Healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) pose a significant challenge to patient safety in hospitals across the United States. The latest CDC report for 2024 indicates a promising trend: a steady decline in these infections throughout acute care settings, marking a pivotal moment for healthcare providers aiming to improve hospital safety statistics. With notable reductions, such as a 9% decrease in central line-associated bloodstream infections and a 10% drop in catheter-associated urinary tract infections, the findings highlight the effectiveness of robust infection control measures. This positive trajectory calls for ongoing efforts in reducing hospital infections, as hospitals work diligently to maintain these gains and foster a safer environment for patients. As we celebrate the decline in HAIs, understanding the underlying strategies remains crucial for sustaining these improvements and ultimately achieving better health outcomes for all.
Infections acquired during medical care, often referred to as nosocomial infections, continue to be a leading concern for healthcare facilities. Recent data showcases a significant turnaround in infection rates, reflecting the commitment to improving patient outcomes and adhering to stringent hygiene protocols. The focus on antimicrobial stewardship and other infection control initiatives has proven essential in the fight against hospital-associated infections. As healthcare providers recognize the importance of tracking and analyzing hospital safety statistics, progress is evident in various departments, revealing hopeful trends. This ongoing battle against healthcare-related infections emphasizes a collective responsibility among medical professionals to prioritize patient health and safety.
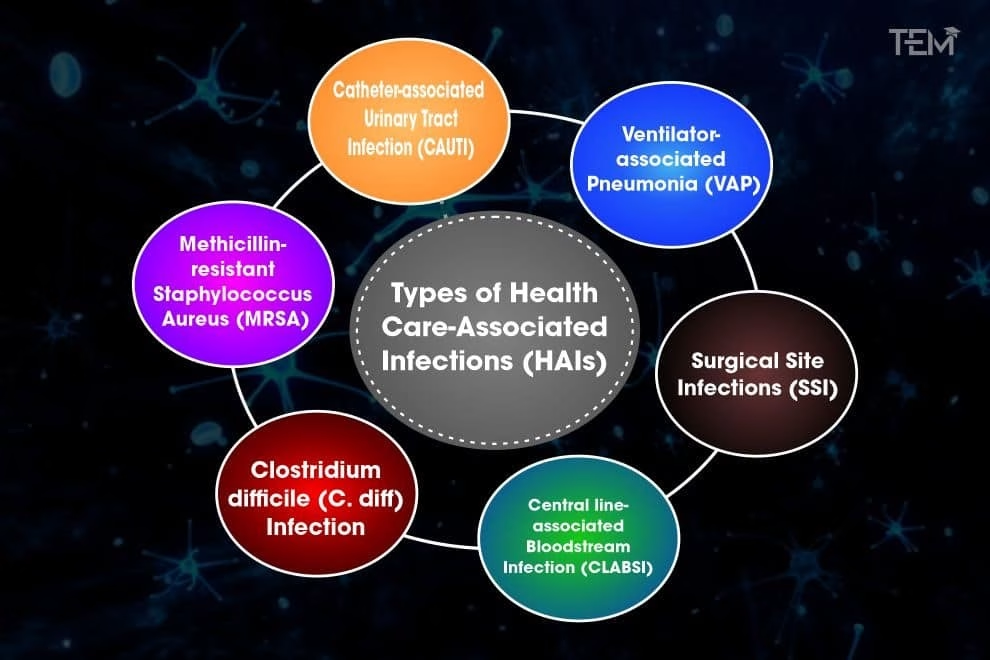
Overview of Healthcare-Associated Infections (HAIs)
Healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) represent a significant challenge for hospitals and healthcare providers across the United States. Defined as infections that patients acquire while receiving treatment for medical or surgical conditions, these infections can lead to serious complications, prolonged hospital stays, and increased healthcare costs. According to the latest CDC report for 2024, there has been a marked decline in the incidence of various HAIs in acute care settings, showcasing the effectiveness of targeted infection control measures over the past few years.
With specific reductions noted, such as a 9% decrease in central line-associated bloodstream infections and a remarkable 10% drop in catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs), it is evident that hospitals are making significant strides in improving patient safety. The report emphasizes the importance of continued vigilance, as the risks associated with these infections remain a critical concern within hospital environments. Comprehensive strategies and the implementation of best practices can steer efforts towards further minimizing these incidents.
Key Findings from the CDC Report 2024
The CDC’s 2024 National and State HAI Progress Report reveals encouraging statistics regarding the decrease in hospital-associated infections. In particular, the report highlights an 11% reduction in Clostridioides difficile infections and a significant 7% drop in cases of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) bacteremia. These findings reflect a broader trend of reducing hospital infections, attributed to continuous education and improved infection control measures. As highlighted by healthcare analysts, this ongoing decline is partly due to the implementation of robust antimicrobial stewardship programs, which have become crucial in managing antibiotic resistance.
