Human Babesiosis is a concerning tick-borne disease caused by the protozoan parasite Babesia venatorum. Recently reported in Siberia, this illness poses significant health issues, particularly for immunocompetent individuals who may experience unexpected acute babesiosis symptoms. Following an influenza-like syndrome, affected patients can develop a range of complications, highlighting the need for timely diagnosis. With the increase of tick-borne diseases across various regions, awareness of the risks associated with Babesia venatorum is crucial for effective health management. This emerging pathogen not only underscores the importance of understanding such infections but also emphasizes the need for preventive measures in at-risk areas like Siberia.
Babesiosis, often referred to as a tick-borne infection, has been increasingly recognized as a substantial public health concern. The infection is caused by protozoans, such as Babesia venatorum, leading to varying degrees of illness among affected individuals. Especially in regions like Siberia, where tick exposure is common, the emergence of babesiosis should not be underestimated. Acute symptoms may mimic those of common viral infections, complicating diagnosis for health professionals. Hence, understanding the epidemiology and clinical presentations of tick-borne diseases is vital for improving patient outcomes in affected populations.
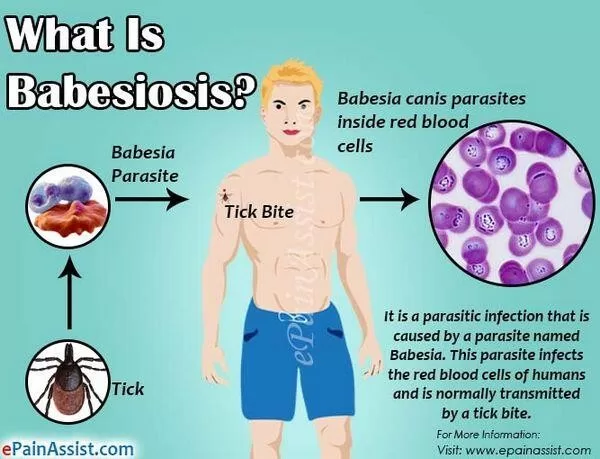
Understanding Human Babesiosis and Its Symptoms
Human babesiosis, a tick-borne disease caused primarily by the protozoan parasite Babesia venatorum, often presents with non-specific acute symptoms that can mimic influenza. Affected individuals may experience fever, fatigue, malaise, and jaundice. As was the case with a 63-year-old man in Siberia, the onset of symptoms may vary, starting with flu-like signs that can lead to more alarming conditions such as dark urine and significant general weakness. The initial overlap with common illnesses presents challenges in timely diagnosis, making awareness of such presentations crucial.
In immunocompetent individuals, the disease may display milder symptoms, but depending on the person’s health status and the timing of treatment, conditions can worsen rapidly. It’s essential to differentiate between babesiosis and other diseases in a clinical setting, especially in regions where tick populations are prevalent. Awareness about acute babesiosis symptoms can facilitate quicker medical interventions, which are vital in managing the disease effectively and preventing severe consequences.
The Role of Babesia venatorum in Tick-Borne Diseases
Babesia venatorum plays an increasingly significant role in the spectrum of tick-borne diseases, particularly within the geographical confines of Siberia and neighboring regions. While previously overshadowed by other Babesia species, recent cases — including those reported from the Siberian area — have underscored its emergence as a notable pathogen. Studies indicate that B. venatorum can often be misdiagnosed for other infections like those caused by Plasmodium spp. due to its similar clinical presentation, potentially leading to mismanaged treatments.
The unique molecular characteristics of B. venatorum, as highlighted in the case study, position it distinctively within the Babesia family. With advanced PCR testing confirming its presence and the evolutionary dynamics displayed through phylogenetic analysis, B. venatorum represents not just a public health concern but also an area requiring further scientific exploration. As tick-borne diseases continue to rise globally, understanding the mechanisms and impacts of infections like those caused by Babesia venatorum is vital for health strategies, particularly in Siberia where environmental changes may elevate tick encounters.
Impact of Tick-Borne Diseases in Siberia
The northern regions of Russia, specifically Siberia, are grappling with the growing threat of tick-borne diseases. Conditions like human babesiosis, driven primarily by Babesia venatorum, are becoming more common as the climate warms and tick habitats expand. This shift in the ecology has led to increased encounters between humans and infected ticks, thus raising the risk of transmission and subsequent health issues among residents. A comprehensive understanding of these environmental factors is critical to address the public health crisis posed by such infections.
