Flu vaccine effectiveness is a critical concern each flu season, especially as health officials strive to reduce the burden of influenza across communities. Every year, the CDC conducts rigorous studies to assess how well flu vaccinations hold up against varying strains of the virus. These vaccine effectiveness (VE) evaluations not only help estimate the public health impact of influenza vaccines but also inform decisions about vaccination strategies. By utilizing extensive networks of medical professionals, the CDC processes valuable data that reveal trends in flu season vaccine performance. Of course, understanding influenza vaccine effectiveness allows individuals and healthcare providers alike to make informed decisions during flu season, ensuring better health outcomes for populations at risk.
The efficacy of the flu shot and its capacity to prevent illness are paramount discussions during the influenza season. By analyzing data collected through CDC flu studies and networks, researchers are able to monitor and report on how effective the seasonal flu vaccine truly is. Observational studies assess the ability of these immunizations to curb hospitalizations as well as the incidence of laboratory-confirmed cases of influenza. With the influence of varying factors such as age and health status, influenza vaccine effectiveness varies each year, prompting a deeper inquiry into the annual flu vaccine’s reliability. Overall, these nuanced discussions about the vaccine’s performance underscore the importance of vaccination in safeguarding public health.
Understanding Flu Vaccine Effectiveness
Flu vaccine effectiveness (VE) is a critical metric measured annually by the CDC to assess how well the flu vaccines protect against the virus. Through rigorous studies, including observational designs and laboratory confirmations, researchers track the effectiveness of various vaccine formulations against circulating strains of influenza. This information is crucial for public health as it helps in guiding vaccination strategies and informing the public about how well the vaccines are likely to work each season.
Data from the CDC flu studies reveal variations in effectiveness based on multiple factors, such as the specific season, the demographics of vaccinated populations, and even the match between the vaccine strains and circulating viruses. Understanding these complexities allows healthcare providers and policymakers to make informed decisions about flu vaccine recommendations, ensuring maximum protection for the public during the flu season.
CDC’s Flu Vaccine Effectiveness Networks
The CDC has established robust vaccine effectiveness networks since the 2003-2004 flu season, facilitating a deeper understanding of flu vaccine performance across diverse populations. These networks include key partnerships with universities and hospitals, designed to estimate the real-world effectiveness of the flu vaccine through extensive observational studies. By confirming flu cases in laboratories, these studies provide reliable data on how well the vaccines mitigate the impact of seasonal influenza.
These collaborative CDC vaccine networks play a vital role in enhancing the effectiveness of immunization programs. The findings from these studies tend to inform both national vaccination policies and local health interventions, ultimately aiming to reduce the incidence of flu-related hospitalizations and fatalities. As flu seasons unfold, continuing research from these networks will shed light on how well the current vaccines are performing against emerging strains.
Analyzing Results from Past Flu Seasons
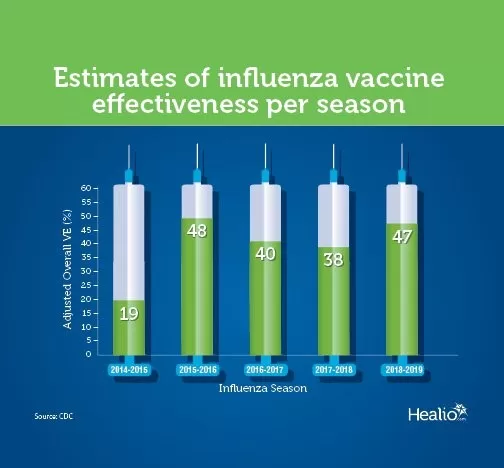
Analyzing the historical data on influenza vaccine effectiveness offers crucial insights into its performance over the years. The CDC has compiled adjusted overall VE estimates for flu seasons ranging from 2009 to 2024, revealing fluctuations in effectiveness. For instance, while the vaccine showed an effectiveness of 56% in the 2009-10 season, this dropped to just 19% during the 2014-15 season. Such variance stresses the importance of ongoing research to optimize future vaccine formulations and strategies.
