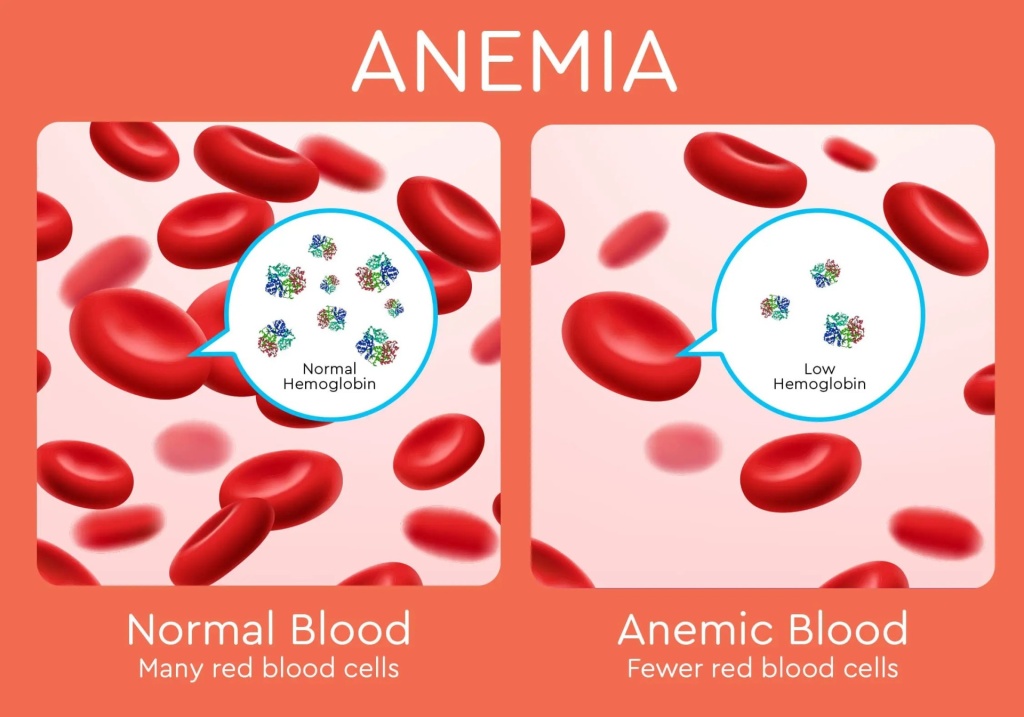
Iron deficiency anemia (IDA) is a widespread yet frequently underestimated health issue that impacts millions globally. This condition arises when the body lacks sufficient iron to produce adequate hemoglobin, which is vital for transporting oxygen in the bloodstream. Individuals suffering from iron deficiency anemia may experience a range of symptoms, including fatigue, shortness of breath, and pale skin, which can significantly hinder day-to-day activities. Effective treatment for iron deficiency anemia typically involves dietary modifications and sometimes supplementation to restore iron levels and enhance overall well-being. As awareness of iron deficiency anemia symptoms grows, it’s critical for both individuals and healthcare providers to stay informed about the latest developments regarding diagnosis and nutrition for iron deficiency anemia.
Iron deficiency anemia, often referred to as IDA, is a common condition characterized by a shortage of iron that leads to reduced hemoglobin production in the body. This deficiency can manifest in various ways, impacting overall health and quality of life. Alternative terms such as low iron syndrome or iron depletion may also be used to describe this condition, which is particularly prevalent among certain demographics, including pregnant women and those with specific dietary restrictions. Addressing iron deficiency anemia requires a thorough understanding of its symptoms, appropriate treatment options, and the latest nutritional strategies available to improve iron levels. By recognizing the importance of maintaining adequate iron stores, individuals can better manage their health and prevent complications associated with this prevalent condition.
Understanding the Symptoms of Iron Deficiency Anemia
Iron deficiency anemia (IDA) is characterized by a range of symptoms that can significantly disrupt daily life. Common symptoms include persistent fatigue and weakness, which occur due to the reduced capacity of the blood to transport oxygen. Individuals may find themselves unable to perform even simple tasks without feeling exhausted. Additionally, pale skin is a frequent indicator of IDA, stemming from diminished hemoglobin levels. This symptom not only affects appearance but also serves as a critical warning sign that should prompt further investigation.
Shortness of breath is another alarming symptom associated with iron deficiency anemia, particularly during physical exertion. As the body struggles to deliver sufficient oxygen, individuals may experience increased heart rates and difficulty catching their breath. Moreover, dizziness and lightheadedness can arise from insufficient oxygen flow to the brain, leading to a concerning sense of instability. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for timely diagnosis and intervention, as untreated IDA can lead to severe complications.
Recent Developments in Iron Deficiency Anemia Cases
The rise in hospital admissions related to iron deficiency anemia has alarmed healthcare professionals globally. Reports indicate that admissions have grown significantly, with nearly a tenfold increase since 1999. This dramatic rise, totaling approximately 200,000 cases in the year 2023/2024 alone, suggests a pressing public health issue that warrants attention. A combination of increased awareness and improved diagnostic practices may account for some of this surge, but underlying factors such as dietary changes and socio-economic challenges play a critical role.
Moreover, the evolving dietary habits, particularly in developed nations, may have contributed to lower iron intake among populations. With more individuals adopting vegetarian or vegan diets, the reliance on plant-based sources of iron, which are less readily absorbed than animal sources, has increased. This shift necessitates a reevaluation of nutritional guidelines and public health strategies to ensure that individuals, especially vulnerable groups like women and children, receive adequate iron to prevent deficiencies.
