Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) has recently garnered attention due to alarming reports of an outbreak in China, although health officials have not yet confirmed widespread cases. This virus, identified only in the early 2000s, is known for causing flu-like illnesses that can significantly impact vulnerable groups such as young children and the elderly. According to data from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, HMPV is leading a rise in respiratory illnesses, accounting for 6.2 percent of positive test results among patients with such symptoms. As many people begin to experience typical HMPV symptoms, including cough, fever, and nasal congestion, awareness is critical in managing this respiratory illness. With the backdrop of ongoing flu-like outbreaks, the focus on HMPV becomes paramount in understanding potential health risks and prevention measures.
Also referred to as HMPV, this respiratory virus is recognized as a significant pathogen responsible for a range of illnesses resembling seasonal flu. Despite its recent discovery, its prevalence has been noted during influenza seasons, often resulting in severe respiratory conditions among those susceptible. Reports indicate a concerning rise in flu-like symptoms among populations, with HMPV emerging as a noteworthy contributor in the ongoing health landscape. In light of the current surge in respiratory illness in regions like China, understanding the implications of this virus is essential. As discussions around similar pathogens such as adenovirus and RSV continue, HMPV remains a focal point in conversations about respiratory health and disease prevention.
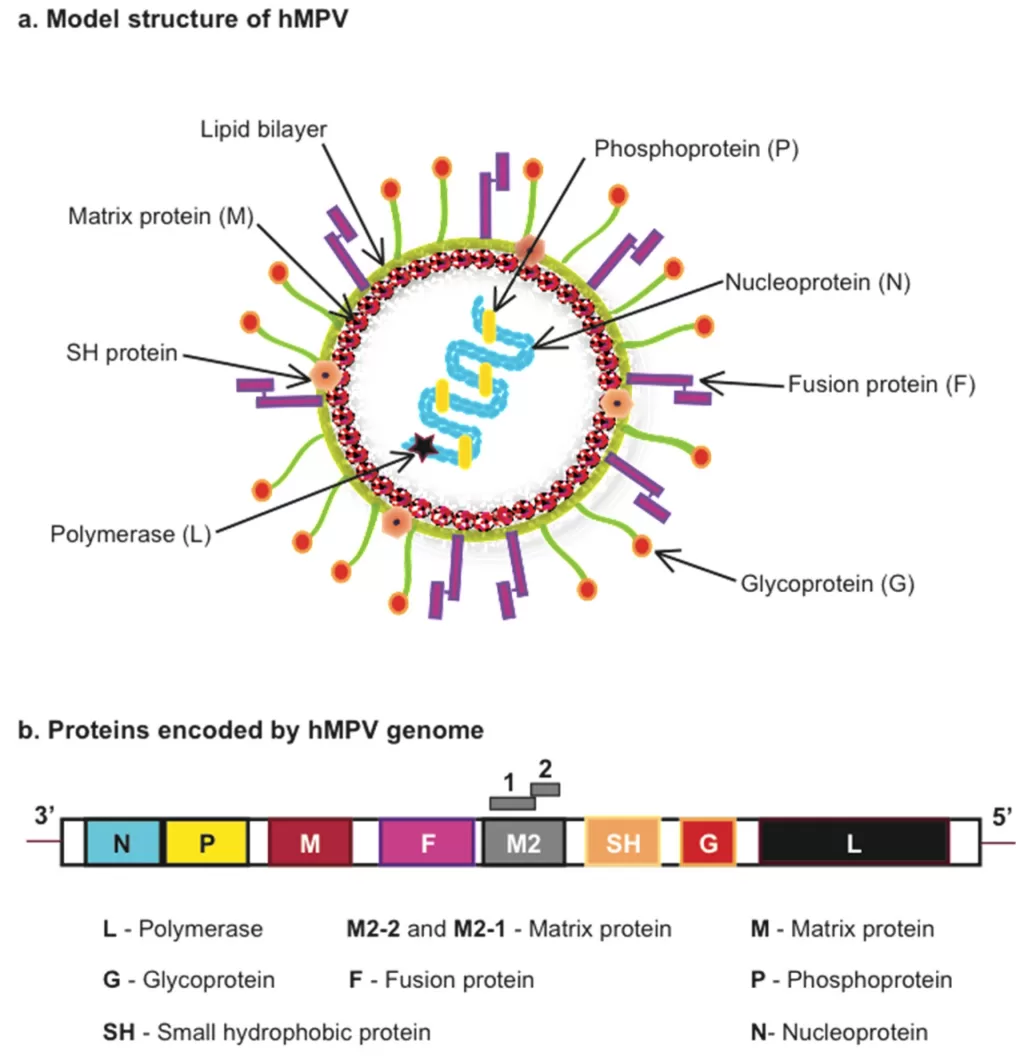
Understanding Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a respiratory virus that was first identified in 2001. It belongs to the Metapneumovirus genus, which includes viruses known to cause significant respiratory illness. Unlike some other viruses, HMPV is known to affect individuals across all age groups, but it poses particularly high risks to young children, older adults, and individuals with compromised immune systems. Symptoms of HMPV are similar to common flu-like illnesses, making it challenging to differentiate without specific testing.