Furthermore, the occurrence of babesiosis reinforces the need for educational initiatives in local communities to inform residents about preventive measures against tick bites. Individuals should be educated on recognizing symptoms promptly to seek timely medical intervention. Public health resources must focus on surveillance of tick populations and foster community engagement to combat the rise of tick-borne diseases effectively. Only through a joint effort can we mitigate the health risks associated with these infections in Siberia.
Diagnosis Challenges in Babesiosis Cases
Diagnosing human babesiosis can be complex, especially considering the non-specific nature of its symptoms. In many instances, initial presentations may resemble influenza or even malaria, leading to potential delays in correct identification. The case of a patient in Siberia illustrates this diagnostic challenge — early misidentification of Plasmodium spp. rather than B. venatorum delayed appropriate treatment. As such, healthcare providers must remain alert to the possibility of babesiosis in patients exhibiting flu-like symptoms, particularly in endemic areas.
Advanced diagnostic tools like PCR play a pivotal role in confirming the presence of Babesia venatorum. However, accessibility and availability of such testing can vary significantly across regions, impacting prompt care. It is paramount for healthcare systems to enhance diagnostic capabilities and protocols regarding tick-borne diseases. The integration of trained professionals and updated technological resources can significantly improve diagnosis accuracy and lead to better health outcomes for patients suffering from babesiosis.
Treatment Approaches for Babesia venatorum Infections
Effective treatment of babesiosis caused by Babesia venatorum typically involves the use of specific antiprotozoal medications. As noted in the highlighted case, the patient responded well to a combination of clindamycin and quinine sulfate, resulting in the resolution of parasitemia by the ninth day of treatment. This demonstrates that early recognition and prompt treatment are crucial in managing infections and reducing complications associated with the disease.
Management strategies for babesiosis should also consider the patient’s overall health status and the severity of the disease. While immunocompetent individuals may experience milder symptoms, those with compromised immune systems or other health issues may require more aggressive interventions. Thus, healthcare practitioners should tailor treatment plans that reflect the individual’s clinical presentation, contributing to better recovery rates and minimizing the risk of fatal outcomes.
Prevention Strategies Against Tick-Borne Diseases
Preventing tick-borne diseases like human babesiosis starts with public awareness and education on tick safety. Residents in endemic areas such as Siberia should be informed about avoiding tick habitats during peak seasons and employing protective measures such as wearing long clothing, using insect repellents, and performing thorough tick checks after outdoor activities. Educational campaigns can help promote these strategies, thereby lowering the incidence of tick bites and subsequent infections.
Community initiatives should also include the establishment of tick surveillance programs, which can help track tick populations and monitor the prevalence of pathogens like Babesia venatorum. Additionally, collaboration among public health authorities, researchers, and local communities is essential for executing effective prevention strategies. With increased awareness and proactive measures, the chances of transmission can be significantly reduced, underscoring the importance of an integrated approach in combatting tick-borne diseases.
The Significance of Molecular Analysis in Babesiosis
Molecular analysis has become an integral aspect of accurately diagnosing and understanding the epidemiology of babesiosis. In the case presented, the use of PCR allowed for the precise identification of Babesia venatorum as the causative agent of the infection. This level of specificity not only aids in prompt diagnosis but also informs treatment protocols, helping to ensure that patients receive the most effective care.
Moreover, studying the genetic structure of Babesia species through molecular techniques provides insight into their transmission dynamics, host interactions, and geographic distribution. As more cases are identified, continuous molecular investigations will be essential for tracking changes in the parasite’s population structure and potential shifts in virulence, thereby guiding public health responses in areas at risk.
Public Awareness and Health Education Regarding Babesiosis
Heightening public awareness concerning babesiosis and its causes is critical for effective disease management, particularly in regions like Siberia where cases are emerging. Educational programs should aim to inform individuals about the transmission pathways of Babesia venatorum and the importance of recognizing early symptoms. Such awareness will empower communities to take preventive measures, thus lowering the risk of infection.
Inclusion of local healthcare providers in these educational campaigns can also enhance the recognition of babesiosis among patients exhibiting flu-like symptoms. By fostering a collaborative approach between public health initiatives and community education, residents will be better equipped to seek timely medical help, which is essential to reduce morbidity and mortality rates associated with human babesiosis.
Future Research Directions in Babesiosis
As the understanding of babesiosis, particularly caused by Babesia venatorum, continues to evolve, future research must focus on various fronts. Investigating host-parasite interactions, transmission pathways, and the ecological implications of changing climate patterns on tick populations will yield crucial insights. Such research will help predict outbreaks and enhance preventive strategies against babesiosis and other tick-borne diseases.
