Jorge Lobo’s disease (JLD) is a rare yet significant fungal infection primarily caused by *Paracoccidioides lobogeorgii*, most commonly reported among residents of the Amazon Basin. This neglected tropical disease presents unique challenges, especially when it affects pediatric populations, as evidenced by the clinical case of a 9-year-old child in Brazil who developed JLD after being bitten by a tick. Understanding Jorge Lobo’s disease symptoms is crucial for early detection and intervention, as the potential link between tick exposure and the disease highlights the need for increased clinical awareness. Complications can arise from this infection, underlining the importance of recognizing its manifestations, particularly in children who might present atypical symptoms. Ensuring the availability of accurate information on tick exposure diseases and related fungal infections is essential, especially for healthcare providers operating in endemic regions.
Often referred to as a chronic fungal infection endemic to the Amazon region, Jorge Lobo’s disease poses significant health risks, particularly following instances of tick bites or similar skin traumas. The primary causative agent, *Paracoccidioides lobogeorgii*, is part of a group of pathogenic fungi that are critical to understand in the context of pediatric health. Moreover, discussions surrounding pediatric fungal infections reveal that this disease is not only preventable but also treatable with timely medical intervention. The unique challenges surrounding beetle-borne diseases emphasize the need for vigilant surveillance and education in endemic areas. By raising awareness about the signs and symptoms of this infection, healthcare professionals can work towards reducing the incidence of complications in affected children.
Understanding Jorge Lobo’s Disease: Overview and Symptoms
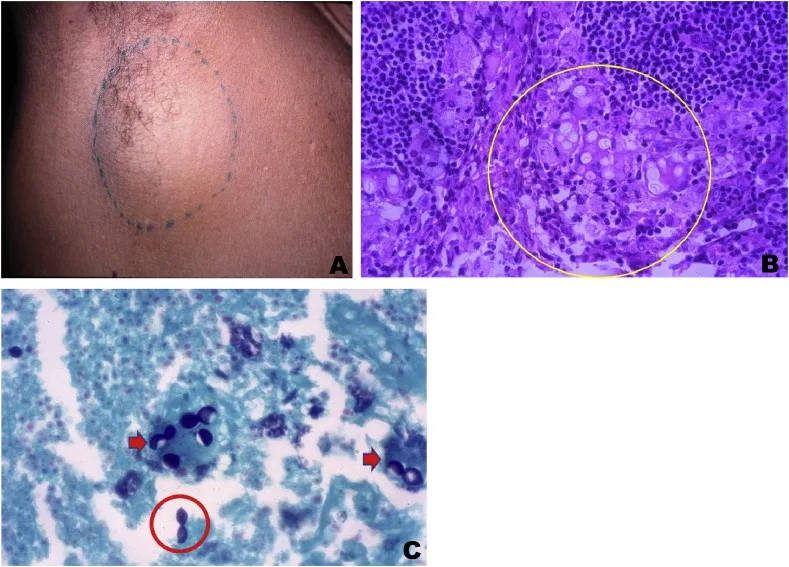
Jorge Lobo’s Disease (JLD) is a chronic fungal infection caused by the pathogen *Paracoccidioides lobogeorgii*, primarily affecting individuals residing in the Amazon Basin and other tropical regions. The disease is known for its insidious onset and can manifest in a variety of symptoms ranging from skin lesions to respiratory complications. Symptoms often include granulomatous inflammation, which can be misdiagnosed as other skin conditions, leading to delayed treatment. Recognizing the signs early is crucial, particularly for pediatric patients, as the disease can progress rapidly if not diagnosed correctly.
Patients may present with various clinical features, including localized skin lesions, fever, and lymphadenopathy. In endemic regions, healthcare providers need to maintain a high index of suspicion for JLD, especially in cases presenting with atypical dermatological symptoms. Increased awareness of the potential for tick exposure, as in the case presented, underscores the need for a comprehensive diagnostic approach that includes a thorough history and examination for relevant exposure to contaminated environments.
The Connection Between Tick Exposure and Fungal Infections
Tick bites are a recognized route of exposure for various pathogens, but their relationship with fungal infections, particularly Jorge Lobo’s disease, is less well understood. In the presented case, a 9-year-old boy developed JLD after being bitten by a tick, indicating a possible pathway through which the fungal spores can enter the body. This association raises important questions regarding the mechanisms of fungal transmission and the role of environmental factors, especially in regions where multiple infectious agents coexist.
