Hand, foot, and mouth disease is a rapidly spreading contagious childhood illness that has parents across the country on high alert. This common viral infection primarily affects young children, leading to unpleasant symptoms such as fever, mouth sores, and a painful blistering rash on the hands and feet. As outbreaks become increasingly reported, many families are asking how to prevent hand, foot, and mouth and what steps to take for effective hand, foot, and mouth treatment. With the virus easily transmitted through close contact and contaminated surfaces, childcare providers are grappling with the challenges of maintaining a safe environment. As parents share their experiences online, the urgency to manage this outbreak and protect our children from this illness intensifies.
Commonly referred to as HFMD, the illness characterized by sores and rashes can lead to significant discomfort, particularly in children. Parents are understandably concerned as they navigate the ongoing spread, with many schools and nurseries implementing guidelines for when children should stay home. Euphorically known as a viral outbreak among little ones, it draws attention due to its capacity for swift contagion. During this period, families are eager to explore alternative strategies and precautionary measures to mitigate the impact of this common pediatric virus. Keeping a close watch over symptoms and fostering an environment of thorough hygiene practices can significantly aid in reducing the incidence of this widespread health issue.
Understanding Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
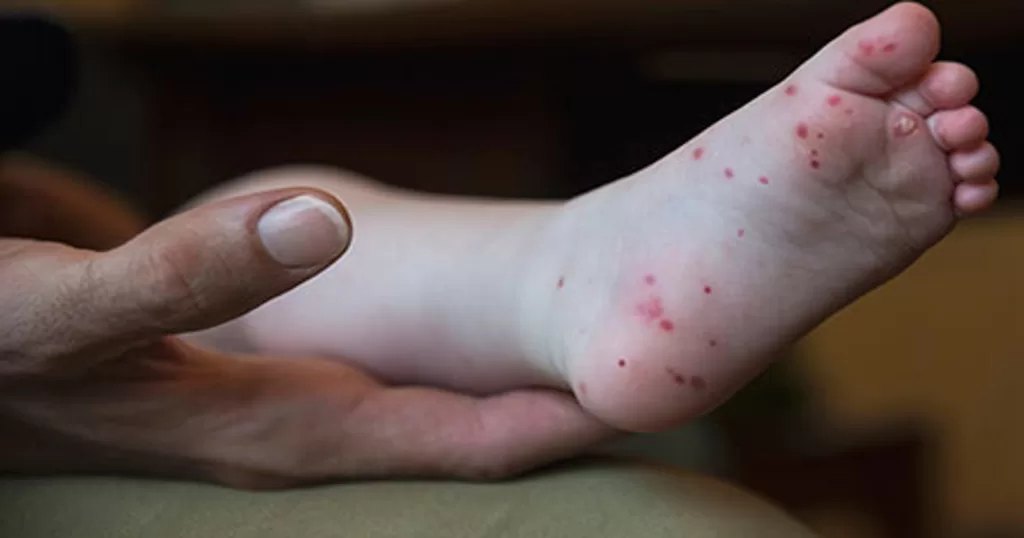
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a viral infection primarily seen in children under the age of five but can occur in older children and adults. It is characterized by fever, mouth sores, and a rash on the hands and feet. The virus responsible for this illness is highly contagious and is spread through direct contact with contaminated surfaces or close contact with an infected individual. Most notably, symptoms can manifest within three to seven days after exposure, which makes it challenging for parents to manage outbreaks effectively.
Common symptoms of hand, foot, and mouth disease include painful sores in the mouth, which can make eating and drinking difficult for young children. In addition to a sore throat and fever, the presence of distinctive red blisters on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet is a hallmark sign of the infection. As parents navigate these symptoms, awareness of HFMD’s contagious nature is paramount. Understanding how the illness spreads can empower parents to take proactive measures in their homes and communities.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
Diagnosing hand, foot, and mouth disease typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare provider who will look for the characteristic rashes and sores associated with the illness. Parents should be aware that these symptoms can resemble those of other viral infections, making it crucial to seek medical guidance if there are any concerns. Early diagnosis can facilitate prompt management and help control the spread of the disease within congregate living settings like nurseries.
Symptoms that accompany the illness can vary but generally include a mild fever, irritable behavior in infants and toddlers, and loss of appetite due to painful lesions in the mouth. It’s important for parents to monitor their child’s symptoms and maintain hydration, as avoidance of liquids can lead to dehydration, particularly in younger children who may refuse to drink due to mouth sores.
Preventing Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Outbreaks
Preventing an outbreak of hand, foot, and mouth disease requires vigilance in hygiene practices, especially in environments like nurseries where children interact closely. Regular handwashing with soap and water is vital, particularly after using the restroom and before eating. Encouraging children to wash their hands after coughing or sneezing can significantly reduce transmission risks. Additionally, keeping toys and surfaces clean and disinfected is essential in mitigating the spread of this contagious illness.
Parents and caregivers should also educate children on the importance of not sharing cups, utensils, or personal items to minimize exposure to the virus. In instances where a child is diagnosed, it is advisable to keep them at home until symptoms have resolved to help prevent further infections. Following these precautionary steps can make a substantial difference in controlling the spread of hand, foot, and mouth disease within the community.
Effective Treatment for Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
While there is no specific treatment for hand, foot, and mouth disease, management focuses on alleviating symptoms and maintaining hydration. Over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help relieve pain and reduce fever, making the child more comfortable during the infection period. Parents should ensure that children are drinking plenty of fluids, as staying hydrated is crucial during this time.
