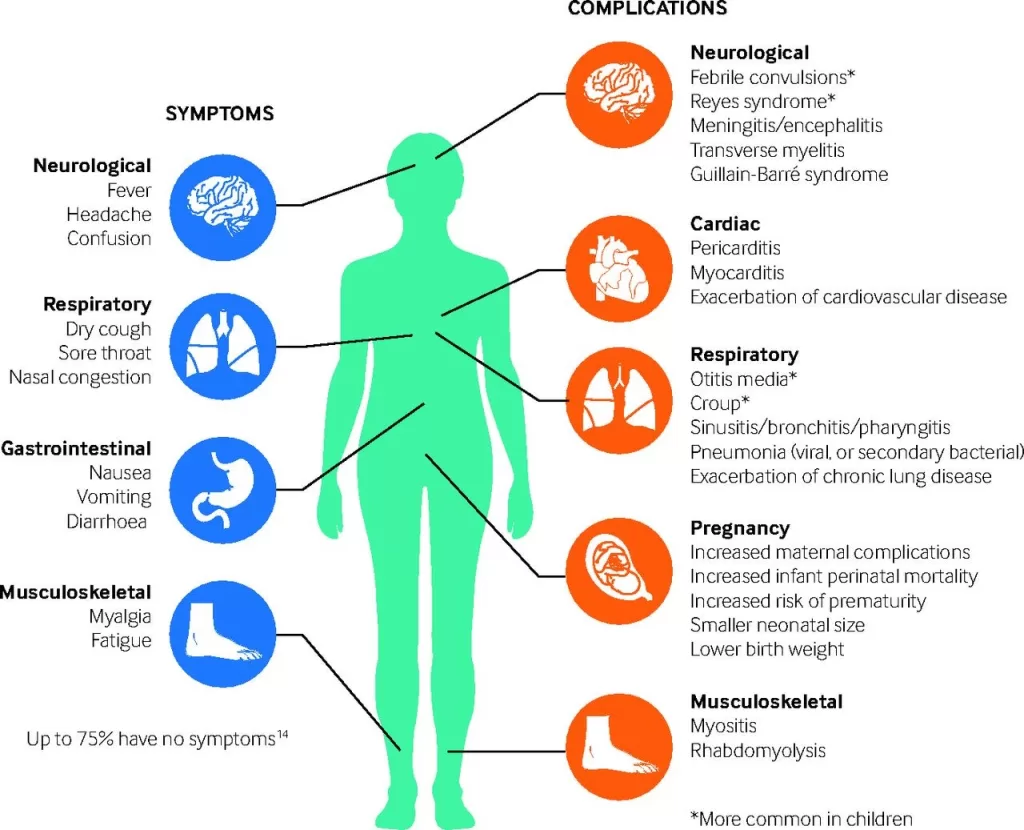
The long-term effects of the flu can significantly impact one’s health, often leading to serious complications that extend well beyond the initial infection. Respiratory illnesses like influenza are not just seasonal nuisances; they can cause heart complications, pneumonia, and even contribute to physical decline, especially in older adults. Each year, flu-related complications claim thousands of lives, underscoring the importance of flu vaccination in preventing severe outcomes. Moreover, understanding the risks associated with the flu can illuminate why it is essential to prioritize flu vaccine importance, especially for vulnerable populations. By focusing on preventing flu effects through vaccination and awareness, we can safeguard our health and mitigate the risks of long-term flu complications.
When discussing the repercussions of influenza, it is essential to recognize the enduring ramifications that can ensue after the initial viral battle. This common virus can lead to significant health issues, including the development of heart ailments, secondary infections like pneumonia, and an overall deterioration in physical health, particularly among seniors. The implications of flu complications extend beyond the immediate symptoms, making it increasingly vital to consider preventative measures such as annual flu shots. Emphasizing the vital role of flu vaccination can serve as a crucial line of defense, aiding in preventing serious illness and promoting long-term wellness. Ultimately, mitigating the lingering impacts of influenza calls for proactive healthcare strategies, tailored to individuals with elevated risk factors.