These results not only serve as feedback for vaccine developers but also impact public perception and compliance regarding flu vaccinations. Understanding past performance empowers public health officials to communicate effectively about vaccine recommendations, especially in seasons where effectiveness is notably lower. With this historical context, the CDC can also strategize adaptive responses for upcoming flu seasons, ensuring better preparedness in combating influenza.
Research Supporting Flu Vaccine Effectiveness
Numerous studies have been published in medical journals evaluating the effectiveness of the flu vaccine, contributing to a growing body of evidence advocating for flu immunization. These investigations frequently highlight how effective vaccines can lower hospitalization rates, particularly in vulnerable populations such as the elderly and individuals with chronic health conditions. By evidencing a direct correlation between vaccination rates and reduced flu-associated health burdens, these studies bolster public health messaging and vaccination campaigns.
Moreover, these rigorous assessments by CDC and allied researchers provide data crucial for understanding demographic differences in vaccine responsiveness and effectiveness. By identifying specific populations that might marginally benefit from enhanced vaccine formulations or targeted public health interventions, the CDC can tailor its strategies to maximize community-wide immunity against influenza, thereby enhancing overall public health safety.
The Impact of Seasonal Flu Vaccines
Seasonal flu vaccines play a pivotal role in maintaining public health, especially among groups susceptible to severe influenza. By reducing the risk of contracting the flu, these vaccines contribute significantly to the overall well-being of the population. Efficacy studies led by the CDC have shown that even during seasons with lower vaccine effectiveness, the risk of severe illness can be substantially mitigated, underscoring the importance of yearly vaccination.
Moreover, the vaccines not only protect vaccinated individuals but also foster herd immunity, which is crucial in protecting those who cannot be vaccinated due to medical reasons. This collective defense mechanism stems from widespread vaccination, leading to fewer cases in the community and less strain on healthcare resources. Thus, obtaining the flu vaccine annually is essential in safeguarding public health, particularly during peak flu seasons.
Exploring Benefits of Flu Vaccination
The benefits of receiving the seasonal flu vaccine extend beyond individual protection; they contribute to broader public health outcomes. Vaccination has been shown to significantly reduce hospital admissions and emergency department visits due to flu-related complications. The CDC highlights these benefits in its CDC flu studies, which underscore the vaccine’s role in alleviating healthcare burden during flu season.
Furthermore, the economic aspect of flu vaccination cannot be overlooked. Wider vaccination rates correlate with decreased healthcare costs associated with treating severe influenza cases. By investing in immunization efforts, communities can save resources, improve workforce productivity, and reduce absenteeism during peak flu seasons. Thus, promoting flu vaccination can yield significant public health and economic benefits.
Understanding CDC’s Role in Influenza Public Health
The CDC serves as a cornerstone of influenza public health strategy, guiding vaccine development and implementation through extensive research and data collection. By conducting well-designed studies on vaccine effectiveness, the agency informs both healthcare providers and the general public about the best practices for flu prevention each season. The effectiveness data provided by the CDC is crucial for adapting strategies to current flu strains and understanding seasonal dynamics.
Additionally, the CDC plays a vital role in fostering collaboration among healthcare systems, researchers, and the public. By sharing findings through its networks, the CDC enhances the overall trust in vaccination efforts and promotes compliance within the community, making significant strides towards curbing influenza’s impact. This cohesive approach ensures that public health measures remain robust and responsive to the changing landscape of influenza activity.
Engaging Communities in Flu Vaccine Awareness
Engaging communities in flu vaccine awareness is essential for optimizing vaccination rates and enhancing public health outcomes. The CDC encourages local health departments and organizations to raise awareness through education campaigns that highlight the importance, benefits, and effectiveness of the flu vaccine. Educational efforts can demystify misconceptions about the flu vaccine, offering evidence-based information to counteract hesitancy and foster a culture of proactive health behaviors.