Moreover, the report specifies that 17 states saw improvements in at least two infection types compared to 2023, marking a positive shift in the nationwide battle against HAIs. These figures underscore the commitment of healthcare organizations to enhance hospital safety statistics and emphasize the effectiveness of maintaining rigorous infection prevention protocols across various healthcare environments.
Trends in Infection Control Measures
In response to the rising rates of healthcare-associated infections, hospitals have steadily adopted enhanced infection control measures that prioritize patient safety and overall healthcare quality. The 2024 report by the CDC illustrates how the implementation of these strategies has led to a significant decline in hospital infections. For example, hospitals have improved their central line management protocols and implemented comprehensive catheter care practices, which have been proven to reduce rates of bloodstream and urinary tract infections significantly.
Additionally, the CDC has advocated for more rigorous surveillance of HAIs through the NHSN (National Healthcare Safety Network), which facilitates real-time reporting and analysis of infection data across healthcare facilities. By adopting data-driven approaches, hospitals can identify specific infection trends and allocate resources more effectively to target high-risk areas. This shift towards evidence-based infection control not only enhances healthcare outcomes but also promotes a culture of safety and accountability within the healthcare system.
Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on HAIs
The COVID-19 pandemic has undeniably altered the landscape of healthcare, with significant implications for healthcare-associated infections (HAIs). Initially, during the height of the pandemic, many hospitals faced challenges related to overstretched resources, which inadvertently opened pathways for the spread of infections due to inadequate staffing and supply shortages. The increased pressure on healthcare delivery systems revealed vulnerabilities in infection control protocols, leading to rising infection rates.
However, as reflected in the CDC’s 2024 report, the lessons learned from the pandemic have prompted hospitals to reassess and reinforce their infection prevention strategies. Enhanced emphasis on training healthcare staff about the importance of infection control measures, along with greater focus on proper hygiene practices and sterile techniques, contributed to a notable decline in HAIs. The collective experiences from the pandemic advocate for continuous improvement in hospital protocols to not only mitigate current infection rates but also prepare for future public health emergencies.
Antimicrobial Stewardship and Its Role
Antimicrobial stewardship programs play a pivotal role in combating healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) and their associated complications. These programs are designed to optimize the use of antimicrobials, thereby ensuring effective treatment while minimizing the risk of developing resistant strains of bacteria. The CDC’s findings in 2024 underline the importance of these strategies in promoting appropriate antibiotic prescribing practices, which have been linked to the significant reductions in HAIs.
By implementing robust antimicrobial stewardship initiatives, hospitals can not only lower the incidence of infections but also enhance patient safety outcomes. This approach encourages healthcare providers to collaborate, share strategies, and monitor antibiotic usage closely, ultimately fostering a culture of responsible prescribing. As such, the continued investment in antimicrobial stewardship will be essential for sustaining progress in the decline of HAIs and ensuring that such trends are maintained in the future.
Improving Hospital Safety Statistics
The recent CDC report emphasizes a remarkable improvement in hospital safety statistics, reflecting reduced rates of healthcare-associated infections across many acute care facilities in the United States. This improvement can be directly linked to the proactive measures hospitals have taken to mitigate infection risks. With a focus on maintaining rigorous basic hygiene, updated protocols for surgical site management, and enhanced surveillance measures, the effort towards improving safety within healthcare environments has never been more evident.
Moreover, state-level collaborations and initiatives have further strengthened these safety measures, enabling healthcare systems to benchmark their performance and engage in shared learning. These cooperative efforts aim to not only maintain but also continuously enhance the quality and safety of care provided to patients. Ultimately, the pursuit of improved hospital safety statistics illustrates the ongoing commitment to patient health and the drive to create environments where infections are significantly reduced.
State-Level Performance in Infection Control
The CDC report highlights notable advancements in state-level performance metrics regarding infection control across the United States. In 2024, 17 states demonstrated significant improvements in at least two types of healthcare-associated infections compared to the previous year. This progress showcases both the effectiveness of localized infection control initiatives and the commitment of healthcare authorities to prioritizing patient safety.
By analyzing state performance, healthcare leaders can identify successful strategies and best practices that contribute to a greater decline in HAIs. State health departments have played a crucial role by offering targeted assistance, resources, and education to hospitals, helping them adopt the most effective infection control measures. As states continue to monitor and report their progress, it fosters an environment of accountability and drives the continuous improvement of patient care across the spectrum.