The discovery of HMPV highlighted a gap in understanding respiratory viruses, showing that multiple pathogens could be responsible for flu-like symptoms. The increased rates of HMPV infections have led to a rise in awareness among healthcare professionals about its potential implications. As rates of flu-like illnesses continue to rise, understanding the role of HMPV becomes crucial in addressing respiratory illness outbreaks effectively.
HMPV Transmission and Prevention Strategies
HMPV spreads through respiratory droplets, similar to other pathogens like the influenza virus. Transmission can occur when an infected person coughs or sneezes, sending droplets into the air that can be inhaled by nearby individuals. Additionally, touching surfaces or objects contaminated with the virus can facilitate spread, especially if one’s hands subsequently touch the face. Understanding these transmission dynamics is essential in preventing outbreaks, especially in crowded settings like schools and hospitals.
Preventative measures recommended by health officials include frequent hand washing, avoiding close contact with sick individuals, and practicing respiratory hygiene. Covering the mouth and nose with a tissue or elbow when coughing or sneezing can also greatly reduce the risk of transmission. With the seasonal circulation of HMPV alongside the flu, individuals are encouraged to adopt these preventive behaviors consistently, particularly during peak seasons.
Recognizing HMPV Symptoms
Symptoms of HMPV generally resemble those of other respiratory infections, making diagnosis difficult without laboratory testing. Common symptoms include fever, cough, nasal congestion, and a runny nose. Some individuals may also experience shortness of breath, which could escalate to more severe conditions such as bronchitis or pneumonia if not addressed promptly. Understanding these symptoms is critical, especially during times when respiratory illnesses are prevalent, such as winter and early spring.
Monitoring one’s health and seeking medical attention if severe symptoms develop can mitigate the risk of complications. Patients displaying flu-like symptoms should take care to isolate themselves to avoid spreading the virus, and healthcare providers should remain vigilant for HMPV, particularly during periods of increased respiratory illness activity.
HMPV Outbreaks and Public Health Implications
Reports of rising HMPV infection rates underscore the importance of public health surveillance as communities face potential outbreaks. In recent weeks, China has noted a significant increase in flu-like illnesses, raising concerns about the overall impact of HMPV in these scenarios. Flu-like illnesses can overwhelm healthcare systems, necessitating awareness and preparedness for associated outbreaks.
The implications of the HMPV outbreaks extend beyond statistical data, affecting healthcare resources and public health policies. As officials monitor the situation, understanding the interplay between HMPV and other respiratory viruses is critical to developing effective responses to outbreaks. As health officials in China respond to reports of increased respiratory illnesses, awareness around HMPV will likely influence public communication strategies and health initiatives.
Flu-Like Illnesses and HMPV
Flu-like illnesses encompass a range of viral pathogens, including HMPV. This overlap can create confusion when diagnosing patients presenting with similar symptoms. Data emerging from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention indicates a growing prevalence of multiple viruses, including influenza and HMPV, leading to hospitalizations for respiratory illnesses. This underscores the need for comprehensive testing to identify specific pathogens responsible for outbreaks.
The rise in flu-like symptoms during peak respiratory illness seasons can strain healthcare resources, prompting public health campaigns that promote vaccination against the flu and increased awareness regarding HMPV. Understanding the dynamics of these illnesses is essential for both individuals and healthcare systems, providing a foundation for better management of respiratory infections, including targeted interventions for more vulnerable populations.
Current Landscape of HMPV in China
As news outlets report on the rising number of flu-like illnesses across China, the role of HMPV in this landscape cannot be overlooked. Current data suggests that HMPV is responsible for a notable percentage of respiratory illness cases, contributing to concerns about public health readiness. The statistics revealing that 6.2% of positive respiratory illness tests are attributed to HMPV signal a critical need for continued monitoring and effective public health responses.
The situation is dynamic, with health authorities closely observing trends in respiratory illnesses, including influenza and HMPV. This ongoing analysis is essential to inform prevention strategies and resource allocation. Policymakers must remain agile in their responses to emerging data, reinforcing the importance of early detection and robust healthcare infrastructure to counter potential outbreaks.
Managing Risks of HMPV Infections
Managing the risks associated with HMPV infections requires a combination of public health strategies and individual responsibility. Individuals showing symptoms consistent with respiratory infections should be encouraged to seek medical care while practicing self-isolation to minimize spread. Community awareness campaigns can enhance understanding of HMPV, identifying it as an important cause of flu-like illness.
Public health bodies must also ensure that accurate information circulates about managing flu-like symptoms at home, as specific treatments for HMPV are not yet accessible. Empowering individuals with knowledge about symptom management and the importance of getting tested can alleviate pressure on healthcare services while controlling potential outbreaks effectively.