In more severe cases where mouth sores cause significant pain, a doctor might recommend topical remedies or prescription medications to alleviate discomfort. Additionally, parents should be encouraged to monitor for any signs of complications, such as dehydration or worsening symptoms, which might warrant further medical attention.
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease in Nurseries and Schools
Hand, foot, and mouth disease outbreaks are particularly common in settings like nurseries and schools, where young children are in close contact with each other. The nature of group activities can facilitate the rapid spread of the virus, resulting in many absences at once. Maintaining open communication between parents and nursery staff about reported cases can help parents take the necessary precautions at home.
As reported by parents, the absence of children from nurseries due to HFMD can create significant disruptions for families. Understanding how the illness spreads in group settings emphasizes the importance of adhering to health guidelines. Nursery and school officials play a crucial role by promoting hygiene education and encouraging parents to keep symptomatic children at home.
Social Media Reactions to Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Outbreaks
As the outbreak of hand, foot, and mouth disease has gained attention, parents are turning to social media platforms to share their experiences and seek advice. Many are using online forums to express their frustrations about sudden illnesses sidelining family activities and create a sense of community among those affected. By sharing personal stories, parents not only raise awareness about symptoms but also validate the experiences of others tolling under the weight of managing HFMD outbreaks.
The online conversations surrounding hand, foot, and mouth disease also serve to educate parents about preventative measures, symptom management, and support systems. Connecting with other parents facing similar challenges can alleviate feelings of isolation and uncertainty. As communities come together to address the issue, the sharing of resources and information can lead to more effective responses to the virus.
The Contagious Nature of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
Recognizing the contagious nature of hand, foot, and mouth disease is essential for parents and childcare providers alike. The illness can spread through direct contact with infected surfaces, respiratory droplets, and even feces. Due to this high level of contagion, outbreaks can proliferate quickly within community settings, necessitating that those affected avoid close contact with others until they have fully recovered.
In addition to the common symptoms, understanding how the virus transmits can help families implement appropriate protective measures. Parents are urged to take immediate action when close contacts are identified and be vigilant about hygiene practices to safeguard their children and others in their community.
Long-term Implications of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
While hand, foot, and mouth disease is generally benign and resolves without long-term effects, its impact can be challenging for families during active outbreaks. Children may experience discomfort and disruption in their daily routines, including missed classes and playdates, and parents may need to adjust their work schedules to care for sick children. The emotional weight of managing such illnesses can be equally significant.
For most, HFMD does not lead to serious complications; however, occasional severe cases can result in aseptic meningitis or other neurological issues. Understanding these rare outcomes, while focusing on the preventative steps and treatment options available, can help ease worries for families. Ultimately, the cyclical nature of outbreaks reminds the community of the need for vigilance during warm seasons when HFMD is most prevalent.
Community Response to Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Outbreaks
Communities must come together to address outbreaks of hand, foot, and mouth disease effectively. Public health officials play a key role in managing communication about symptoms and preventative measures to help minimize the spread. Engaging in community efforts, such as distributing educational pamphlets on hygiene and symptoms, can enhance collective awareness and encourage proactive practices.
When parents and caregivers rally together, the impact of health crises can be lessened. Creating support networks and rallying around affected families not only fosters a sense of solidarity but also encourages shared responsibility in combating the viral spread. By working collaboratively, communities can significantly reduce the incidence and impact of hand, foot, and mouth disease outbreaks.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common hand foot mouth symptoms that parents should look out for?
Common hand foot mouth symptoms include fever, sore throat, painful mouth sores, and a characteristic blistering rash on the hands and feet. These signs typically appear within 3 to 7 days after exposure to the virus.
How can parents prevent hand foot mouth disease in their children?
To prevent hand foot mouth disease, parents should emphasize strict hygiene practices such as regular handwashing, using tissues when coughing or sneezing, and avoiding the sharing of utensils. Keeping sick children at home can also help limit the spread.
What is the best hand foot mouth treatment available for symptomatic relief?
While there is no specific cure for hand foot mouth disease, symptom relief can be achieved with over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen or paracetamol for pain and fever. It’s also important to keep the affected child hydrated.
What should parents do during a hand foot mouth disease outbreak in their child’s nursery?
During a hand foot mouth disease outbreak, parents should keep symptomatic children at home, follow hygiene guidelines, and monitor for symptoms. Communicating with school or nursery staff can also help manage the situation.
How contagious is hand foot mouth disease, and when is a child most infectious?
Hand foot mouth disease is highly contagious, especially in the first week of illness when symptoms are present. The virus spreads through close contact, airborne transmission, and contact with contaminated surfaces.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Hand, foot, and mouth disease is a contagious viral illness primarily affecting children. |
| Symptoms include sore throat, fever, mouth sores, and blistering rash on hands and feet. |
| NHS guidelines recommend that infected children should stay home until symptom-free. |
| The outbreak is causing disruptions for parents balancing work and childcare. |
| Good hygiene practices are essential to prevent further spread of the infection. |
| Over-the-counter medications can help manage symptoms like pain and fever. |
| The illness typically resolves on its own within 7-10 days. |
Summary
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is currently a pressing concern affecting many families across the UK. This highly contagious childhood illness presents symptoms such as sores and rashes, severely impacting attendance in nurseries and schools. Parents are advised to keep sick children at home to mitigate spread and ensure proper recovery. As this outbreak highlights the importance of hygiene and childcare management, it’s crucial for families to remain vigilant and to instill effective preventive measures.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.