Challenges Facing Healthcare Facilities
While the CDC report for 2024 indicates a notable decline in healthcare-associated infections, challenges remain prevalent in many healthcare environments. Factors such as staffing shortages, the emergence of new antibiotic-resistant organisms, and the ongoing impact of the COVID-19 pandemic present formidable barriers to achieving sustained reductions in HAIs. Healthcare facilities must navigate these complexities while striving to enhance the quality of care provided to patients.
To address these persisting challenges effectively, hospitals need to bolster their infection control measures and prioritize staff education on the importance of hygiene and compliance with protocols. Moreover, fostering a culture of safety and support within healthcare teams is essential for overcoming the obstacles that may hinder progress. Recognizing these challenges is imperative to ensure that the momentum gained in reducing healthcare-associated infections does not wane.
Future Directions for Infection Prevention
Looking ahead, the findings outlined in the 2024 CDC report indicate a need for continued commitment to infection prevention practices, with a focus on sustained improvements in healthcare-associated infection rates. Future directions may include the integration of advanced technologies, such as real-time data analytics, to monitor infection trends more accurately and swiftly. Using data to identify at-risk patients and areas of susceptibility can help healthcare organizations tailor their infection control efforts efficiently.
Additionally, ongoing research and public health initiatives aimed at enhancing antimicrobial stewardship and promising infection prevention strategies remain pivotal. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, collaboration between public health stakeholders, policymakers, and healthcare providers will be essential in driving innovations and promoting sustained success in reducing HAIs and maintaining hospital safety.
Frequently Asked Questions
What healthcare-associated infections saw a decline according to the CDC report 2024?
According to the CDC report 2024, healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) such as central line-associated bloodstream infections decreased by 9%, catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs) declined by 10%, and hospital-onset Clostridioides difficile infections dropped by 11%. Moreover, there were reductions in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia and surgical site infections.
How can hospitals further reduce healthcare-associated infections as noted in the CDC report?
The CDC report highlights the importance of strengthening infection control measures to reduce healthcare-associated infections (HAIs). Hospitals are encouraged to enhance their infection prevention and control (IPC) practices, which have been linked to previous reductions in HAIs since 2015, including financial incentives supporting these improvements.
What is the impact of antimicrobial stewardship on healthcare-associated infections?
Antimicrobial stewardship is crucial in reducing healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) as it helps manage antibiotic use, thus mitigating the rise of antibiotic-resistant pathogens. The CDC emphasizes that effective stewardship programs contribute to lower rates of HAIs by improving patient safety and optimizing treatment outcomes.
What are the hospital safety statistics related to healthcare-associated infections from the 2024 CDC report?
The 2024 CDC report reveals encouraging hospital safety statistics showing declines in healthcare-associated infections (HAIs). Specifically, US hospitals reported significant decreases, with a 10% decline in CAUTIs and an 11% reduction in C. difficile infections, marking three consecutive years of improvement.
Why is it essential for hospitals to continue tracking healthcare-associated infections?
Continuous tracking of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) is essential for hospitals to identify trends, improve infection control measures, and ensure patient safety. The CDC’s 2024 report underlines that despite observed declines, ongoing monitoring and research are necessary to sustain progress and eventually eliminate HAIs.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Overall Decline in HAIs | Majority of healthcare-associated infections decreased in US acute care hospitals from 2023 to 2024. |
| Significant Declines in Specific Infections | 9% reduction in central line-associated bloodstream infections; 10% drop in catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs). |
| Other Infection Reductions | 11% decrease in C. difficile infections; 7% drop in MRSA bacteremia; 4% reduction in surgical site infections; 2% decrease in ventilator-associated events (VAEs). |
| Long-term Care Hospitals Improvement | 23% decrease in VAEs; 15% drop in C. difficile cases.“ |
| State-Level Performance | 17 states improved in at least two infection types in 2024; 50 states showed improvement from baseline year of 2015. |
| Ongoing Need for IPC Measures | While progress is impressive, continued focus on infection prevention and control practices is essential to eliminate HAIs. |
Summary
Healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) have seen a significant decline in US acute care hospitals from 2023 to 2024, as per the recent CDC report. This decline is indicative of the successful implementation of infection prevention and control measures over the past years. With notable reductions in several serious types of HAIs, it is crucial to maintain and strengthen these initiatives to ensure the safety of patients in healthcare settings. The consistency of improvement across multiple states further highlights the effectiveness of ongoing efforts, pointing towards a path of continued vigilance in combating HAIs.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.