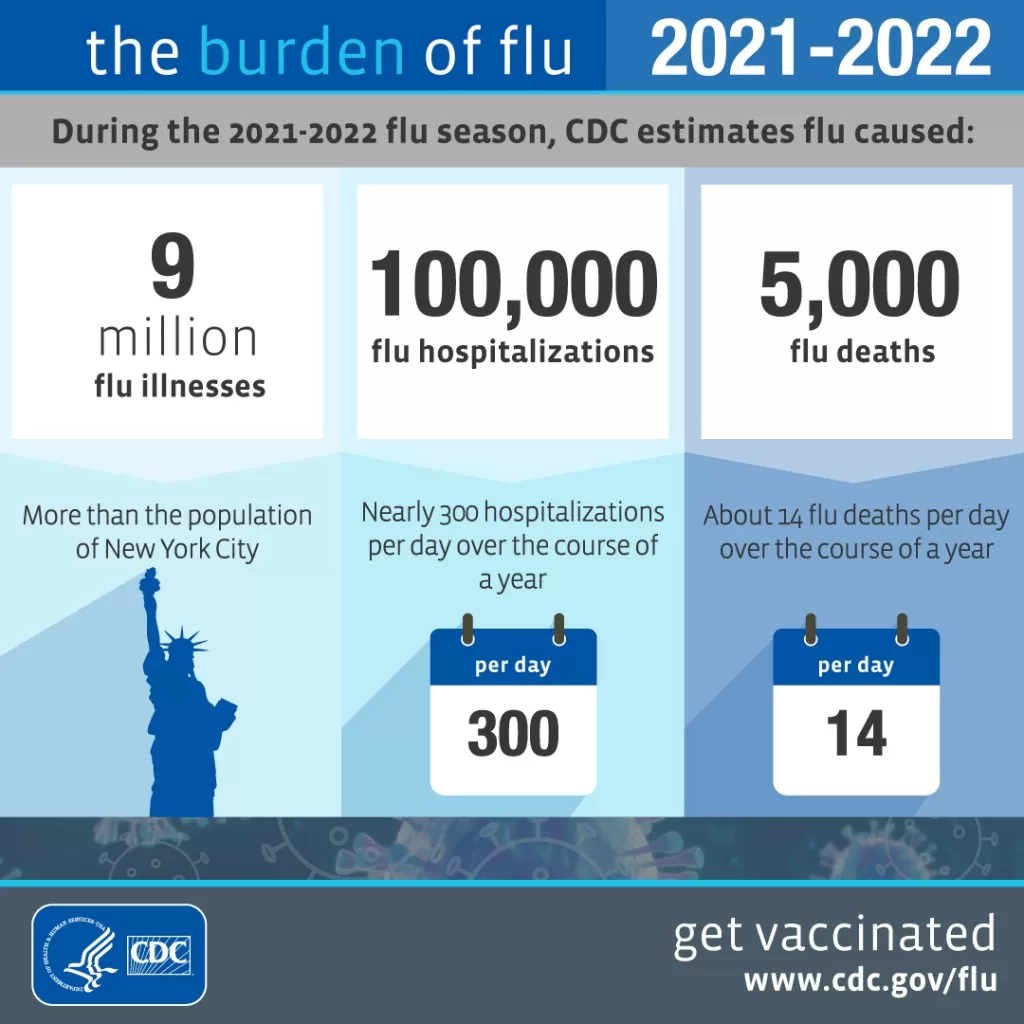
The flu burden represents a profound and often underestimated health threat, impacting millions in the United States each year. According to CDC flu estimates, this seasonal illness results in tens of millions of flu-related illnesses annually, highlighting the critical need for flu vaccination among all age groups, especially those at higher risk. With influenza hospitalizations averaging between 120,000 and 710,000 per year, the importance of prevention cannot be overstated. Seasonal flu statistics reveal that these hospitalizations often lead to further health complications, particularly in patients with pre-existing medical conditions. In addition, flu-related deaths vary significantly, ranging from 6,300 to a staggering 52,000 since 2010, underscoring the severity of this seasonal epidemic and the necessity of proactive protective measures such as vaccination.