In tropical areas, the overlap of tick exposure and the presence of fungal spores in the environment poses significant risks for inhabitants, particularly children. Healthcare professionals need to consider the potential for pediatric fungal infections in conjunction with vector-borne diseases. Collaborative efforts among specialists in infectious diseases, dermatology, and pediatrics are essential to improve diagnosis and treatment strategies for patients facing such dual risks.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment of Jorge Lobo’s Disease
Early diagnosis and treatment of Jorge Lobo’s disease are paramount in preventing complications and ensuring better patient outcomes. Delayed recognition can lead to severe manifestations, including systemic involvement, which is particularly concerning in children whose immune systems may be more vulnerable. The case illustrated emphasizes the need for clinicians to adopt proactive approaches to diagnosis when faced with unexplained skin lesions or similar symptoms, particularly in children with a history of tick bites.
Timely initiation of multidrug therapy can significantly reduce the risk of disease recurrence and associated health complications. Education and training for healthcare providers in endemic areas regarding the signs and symptoms of JLD are vital. Enhanced surveillance systems and diagnostic protocols can facilitate earlier intervention, thereby improving the overall health and quality of life for those at risk in the Amazon Basin and surrounding regions.
Jorge Lobo’s Disease in Pediatric Populations: Symptoms and Challenges
When considering Jorge Lobo’s disease in pediatric populations, it is crucial to recognize that symptoms may differ from those typically observed in adults. Children may present with more subtle symptoms or atypical manifestations, which can lead to misdiagnosis or delayed treatment. Common symptoms observed include localized skin lesions, which may resemble benign dermatological conditions, complicating the clinical picture.
Healthcare providers must be vigilant and consider JLD when evaluating skin lesions in children, especially in areas where the disease is endemic. The nuances of presenting symptoms, coupled with the potential for rapid disease progression, highlight the challenges in diagnosing this fungal infection in pediatric patients. Increasing awareness about the disease’s presentation in children can encourage timely interventions that can drastically improve patient outcomes.
Preventive Strategies for Jorge Lobo’s Disease in Endemic Regions
Implementing preventive strategies in endemic regions is essential for mitigating the impact of Jorge Lobo’s disease among vulnerable populations, particularly children. These strategies include public health education initiatives that inform communities about the risks associated with tick exposure and the importance of maintaining hygiene and sanitation practices to reduce the risk of fungal infections. Awareness campaigns can help residents recognize symptoms early and encourage timely medical consultations.
Additionally, environmental management strategies aimed at reducing tick populations and controlling fungal spores in the soil can also play a vital role in prevention. Regular monitoring and community engagement can empower residents to take proactive measures in their environments. Coupled with enhanced healthcare access, these preventive approaches can significantly lower the incidence of JLD and improve the overall health outcomes for children living in high-risk areas.
Clinical Management of Jorge Lobo’s Disease: Case Studies and Outcomes
The clinical management of Jorge Lobo’s disease has evolved based on various case studies that illustrate diverse outcomes and treatment approaches. Properly managed cases demonstrate that early intervention with antifungal therapies, such as itraconazole and amphotericin B, can lead to successful recovery and resolution of symptoms. The case of the 9-year-old boy, who underwent multidrug therapy and achieved lesion-free status, highlights the importance of tailored treatment regimens.
However, the recurrence of symptoms, as noted in the same clinical case, sheds light on the challenges of long-term management in pediatric patients. This necessitates continuous monitoring and the possibility of re-treatment as a standard part of care for JLD. Learning from clinical outcomes can guide healthcare providers in developing best practices for managing this disease, particularly among children who may face unique challenges during treatment.
Research Developments in Jorge Lobo’s Disease and Related Infections
Research into Jorge Lobo’s disease and related fungal infections has intensified in recent years, focusing on improved diagnostic methods and understanding the epidemiology of *Paracoccidioides lobogeorgii*. Advances in molecular techniques, such as PCR, allow for earlier detection of the pathogen, which can significantly enhance treatment outcomes. Such research is critical, especially in areas where the disease may be underrecognized or misdiagnosed.
Additionally, studies that investigate the environmental factors contributing to the spread of JLD and other fungal infections can help public health officials formulate effective strategies for prevention and control. Growing interdisciplinary collaboration among mycologists, epidemiologists, and healthcare providers is vital to address the complexities of this disease and improve awareness, surveillance, and research into effective treatment options.
Global Perspectives on Fungal Infections: The Role of Jorge Lobo’s Disease
Fungal infections, including Jorge Lobo’s disease, represent a growing global health concern, particularly in tropical climates where the biodiversity can contribute to various disease outbreaks. The unique circumstances surrounding JLD, such as its transmission through environmental exposure to fungi, underline the importance of understanding and addressing fungal pathogens on a global scale. Collaborative international efforts can promote research initiatives aimed at understanding the impact of climate change on fungal disease epidemiology.
Countries like Brazil, where Jorge Lobo’s disease is endemic, must work together with international health organizations to monitor and report cases effectively. Efforts to create awareness and education programs can lead to better preventive measures both locally and globally, thereby reducing the incidence of fungal infections and ensuring more robust health care for affected populations.