Understanding Heart Complications After the Flu
Heart complications are a significant long-term effect of influenza that many people may overlook. Studies have shown that the risk of heart attacks increases notably in the weeks following a flu diagnosis. Specifically, individuals diagnosed with the flu are six times more likely to experience a heart attack compared to the year before or after their flu infection. This connection highlights the critical importance of the flu vaccine, especially for individuals with pre-existing heart conditions, as vaccination can dramatically reduce their risk of serious cardiovascular events associated with influenza.
Moreover, heart issues stemming from the flu can manifest in unexpected ways. Research indicates that approximately 12% of hospitalized flu patients develop heart complications, which can lead to long-term health challenges. This sobering statistic serves as a reminder for at-risk populations, including the elderly and those with existing heart diseases, to prioritize their annual flu vaccination. By doing so, they not only protect themselves from the immediate effects of the virus but also significantly decrease their chances of enduring life-altering heart complications.
Long-Term Physical Decline and Its Implications
One of the lesser-known impacts of the flu is the potential for long-term physical decline, particularly in older adults. A significant number of older individuals do not fully recover their stamina and strength after fighting the flu, which can lead to a downward spiral in their overall health. For many, this results in decreased mobility and increased dependence on assistive care or family members. The importance of physical therapy and rehabilitation becomes crucial, as recovery from the flu may require additional support to regain lost muscle tone and endurance.
In younger individuals, while the decline may not be as pronounced, the potential impacts should not be dismissed. Engaging in rehabilitation through low-intensity exercises can facilitate a more robust recovery. Experts recommend cautious re-entry into physical activity, as overexertion can easily lead to relapsed symptoms. Therefore, continuing with structured recovery plans post-flu, guided by healthcare professionals, can aid in preventing long-term issues and promote better health outcomes.
Preventing Flu Complications with Vaccination
The importance of flu vaccination cannot be understated as a proactive approach to preventing severe complications and long-term effects. Vaccination not only lessens the likelihood of contracting the flu but also directly reduces the associated risks of heart complications, pneumonia, and other severe outcomes. Annually receiving the flu vaccine is essential, particularly for high-risk groups such as children, the elderly, and those with chronic health issues. By getting vaccinated, you bolster your immune system against the flu virus, thereby minimizing the chances of hospitalizations and subsequent health declines.
In addition to the flu vaccine, several preventive measures can help diminish the flu’s impact. Basic hygiene practices, such as frequent hand washing, disinfecting commonly touched surfaces, and practicing respiratory etiquette, play vital roles in controlling flu spread. For individuals who may develop complications, consulting a healthcare provider early can be critical, as early interventions with antivirals can mitigate further health issues. Collectively, these strategies emphasize the comprehensive approach needed to combat both the flu itself and its long-term effects.
Secondary Infections Following Influenza
The flu not only poses risks by itself but also opens the door for secondary infections, complicating what can already be a challenging recovery process. Pneumonia is one of the most common complications that may arise after influenza, often manifesting when the immune system is already compromised. This can make individuals more susceptible to later illness, particularly in vulnerable populations, such as the elderly or those with chronic conditions. It’s essential to recognize that pneumonia can occur after the initial flu symptoms have subsided, indicating the need for vigilant monitoring of health following a flu infection.
Moreover, secondary infections can sometimes be bacterial, necessitating antibiotic treatment. As such, anyone recovering from the flu should remain attentive to their health and consult with healthcare providers if symptoms persist or worsen. Understanding the connection between influenza and potential complications can inform better preventive strategies and treatment options, thereby improving recovery outcomes. By addressing these risks proactively, individuals can significantly reduce the long-term impact of flu-related complications.
Recognizing Risk Factors for Flu Complications
Certain individuals are far more susceptible to developing serious flu complications than others, which calls for targeted preventive measures. Risk factors prominently include age—children under five and adults over sixty-five are at a substantially higher risk for severe outcomes. Moreover, individuals with pre-existing health conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, or weakened immune systems face increased dangers. Awareness of these risk factors can empower individuals to take proactive steps, including consultation with healthcare providers and timely vaccinations, to maintain their health during flu season.