The impact of seasonal influenza extends far beyond the occasional sniffle; it encompasses a widespread public health challenge that calls for serious attention. Often dubbed as flu season, this annual occurrence leads to significant illness and unscheduled hospital visits, causing disruptions in both personal and professional realms. Alternative terms such as “respiratory virus outbreaks” and “viral infections” reflect the broader implications of influenza’s reach, penetrating communities and straining healthcare systems. With authorities like the CDC working tirelessly to compile and analyze flu-related data, understanding the implications of this pervasive illness becomes crucial for informed decision-making regarding flu vaccinations and health policies. Given the potential for serious complications and increased mortality rates, proactive measures and public awareness are essential to mitigate the flu burden on our society.
Understanding the Flu Burden: Key Statistics
The burden of influenza on public health is significant, with millions falling ill each year in the United States. The CDC reports that since 2010, apart from the 2020-2021 flu season, the annual estimates show between 9.3 million to 41 million cases of flu infections. This staggering statistic not only highlights the prevalence of influenza but also showcases its potential impact on individuals’ daily lives, such as decreased school attendance and workplace productivity. The essential role of the CDC’s monitoring systems ensures that public health officials remain prepared to address flu outbreaks as they occur.
Flu illness affects not just those who contract the virus, but also communities as a whole. With millions seeking medical attention for flu-like symptoms each year, the strain on healthcare systems becomes considerable. The ILINet system tracks these cases, providing crucial insights into flu trends and helping health authorities plan resources. The necessity for public awareness and education about flu vaccines is paramount, as increased vaccination rates can drastically lower the flu burden in communities.
Flu-related Hospitalizations: A Growing Concern
Hospitalizations due to flu have become increasingly common, highlighting the virus’s serious health implications. The CDC estimates that flu results in between 120,000 and 710,000 hospitalizations annually, with specific vulnerable populations—such as the very young, the elderly, and those with chronic conditions—being at heightened risk. Getting vaccinated against the flu remains the best preventive measure not only to protect oneself but also to shield those who are most susceptible to complications from flu-related illnesses.
Understanding the hospitalization statistics is crucial for public health planning. The FluSurv-NET network collaborates with healthcare facilities across the country to monitor flu-related hospitalizations. By refining these statistics and addressing gaps in reporting, efforts can be made to ensure adequate resources are available during peak flu seasons. Increased awareness of seasonal flu vaccines can significantly affect hospitalization figures, illustrating the importance of proactive health measures.
Influenza and Its Potential Fatal Consequences
The impact of influenza extends beyond hospitalization, with annual flu-related deaths representing a critical health concern. Since 2010, CDC estimates show that flu-related deaths in the United States range dramatically, from as low as 6,300 to as high as 52,000. This discrepancy underscores the challenges in accurately counting flu-related fatalities. Many deaths attributed to flu involve underlying conditions, complicating reporting and creating an underrepresentation of the true flu mortality rate.
Children are subject to distinct reporting standards, with flu-related deaths reported to the CDC through specific systems. Even with efforts to track these deaths accurately, the real number likely exceeds reported figures, meaning greater urgency exists in promoting flu vaccination, especially among vulnerable populations. By addressing broader flu burden metrics, we can foster a deeper understanding of how to combat various flu seasons.
Seasonal Flu Statistics: Importance for Public Awareness
Seasonal flu statistics are essential in shaping public health policies and raising awareness. The CDC’s release of timely data regarding flu burden, including estimates of illness, hospitalization, and mortality rates, plays a pivotal role in guiding vaccination campaigns and health initiatives. These seasonal statistics increase community engagement and provide a clear picture of the potential risks associated with flu, particularly in high-risk populations.
With seasonal flu numbers fluctuating each year, understanding these statistics allows individuals and families to make informed decisions about flu vaccinations. Promoting vaccine accessibility and dispelling myths around them drive community participation in preventive measures. Awareness campaigns can harness seasonal flu statistics to highlight the benefits of vaccination, ultimately reducing the incidence of flu illnesses and improving overall public health.
The Role of the CDC in Flu Surveillance and Estimates
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is integral to understanding the flu burden through its comprehensive surveillance systems. By utilizing networks like ILINet for tracking flu-like illnesses and FluSurv-NET for hospitalizations, the CDC gathers essential data that informs public health strategies. This data helps to anticipate flu seasons, allocate resources effectively, and implement vaccination programs targeted at communities most in need.