The Future of Jorge Lobo’s Disease: Surveillance and Community Education
Looking to the future, enhancing surveillance systems for Jorge Lobo’s disease is critical to establish more effective control measures and early intervention strategies. Increased funding for research into fungal pathogens and improved training for healthcare providers in endemic areas can potentially lower the incidence of this disease. Furthermore, community education efforts about prevention and the significance of early symptom recognition can play a vital role in reducing disease impact.
Implementing community-based health initiatives can empower residents to participate actively in the monitoring and prevention of Jorge Lobo’s disease. This collaborative approach not only aids in raising awareness but also fosters a sense of ownership in the communities affected. Continuous evaluation of these initiatives will be essential to gauge their effectiveness and adapt strategies based on evolving epidemiological trends in fungal infections.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of Jorge Lobo’s disease?
Jorge Lobo’s disease (JLD), caused by *Paracoccidioides lobogeorgii*, often presents with symptoms such as granulomatous lesions on the skin, respiratory issues, and fever. The infection typically manifests through skin trauma, especially in areas with tick exposure in the Amazon Basin.
How is Jorge Lobo’s disease transmitted?
Jorge Lobo’s disease is primarily transmitted through direct fungal inoculation, often occurring when individuals come into contact with contaminated vegetation or through skin injuries facilitated by ticks or other arthropods.
Can Jorge Lobo’s disease affect children?
Yes, Jorge Lobo’s disease can affect children, although pediatric cases are rare. Increased clinical awareness is important for early detection and intervention, particularly in endemic regions like the Amazon.
What is the relationship between tick exposure and Jorge Lobo’s disease?
Tick exposure is believed to facilitate the entry of *Paracoccidioides lobogeorgii* into the skin, potentially increasing the risk for developing Jorge Lobo’s disease following bites from infected ticks.
What is the treatment for Jorge Lobo’s disease in pediatric patients?
Treatment for Jorge Lobo’s disease in children usually includes a multidrug therapy approach. Early diagnosis is crucial to eliminate the infection and prevent recurrences.
Why is surveillance important for Jorge Lobo’s disease in endemic areas?
Surveillance is vital for Jorge Lobo’s disease to ensure early detection and intervention, particularly in at-risk populations within the Amazon basin, where the disease is more prevalent due to fungal exposure.
How does Jorge Lobo’s disease impact public health in the Amazon?
Jorge Lobo’s disease represents a significant public health concern in the Amazon basin, as it is largely underdiagnosed. Increased awareness amongst healthcare professionals is essential to improve outcomes and reduce complications in affected populations.
What role does fungal inoculation play in Jorge Lobo’s disease?
Fungal inoculation plays a critical role in the development of Jorge Lobo’s disease, usually occurring through skin trauma when contaminated by *Paracoccidioides lobogeorgii*, often linked to exposure to ticks or other infectious agents.
What should healthcare providers know about pediatric fungal infections like Jorge Lobo’s disease?
Healthcare providers should recognize that pediatric fungal infections like Jorge Lobo’s disease may present atypically. Prompt identification and treatment can mitigate severe health outcomes, especially in endemic regions affected by such infections.
What ongoing efforts are needed to manage Jorge Lobo’s disease effectively?
Ongoing efforts to manage Jorge Lobo’s disease effectively include enhancing surveillance in endemic areas, increasing clinical awareness among healthcare providers, and ensuring timely access to appropriate antifungal therapies for affected individuals.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Jorge Lobo’s Disease (JLD) primarily affects individuals in the Amazon Basin and parts of Central America. |
| Caused by the fungus *Paracoccidioides lobogeorgii*, JLD is a chronic infection associated with skin trauma from contaminated sources. |
| A reported case involved a 9-year-old boy in Brazil diagnosed after a tick bite, emphasizing gaps in pediatric surveillance of the disease. |
| Initial treatment with topical dexamethasone failed; definitive diagnosis was made via histopathology showing granulomatous inflammation. |
| The patient responded well to multidrug therapy but had recurrences, highlighting the chronic nature of JLD. |
| Increased clinical awareness is crucial for the early detection and intervention of JLD, especially in endemic regions. |
| Continued surveillance and outreach are necessary to improve management and outcomes for at-risk populations. |
Summary
Jorge Lobo’s Disease (JLD) is a significant health concern in endemic regions, particularly in the Amazon Basin. This disease highlights the need for heightened awareness and prompt medical attention, especially as evidenced by the recent case involving a child post-tick exposure. Early recognition and treatment of JLD are imperative to prevent complications and manage recurrences effectively. As such, ongoing surveillance and community education are essential components in combating the challenges posed by JLD.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.