With directed education about risk factors, at-risk populations can better understand the need to remain vigilant during flu outbreaks. Ensuring routine vaccinations and engaging in discussions about flu-related health management can help mitigate risks. By preparing ahead and addressing risk factors strategically, individuals can enhance their defense against the flu and its potential long-term effects, contributing to better overall health outcomes for those who might otherwise suffer severe complications.
Post-Flu Care and Routine Testing
After recovering from the flu, it’s crucial to engage in proper post-viral care, as the infection may leave lingering effects that could skew medical assessments. Routine blood tests and health screenings can be impacted post-influenza, with potential changes in white blood cell counts reflecting the recent infection rather than chronic issues. It’s essential for patients to inform their healthcare providers about their recent flu history prior to any medical testing, allowing them to interpret results accurately and make the best healthcare decisions moving forward.
In addition to informing healthcare providers of recent flu infections, integrating supportive care practices can also help in regaining full health. Activities such as gradual physical rehabilitation, nutrition enhancement, and hydration can assist in restoring health post-influenza. This multifaceted approach reinforces the importance of listening to one’s body during recovery, ensuring that any unusual symptoms are promptly addressed to avoid further complications. Proper follow-up care after influenza is beneficial in promoting long-term wellness and health stability.
Understanding the Importance of Preventing Long-Term Effects of the Flu
Actively seeking to prevent the long-term effects of the flu requires a multi-pronged approach, focusing on lifestyle modifications alongside medical interventions. Discussing with healthcare providers about antiviral medications at the onset of flu symptoms can shorten recovery time and reduce the likelihood of complications. Furthermore, incorporating lifestyle practices—such as regular exercise post-recovery and a healthy diet—can significantly bolster one’s immune system and overall health, aiding in the prevention of any long-term decline associated with flu illness.
Moreover, educating oneself and others about the flu’s potential long-term implications is vital for public health. Understanding that the flu can lead to serious complications such as heart issues and physical decline promotes greater adherence to vaccination and preventive measures within communities. When individuals recognize the importance of vaccination and make informed choices to protect themselves and their loved ones, the broader community benefits through reduced flu transmission and lower rates of complications associated with it.
When to Seek Medical Attention During Flu Season
Identifying when to seek help during flu season is critical, especially for those at risk for complications. Symptoms such as persistent high fever, lightheadedness, and difficulty breathing should prompt individuals to contact healthcare providers immediately. Early medical intervention can mean the difference between a manageable illness and one that results in serious health issues. Timely care can also help mitigate the risk of developing long-term effects from the flu, ensuring better recovery outcomes.
Moreover, staying informed about what to look for and when to act is vital for at-risk populations, including those with chronic illnesses or weakened immune systems. Building awareness and understanding of the flu’s progression can empower individuals to take charge of their health, leading to more informed decisions regarding medical care. Ultimately, being proactive about flu-related symptoms and seeking help promptly can greatly reduce the risk of severe complications and foster a quicker return to health.
A Comprehensive Review of Flu Knowledge and Vaccination Benefits
Understanding the flu and its potential long-term impacts remains crucial in public health efforts. The annual flu can lead to serious outcomes such as heart complications, pneumonia, or persistent physical decline, particularly in vulnerable groups. This reality underscores the necessity for routine vaccinations and encourages ongoing education about the flu’s risks and preventive measures. Health literacy regarding flu-related knowledge can empower individuals to make informed health choices and foster community-wide protection against outbreaks.
In conclusion, ensuring adequate flu prevention through vaccination not only protects individual health but also reduces societal healthcare burdens. By actively engaging in flu awareness, vaccination campaigns, and post-infection care, individuals contribute to a culture of health that prioritizes prevention and wellness. The collective commitment to flu safety can lead to healthier communities, reducing hospitalizations and severe diagnoses that arise from the flu’s long-term effects.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the long-term effects of the flu on heart health?
