial in identifying and managing syphilis infections early on, reducing the risk to both mothers and their babies. Education on safe sex practices, such as the consistent use of condoms, is also essential in preventing STIs during pregnancy. Unfortunately, the rising STI rates in pregnancy, coupled with limited access to healthcare services, highlight a critical gap in efforts to prevent maternal syphilis in states like Mississippi.
Moreover, public health initiatives that advocate comprehensive screening protocols can play a significant role in curtailing syphilis infection rates among pregnant women. Currently, states such as Mississippi are mandated to conduct syphilis testing during pregnancy, yet challenges remain in ensuring all women receive adequate prenatal care. Increased funding for health departments and prioritization of maternal health services are essential components to restore effective surveillance and treatment programs aimed at preventing maternal syphilis infections.
Furthermore, outreach efforts to educate high-risk populations, especially women of color and those with limited access to healthcare, can dramatically influence prevention rates. Tailoring education and resources to align with community needs will foster better health outcomes. Drawing from successful public health campaigns in other states, targeted strategies can provide a template for addressing the increasing prevalence of maternal syphilis.
Addressing Healthcare Inequities in Maternal Syphilis
The stark disparities in maternal syphilis rates highlight systemic healthcare inequities that disproportionately affect marginalized communities. In Mississippi, data show that Black women and those lacking comprehensive prenatal care are at the greatest risk for syphilis infections. These disparities underscore a dire need for communities to engage in targeted public health strategies that lift barriers to care. Addressing these inequities is not merely about treating syphilis but involves fostering an equitable healthcare environment that ensures all women, regardless of socioeconomic status, receive proper care.
Public health interventions must be informed by data and community insights to tackle the social determinants of health that contribute to elevated STI rates. This includes enhancing access to contraception, prenatal care, and education on sexual health. Additionally, policymakers must advocate for resources that support the establishment and maintenance of STI clinics, especially in underserved regions. Without addressing the underlying inequities, the fight against maternal syphilis will remain a prolonged struggle, affecting both mothers and their newborns.
The Role of Public Health in Curbing Maternal Syphilis
Public health plays an essential role in combating the rising rates of maternal syphilis, requiring coordinated efforts and resource allocation to reverse current trends. Effective syphilis prevention calls for a robust public health response, including increased testing capabilities and the distribution of educational materials regarding STIs. Unfortunately, funding cuts at the federal and state levels have hindered the ability of public health departments to carry out these fundamental activities, as highlighted by the recent surge in infections.
National health organizations emphasize the need for reinvigorated public health campaigns that promote regular screenings and efficient treatment of STIs among pregnant women. By leveraging data-driven strategies, public health officials can implement culturally competent interventions that resonate with high-risk populations. Ultimately, fostering collaboration between healthcare providers and policy stakeholders is essential to establish comprehensive services aimed at vastly improving maternal health outcomes.
Long-Term Implications of Maternal Syphilis Infections
The long-term implications of rising maternal syphilis rates extend beyond immediate health challenges, posing threats to broader societal health. Mothers who contract syphilis risk leaving a legacy of health concerns for their children, including congenital infections that may lead to severe developmental delays or infant mortality. If these trends persist, we could witness an generation impacted by health issues exacerbated by preventable infections. This not only burdens families but also places significant strain on healthcare systems and resources.
Thus, it is imperative to adopt a forward-thinking perspective that emphasizes preventive measures and education across communities. Implementing holistic strategies that advocate for reproductive health rights and access to quality care may mitigate potential long-term consequences. Investing in maternal health education and outreach can significantly reduce the risks associated with maternal syphilis infections, paving the way toward healthier futures for children and families.
Community Engagement in Preventing Maternal Syphilis
Community engagement plays a pivotal role in preventing maternal syphilis through collaborative efforts between healthcare providers and local organizations. Local community groups can effectively raise awareness about the risks associated with STI rates and the importance of screening during pregnancy. By mobilizing community resources to provide education and access to testing, there exists a greater opportunity for early detection and treatment of syphilis infections among pregnant women.
Moreover, fostering relationships between healthcare systems and community leaders can enhance the effectiveness of prevention campaigns. Engaging local advocates can ensure that messaging is culturally relevant and resonates with diverse populations. As a result, community-driven efforts are vital in creating sustainable prevention strategies that can significantly impact the rising rates of maternal syphilis and ultimately improve the health outcomes for mothers and their newborns.
Innovative Approaches to Maternal Syphilis Screening
Innovative approaches to maternal syphilis screening can greatly enhance detection and treatment rates, especially amidst the ongoing challenges in public health infrastructure. Utilizing technology, such as telemedicine and mobile health clinics, can expand access to screening for women who may face barriers to traditional healthcare settings. This adaptability is particularly important in remote or underserved areas where maternal health services may be limited or non-existent.