Nutritional Strategies for Managing Iron Deficiency Anemia
Effective management of iron deficiency anemia heavily relies on dietary adjustments and nutritional supplementation. Incorporating iron-rich foods into daily meals is essential for boosting hemoglobin levels. Red meat, being a potent source of heme iron, should be emphasized in the diets of those at risk. Additionally, poultry, fish, beans, lentils, and leafy greens also provide valuable iron, making them important components of a balanced diet. For vegetarians, consuming fortified cereals and pairing non-heme iron sources with vitamin C-rich foods can enhance absorption rates significantly.
Natural remedies, such as blackstrap molasses, have also gained popularity among those seeking to improve their iron levels through dietary means. High in iron and other nutrients, blackstrap molasses can be easily incorporated into smoothies, baked goods, or taken directly. Furthermore, educating individuals about the importance of nutrition for iron deficiency anemia is pivotal in promoting long-term health benefits and preventing future occurrences of this condition.
Iron Deficiency Anemia in Pregnancy
Pregnant women face heightened risks of iron deficiency anemia, with studies indicating that a staggering 52% of pregnant women in developing countries do not receive adequate iron intake. The physiological changes during pregnancy, including increased blood volume and nutrient demands from the growing fetus, compound the need for iron. Without sufficient iron, pregnant women may face serious complications like low birth weight and preterm delivery, which can have lasting effects on both mother and child.
Consequently, regular screening for iron levels during pregnancy is vital for ensuring the health of both the mother and the developing fetus. Health care providers often utilize serum ferritin tests to accurately assess iron stores, guiding intervention strategies. By prioritizing iron intake through diet and supplements, pregnant women can significantly reduce the risk of iron deficiency anemia and its associated complications, leading to healthier pregnancy outcomes.
Preventing Iron Deficiency Anemia: Key Considerations
Prevention of iron deficiency anemia involves a multifaceted approach that includes healthy dietary habits, regular screenings, and awareness of symptoms. Individuals, particularly women of reproductive age and pregnant individuals, should aim for a balanced diet rich in iron. Consuming a variety of iron-rich foods and understanding the importance of vitamin C in enhancing iron absorption can dramatically improve overall iron status.
In addition to dietary measures, proactive health management through regular screenings can help identify potential deficiencies early on. Being educated about the symptoms of iron deficiency anemia empowers individuals to seek medical advice promptly, reducing the risk of developing severe anemia. By adopting these preventive strategies, individuals can take control of their health and mitigate the risks associated with iron deficiency anemia.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of iron deficiency anemia?
Common symptoms of iron deficiency anemia include fatigue and weakness, pale skin, shortness of breath during physical activity, dizziness or lightheadedness, and glossitis, which is inflammation of the tongue. Recognizing these iron deficiency anemia symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment.
What treatment options are available for iron deficiency anemia?
Treatment for iron deficiency anemia typically involves dietary changes to include iron-rich foods, such as red meat, poultry, fish, beans, and leafy green vegetables. Iron supplements may also be prescribed. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider for an appropriate iron deficiency anemia treatment plan tailored to individual needs.
How does iron deficiency anemia affect pregnancy?
Iron deficiency anemia during pregnancy can lead to serious complications, including low birth weight and preterm delivery. Pregnant women need increased iron intake, often exceeding 27 mg daily, to support both their health and fetal development. Regular screening for iron levels is recommended for early detection and management.
What are the recent developments regarding iron deficiency anemia?
Recent developments in iron deficiency anemia show a concerning increase in hospital admissions, nearly a tenfold rise since 1999, highlighting the need for better identification and treatment approaches. Factors contributing to this surge include increased awareness and shifts in dietary habits that may lead to lower iron intake.
What nutritional strategies can help manage iron deficiency anemia?
Nutritional strategies for managing iron deficiency anemia include consuming iron-rich foods such as red meat, poultry, and beans, along with pairing non-heme iron sources with vitamin C to enhance absorption. Natural remedies, like blackstrap molasses, can also support red blood cell production and boost iron levels.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| What is Iron Deficiency Anemia? | A condition resulting from insufficient iron to produce hemoglobin, leading to reduced oxygen transport in the body. |
| Common Symptoms | Fatigue, pale skin, shortness of breath, dizziness, glossitis. |
| Surge in Cases | Nearly 200,000 hospital admissions related to IDA in 2023/2024, a significant increase since 1999. |
| Iron Requirements | Women need about 14.8 mg daily; pregnant women may need over 27 mg daily. |
| Nutritional Strategies | Iron-rich foods include red meat, poultry, fish, beans, leafy greens, nuts, and seeds. |
| Pregnancy Considerations | 52% of pregnant women in developing countries may have insufficient iron; regular screening is vital. |
| Prevention and Management | Focus on balanced diets, regular screenings, and awareness of symptoms for early diagnosis. |
Summary
Iron Deficiency Anemia (IDA) is a widespread health issue that affects millions of individuals globally, particularly women and pregnant individuals. Understanding the symptoms, treatment options, and dietary strategies associated with IDA is essential for improving health outcomes. With the recent increase in hospital admissions related to this condition, it is crucial for both individuals and healthcare providers to be aware of the potential risks, necessary nutritional intake, and the importance of regular screenings. By fostering awareness and proactive management, we can better address the challenges posed by iron deficiency anemia and promote overall well-being.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.