The long-term effects of the flu can include serious heart complications. Studies have shown that individuals diagnosed with the flu face a significantly higher risk of heart attacks and other cardiovascular issues. In particular, heart complications occur in about 12% of those hospitalized with flu, making it crucial for those with existing heart conditions to prioritize flu vaccination to prevent these severe outcomes.
How can the flu vaccine help prevent long-term complications?
The flu vaccine plays a vital role in preventing long-term complications associated with the flu. By getting vaccinated, individuals significantly reduce their risk of severe illness, hospitalization, and long-lasting health issues, such as heart problems and secondary infections like pneumonia. Annually receiving the flu shot is particularly important for high-risk groups, including older adults and those with pre-existing health conditions.
What are some common flu complications that can lead to long-term effects?
Common flu complications that can lead to long-term effects include pneumonia, heart issues, and decreased physical endurance. These complications may not only prolong recovery but can also contribute to a decline in overall health, particularly in older adults. Understanding these risks underscores the importance of flu vaccination to minimize potential long-term impacts.
How can one prevent long-term effects of the flu?
Preventing long-term effects of the flu involves several strategies, primarily through vaccination. Receiving the annual flu shot reduces the risk of severe flu cases and their associated complications. Additionally, maintaining good hygiene practices, such as frequent handwashing and covering coughs, can help prevent the spread of the virus and its potential long-term impacts.
Why are older adults at higher risk for long-term effects from the flu?
Older adults are at a higher risk for long-term effects from the flu due to age-related declines in immune function and increased likelihood of pre-existing health conditions. These factors can lead to severe complications, including prolonged illness and decreased quality of life following a flu infection, making it crucial for older individuals to receive the flu vaccine annually.
What should I do if I experience prolonged symptoms after the flu?
If you experience prolonged symptoms after the flu, it is important to consult a healthcare provider. Long-term effects can include persistent fatigue or respiratory issues, and a medical evaluation may be necessary to rule out any complications such as pneumonia or heart problems. Early intervention can help manage and mitigate any lasting health concerns.
Can having the flu increase the risk of secondary infections?
Yes, having the flu can significantly increase the risk of secondary infections, such as pneumonia, due to its impact on the immune system. This vulnerability can lead to additional health issues that may require medical attention and treatment, highlighting the importance of flu vaccination in reducing overall risk.
What are the signs that I should seek medical attention after having the flu?
After having the flu, you should seek medical attention if you experience a high fever, shortness of breath, lightheadedness, or signs of dehydration. These symptoms can indicate serious complications that may require prompt medical care, emphasizing the need for vigilance following flu recovery.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Long-term Effects of the Flu | Includes heart complications, pneumonia, and a decline in physical health, especially among older adults. |
| Heart Complications | Increased risk of heart attacks, particularly in individuals with pre-existing heart conditions. |
| Loss of Endurance and Strength | Bed confinement can lead to muscle loss, necessitating rehabilitation to regain strength. |
| Physical Decline in Older Adults | Older adults face heightened risks of serious illness, hospitalization, and diminished quality of life post-flu. |
| Secondary Infections | Increased susceptibility to secondary infections like pneumonia following flu infection. |
| Risk Factors | Includes age extremes, chronic diseases, and weakened immune systems. |
| Prevention | Vaccination, hygiene practices, and antiviral medications can help reduce risks. |
| When to Seek Help | Immediate medical consultation recommended for high fever, difficulty breathing, or dehydration. |
Summary
The long-term effects of the flu can have significant repercussions on health, particularly in vulnerable populations. These effects include serious heart complications, the onset of pneumonia, and a physical decline that can severely impact the quality of life in older adults. With an annual death toll ranging from 4,900 to 51,000 in the United States alone, understanding the risks associated with the flu is crucial. Vaccination serves as an effective preventive measure against not only the flu itself but also its potential long-term complications. By prioritizing flu vaccination and maintaining good hygiene practices, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of severe illness and protect public health.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.