Additionally, integrating syphilis screening into existing maternal health programs can streamline processes and improve outcomes. By combining prenatal care visits with STI testing, healthcare providers can ensure that expectant mothers receive comprehensive care. The goal is to create a healthcare environment where maternal syphilis screening becomes a routine part of prenatal care, thereby normalizing discussions around STI prevention and treatment.
The Intersection of Maternal Health and STI Epidemiology
Understanding the intersection of maternal health and STI epidemiology is crucial for developing effective public health strategies. Current trends indicate that increased rates of STIs, including syphilis, correlate directly with adverse maternal health outcomes, creating compounding risks for both mothers and infants. With the surge in syphilis infections, it’s paramount that healthcare professionals discern the broader implications of these trends and seek solutions that encompass maternal well-being.
Comprehensive approaches that consider social determinants of health and access to services can elucidate the relationship between maternal health and STI rates. By addressing these factors holistically, it becomes clear that preventing maternal syphilis requires a collaborative response that includes public health education, enhanced testing policies, and community engagement initiatives.
Advocacy for Funding and Resources to Combat Maternal Syphilis
Advocacy for increased funding and resources is vital in the battle against maternal syphilis. With continuous budget cuts to public health departments, stakeholders must rally for the allocation of funds dedicated to maternal and infant health programs. These investments can bolster critical prevention initiatives, including education on STIs, increased testing capacity, and improved access to necessary treatments.
Moreover, mobilizing public support can effectively draw attention to the urgent need for action regarding maternal syphilis rates. Campaigns aimed at raising awareness can not only attract funding but also stimulate policy changes to prioritize maternal health initiatives. By fostering a robust advocacy network, we can create an environment where addressing maternal syphilis is recognized as a public health imperative that requires immediate attention and action.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the rising trends of maternal syphilis in Mississippi?
Mississippi has seen a dramatic increase in maternal syphilis infections, reflecting a trend that may signify broader public health issues across the United States. The rate of maternal syphilis in this state is alarmingly high, leading to increased reports of congenital syphilis, which poses serious health risks to newborns.
How can preventing maternal syphilis impact public health?
Preventing maternal syphilis is crucial for reducing infant and maternal health complications. Public health initiatives that prioritize screening and treating STIs during pregnancy can prevent transmission to infants, thereby decreasing congenital syphilis cases and improving overall maternal health outcomes.
What are the recommendations for preventing maternal syphilis during pregnancy?
To effectively prevent maternal syphilis, health organizations recommend universal screening of pregnant women during their initial prenatal visits. Consistent use of condoms during sexual activity can reduce the risk of syphilis transmission. Treatment for syphilis is highly effective, often requiring just a single injection of penicillin.
What demographic factors contribute to higher rates of maternal syphilis?
Research indicates that higher rates of maternal syphilis are often observed among Black mothers, women aged 24 and under, unmarried women, and those with limited or no access to comprehensive prenatal care. Addressing these disparities is vital for effective maternal health strategies.
What implications do elevated syphilis infection rates have for public health in Mississippi?
Elevated syphilis infection rates in Mississippi highlight the urgent need for enhanced public health resources and funding. As many STI clinics have closed due to budget cuts, reducing support for testing and treatment, the challenge of controlling syphilis outbreaks has intensified, posing serious health risks to pregnant women and infants.
What are the consequences of untreated maternal syphilis infections?
Untreated maternal syphilis infections can lead to severe complications, including stillbirth, preterm birth, and congenital syphilis in infants. These outcomes underscore the importance of early detection, regular screening, and effective treatment during pregnancy.
How does Mississippi’s maternal syphilis rate compare nationally?
Mississippi’s maternal syphilis rate is among the highest in the United States, serving as a critical reflection of national trends in STI rates in pregnancy. The state’s alarming figures may forecast impending challenges that other regions could face if public health measures are not reinforced.
What challenges are faced in addressing maternal syphilis outbreaks in Mississippi?
Challenges in tackling maternal syphilis outbreaks in Mississippi include budget cuts leading to fewer resources for public health, closures of STI clinics, and a shortage of the penicillin needed for treatment during pregnancy. These factors hinder effective tracking, screening, and treatment efforts.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Public Health Efforts | Extensive testing and treatments for STIs, including tracing and treating partners, are vital to controlling syphilis outbreaks. |
| Rising Maternal Syphilis Rates | Mississippi has notably high rates of maternal syphilis infections, signaling dire health challenges for the nation. |
| Preventable Tragedies | Maternal syphilis is preventable through condom use, early screening, and antibiotic treatment. The highest risk groups are young, unmarried, and underserved women. |
| Challenges Ahead | Budget cuts and supply shortages impede efforts in tracking and treating syphilis among pregnant women. |
Summary
Maternal syphilis remains a pressing public health issue, particularly in states like Mississippi where maternal syphilis rates are soaring. Robust public health strategies that include rigorous testing, treatment, and educational efforts are essential for preventing infections and protecting both mothers and infants. Prioritizing maternal health by increasing resources and access to care can significantly mitigate the tragic outcomes associated with maternal syphilis.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.