Potential for HMPV to Contribute to Future Outbreaks
The emergence of HMPV and its recognition as a cause of respiratory illness brings forth concerns regarding its potential to contribute to future outbreaks. As the virus circulates widely, there is an increased chance of more severe cases developing among vulnerable populations. Ongoing monitoring and research are crucial in gauging the virus’s impact and improving public health responses.
While HMPV has not reached the pandemic level of COVID-19, continued vigilance in monitoring its prevalence and impact is warranted. Public health authorities must stay informed and ready to implement protective measures, particularly during acute phases of respiratory illness outbreaks that coincide with flu season.
Comparing HMPV with Other Respiratory Viruses
Understanding how HMPV compares with other respiratory viruses, such as influenza, COVID-19, and rhinoviruses, is necessary for effective management and treatment of flu-like illnesses. Each of these viruses can present overlapping symptoms, but they vary in pathogenicity, transmission rates, and public health responses. For instance, HMPV infections may lead to severe respiratory conditions in vulnerable individuals, similar to influenza, which often complicates the clinical picture.
Effective differentiation between these illnesses is critical for implementing appropriate treatments. Increased public health investment in diagnostics and awareness programs about HMPV will aid healthcare professionals in recognizing these viruses and providing timely interventions, thus reducing the overall burden of respiratory illnesses in the community.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is human metapneumovirus (HMPV)?
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a virus known to cause flu-like illnesses in people of all ages, particularly affecting young children, older adults, and individuals with weakened immune systems. Discovered in 2001, HMPV belongs to the same family as respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and is recognized as a significant cause of respiratory illnesses.
What are the common HMPV symptoms?
Symptoms of HMPV align closely with those of other flu-like illnesses, including cough, fever, nasal congestion, and a runny nose. In more severe cases, symptoms may escalate to shortness of breath, bronchitis, or pneumonia, with illness duration typically comparable to that of the flu.
How does human metapneumovirus spread?
Human metapneumovirus spreads primarily through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Close contact through touching, hugging, or kissing, as well as touching contaminated surfaces, can also facilitate the virus’s transmission. HMPV tends to circulate seasonally, peaking in late winter and spring.
Are there any confirmed HMPV outbreaks reported in China?
Currently, there are warnings about a potential human metapneumovirus outbreak in China, but officials have not confirmed this. Data from the Chinese Center for Disease Control highlights a rise in multiple flu-like illnesses, with HMPV accounting for 6.2% of positive respiratory illness tests.
What measures can be taken to prevent HMPV infections?
To prevent human metapneumovirus infections, individuals should frequently wash their hands, avoid touching their faces with unwashed hands, and minimize close contact with sick individuals. It’s also advisable for anyone with flu-like symptoms to cover their mouth when coughing or sneezing and to stay home until they recover.
Could HMPV lead to another pandemic like COVID-19?
While human metapneumovirus is actively circulating in populations, current data suggests more herd immunity compared to novel viruses such as COVID-19. There is no specific treatment or vaccine for HMPV, so management is akin to flu care. However, the risk of an HMPV pandemic remains unclear given the insufficient information about its recent spread.
How does HMPV compare to other flu-like illnesses such as influenza?
Human metapneumovirus shows similarities to other flu-like illnesses regarding symptoms and modes of transmission. However, recent data indicates that influenza is currently the leading virus causing severe respiratory illnesses in China, while HMPV is detected in around 6.2% of positive tests, suggesting it is a significant, though lesser, contributor.
What actions are health officials taking regarding the HMPV situation?
Health officials are monitoring the situation concerning human metapneumovirus closely, especially regarding potential outbreaks. In addition to tracking flu-like illnesses, they are advising the public on preventive measures to mitigate the risk of spread as they gather more information on the virus’s prevalence.
| Key Point | Detail |
|---|---|
| Current Situation | Reports of a potential outbreak of human metapneumovirus (HMPV) in China, but no official confirmation. |
| Influenza’s Status | Influenza is currently the primary cause of respiratory illness, with 30.2% positive tests. |
| HMPV Statistics | HMPV accounts for 6.2% of respiratory illness tests and 5.4% of hospitalizations. |
| Transmission | HMPV spreads through droplets, person-to-person contact, and contaminated surfaces. |
| Symptoms | Includes cough, fever, nasal congestion, and may lead to bronchitis or pneumonia. |
| Potential for Pandemic | No specific treatment or vaccine; currently unable to assess outbreak severity accurately. |
| Preventive Measures | Frequent hand washing, avoiding face touching, and keeping distance from sick individuals. |
Summary
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) is emerging as a virus of concern, particularly following reports of increased respiratory illnesses in China. While influenza remains the primary illness causing hospitalizations, HMPV has noticeably contributed to respiratory infection rates. Understanding how HMPV spreads, its symptoms, and how to prevent transmission is vital as this virus has been circulating globally since its discovery in 2001. Awareness and preparedness will be crucial in managing future outbreaks and protecting vulnerable populations from potential severe illness.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.