Furthermore, community engagement initiatives can empower individuals to take ownership of their health by emphasizing the collective benefits of vaccination. Local outreach programs can facilitate access to flu shots, especially in underserved populations that may otherwise face barriers to vaccination. Such strategies ensure that the message regarding flu vaccine effectiveness is not just heard, but acted upon, leading to healthier communities overall.
Future Directions in Flu Vaccine Research
As the landscape of influenza continually evolves, future research aimed at enhancing flu vaccine effectiveness is becoming increasingly important. Scientists and public health experts are focused on developing innovative vaccine technologies that can adapt rapidly to changing virus strains. Furthermore, ongoing studies by the CDC highlight the need for a universally effective flu vaccine that could provide long-lasting protection against multiple strains.
Research also delves into understanding the immune response variability among different demographics, exploring how tailored vaccination strategies can improve effectiveness across diverse populations. These advancements not only aspire to improve individual protection but aim to revolutionize flu prevention strategies on a global scale. Thus, continued investment in flu vaccine research remains critical for achieving optimal health outcomes in future flu seasons.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does the CDC determine flu vaccine effectiveness?
The CDC determines flu vaccine effectiveness (VE) by conducting studies each flu season that assess the vaccines’ ability to prevent laboratory-confirmed influenza. These studies vary based on design, population, and outcomes measured.
What are the recent statistics on flu vaccine effectiveness?
According to CDC flu studies, adjusted estimates of vaccine effectiveness over recent flu seasons vary. For example, the overall VE was 36% for the 2021-22 season and 42% for the 2023-24 season, reflecting varying levels of effectiveness.
Why is the flu season vaccine effectiveness important?
Flu season vaccine effectiveness is crucial as it helps public health officials understand how well vaccines protect against influenza, guiding vaccination strategies and informing the public about the importance of getting vaccinated.
What influences the effectiveness of the influenza vaccine?
The influenza vaccine effectiveness can be influenced by several factors, including the specific flu strains circulating, the timing of the vaccination, the population group’s characteristics, and the overall health of individuals receiving the vaccine.
Are there resources available on CDC vaccine networks for flu effectiveness research?
Yes, the CDC provides detailed information on its vaccine effectiveness networks that collaborate with universities and hospitals to study flu vaccine effectiveness. Access to these resources is available on the CDC website.
Can prior flu seasons’ vaccine effectiveness data be accessed?
Yes, the CDC publishes past seasons’ vaccine effectiveness estimates, showcasing how effective flu vaccines have been in reducing influenza cases from 2004 to 2024, providing valuable insights into public health.
What is the average flu vaccine effectiveness based on CDC data?
Based on CDC’s historical data, the average flu vaccine effectiveness varies year to year. For instance, the effectiveness ranged from a low of 19% in the 2014-15 season to a high of 60% in the 2010-11 season.
What additional research supports flu vaccine effectiveness findings?
Various supporting research studies, including peer-reviewed articles, evaluate flu vaccine effectiveness by measuring its impact on reducing hospitalizations and laboratory-confirmed flu cases across diverse populations.
| Influenza Season | Adjusted Overall VE (%) |
|---|---|
| 2009-10 | 56 |
| 2010-11 | 60 |
| 2011-12 | 47 |
| 2012-13 | 49 |
| 2013-14 | 52 |
| 2014-15 | 19 |
| 2015-16 | 48 |
| 2016-17 | 40 |
| 2017-18 | 38 |
| 2018-19 | 29 |
| 2019-20 | 39 |
| 2020-21* | Not enough data to compute |
| 2021-22 | 36 |
| 2022-23** | 30 |
| 2023-24†† | 42 |
Summary
The flu vaccine effectiveness has been a vital area of research for public health, demonstrating varying efficacy across different seasons from 2009 to 2024. The effectiveness varies yearly, influenced by factors such as circulating virus strains and population characteristics. While some years exhibit high effectiveness (like 60% in 2010-11), others present lower rates (as seen with 19% in 2014-15). Despite fluctuations, the flu vaccine continues to play a crucial role in reducing flu-related illnesses. Thus, staying informed about flu vaccine effectiveness helps individuals make better health decisions each flu season.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.