Additionally, development of a vaccine against Babesia species would represent a significant advancement in public health. As incidence rates rise globally, collaborative research efforts between countries should prioritize determining the feasibility of preventive measures, as well as exploring novel treatments to expand therapeutic options for patients affected by this infection. The continuous advancement in research will be paramount to effectively tackling the challenges posed by tick-borne diseases.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Human Babesiosis and how is Babesia venatorum related to it?
Human Babesiosis is a tick-borne infection caused by protozoan parasites, and Babesia venatorum is one of the species responsible for this disease. It commonly affects immunocompetent individuals in regions like Siberia, where ticks can transmit the infection.
What are the acute babesiosis symptoms associated with Babesia venatorum?
Acute babesiosis symptoms from Babesia venatorum often include fever, jaundice, dark urine, and general weakness. These symptoms can resemble influenza-like illnesses, making early diagnosis challenging.
How prevalent is Babesia venatorum in Siberia and what should individuals be aware of?
Babesia venatorum has been identified in Siberia, with rising concerns due to the increasing number of cases reported. Individuals in this region should be aware of tick-borne diseases and monitor for acute babesiosis symptoms after potential tick exposure.
Can immunocompetent individuals contract Human Babesiosis from Babesia venatorum?
Yes, immunocompetent individuals can contract Human Babesiosis from Babesia venatorum, as demonstrated in cases documented in Siberia. It’s important for those in endemic areas to recognize symptoms and seek prompt medical care.
What are the treatment options for Human Babesiosis caused by Babesia venatorum?
Treatment for Human Babesiosis caused by Babesia venatorum typically includes antibiotics such as clindamycin and quinine sulfate, which have been effective in resolving parasitemia in affected patients.
What does molecular analysis reveal about Babesia venatorum in acute babesiosis cases?
Molecular analysis using PCR testing confirms the presence of Babesia venatorum DNA in acute babesiosis cases, indicating its role in the disease and helping differentiate it from other pathogens like Plasmodium spp.
Why is it crucial to recognize acute babesiosis symptoms in Siberia?
Recognizing acute babesiosis symptoms is crucial in Siberia to ensure timely diagnosis and response to Babesia venatorum infection, particularly since symptoms can mimic other illnesses, leading to misdiagnosis.
What role do tick-borne diseases play in Siberia health issues?
Tick-borne diseases, including Human Babesiosis from Babesia venatorum, are significant health issues in Siberia, prompting the need for increased awareness and preventive measures among residents and travelers.
Are there differences between Babesia venatorum and other Babesia species in terms of disease severity?
Yes, Babesia venatorum often presents milder symptoms compared to other species, such as Babesia divergens. However, it can still lead to severe health complications, especially in vulnerable populations.
What findings suggest a shift in parasite population structure of Babesia venatorum?
Recent findings suggest a shift from single to multioccupancy of erythrocytes by Babesia venatorum, indicating changes in its population structure without an overall increase in parasitemia, which may have implications for treatment outcomes.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Title | Human Babesiosis Caused by Babesia venatorum, Russia, 2024 |
| Authors | Olga P. Zelya, Irina V. Kukina, Ludmila S. Karan, Elena A. Krasilovskaya, Vadim V. Garin |
| Background | Emerging tick-borne infection caused by intraerythrocytic protozoa; this report discusses a case linked to B. venatorum. |
| Case Description | 63-year-old man in Siberia exhibited influenza-like symptoms; confirmed infection via PCR testing. |
| Molecular Analysis | PCR revealed only B. venatorum, highlighting dynamics in the infection without increased parasitemia. |
| Treatment | Clindamycin and quinine sulfate led to resolution of parasitemia by day nine. |
| Significance | Highlights the risk of B. venatorum in Siberia; awareness of symptoms is critical for diagnosis. |
| Conclusion | Emphasizes the importance of understanding babesiosis dynamics in tick-prevalent regions. |
Summary
Human Babesiosis is a critical public health concern, particularly highlighted by recent cases involving Babesia venatorum in Siberia, Russia. This case study of a 63-year-old man underscores the need for heightened awareness of babesiosis as it can mimic influenza-like illnesses. Through molecular confirmation and effective treatment, significant insights into the patterns of this tick-borne disease have been gained, illuminating the importance of vigilance in areas prone to such infections.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.