Moreover, the CDC’s continuous effort to update flu burden estimates as new data emerges emphasizes the dynamic nature of influenza and its unpredictable strains. This commitment is crucial for addressing seasonal epidemics, as it equips healthcare providers and policymakers with the information needed to respond effectively. As flu dynamics evolve, so too must our strategies for prevention and public education.
The Significance of Annual Flu Vaccination
Flu vaccination stands as a primary defense against the seasonal flu burden. The CDC recommends annual flu vaccinations for everyone aged six months and older, highlighting the compelling need for everyone to participate in preventative health measures. Vaccination not only protects individuals but also contributes to herd immunity within communities, ultimately reducing overall flu transmission rates.
Despite the proven efficacy of flu vaccines in reducing hospitalizations and deaths, misconceptions about their safety and effectiveness persist. Addressing these misconceptions through evidence-based education can significantly improve vaccination rates. Public health campaigns that emphasize the vital role of the flu vaccine in preventing serious health complications are essential to reducing the burden of flu nationwide.
Tracking Flu-related Death Estimates: Challenges and Importance
Estimating flu-related deaths presents considerable challenges, with many factors complicating accurate counts. The CDC relies on statistical modeling to provide estimates of deaths linked to influenza, often drawing on data regarding hospitalizations and illness severity. This reliance on modeling acknowledges the complexities of flu fatalities, particularly when differentiating between deaths attributable directly to flu and those resulting from related complications.
Flu-related death estimation is further complicated by under-reporting, especially among vulnerable groups such as children and the elderly. As flu-related pediatric deaths are nationally notifiable, greater efforts to improve reporting accuracy can enhance the understanding of flu’s mortality impact. Continuous advocacy for testing in hospitals and healthcare settings could lead to more precise data, aiding in effective flu management strategies.
Revisiting Flu Burden Data: Continuous Improvement Needed
Data on flu burden must be revisited and refined continuously to ensure public health strategies remain effective. The CDC adapts its strategies as new data becomes available, learning from previous flu seasons to improve future responses. This iterative process is critical to addressing the ever-evolving nature of influenza and its potential impacts on health systems.
Encouraging collaboration among healthcare providers, public health officials, and communities fosters a proactive approach to managing flu seasons. By sharing updated statistics and bolstering vaccination efforts based on the latest data, health officials can create more effective preventative strategies. The ongoing evaluation of flu burden helps refine public health messages, strengthening community engagement in combating influenza.
Public Awareness: Reducing the Impact of Seasonal Flu
Public awareness campaigns play a crucial role in mitigating the impact of seasonal flu. By informing individuals about flu symptoms, vaccination benefits, and the importance of seeking care, these campaigns foster a culture of health vigilance. As communities become educated about the flu burden, they are more likely to engage in preventive measures, thereby reducing overall incidence rates.
Additionally, tailoring public health messages to specific demographics ensures that the information resonates with diverse community groups. Accessibility to vaccines, alongside clear communication regarding flu risks, can significantly enhance participation in vaccination programs. As public understanding of flu-related statistics improves, we can expect higher vaccination uptake and decreased flu burden in the long term.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the estimated flu burden in the U.S. for illness and hospitalizations?
The estimated flu burden in the U.S. indicates that since 2010, seasonal flu has caused between 9.3 million and 41 million illnesses annually. Additionally, flu-related hospitalizations range from 120,000 to 710,000 each year, reflecting the substantial impact of influenza on public health.
How does the CDC estimate flu-related deaths each year?
The CDC uses statistical models to estimate flu-related deaths each year, accounting for under-reporting and variations in testing. Since 2010, flu-related deaths have been estimated between 6,300 and 52,000 annually, highlighting the challenges in pinpointing exact numbers due to reporting inconsistencies.
Why is the flu vaccine important in reducing flu burden?
The flu vaccine is crucial in reducing flu burden as it significantly lowers the risk of illness, hospitalizations, and flu-related deaths. Vaccination is recommended for everyone 6 months and older, especially those at higher risk of complications.
What are the key seasonal flu statistics provided by the CDC?
Key seasonal flu statistics from the CDC include estimates of 9.3 to 41 million illnesses, 120,000 to 710,000 hospitalizations, and 6,300 to 52,000 deaths each year. These statistics underline the importance of vaccination and public health awareness.
How do flu-related hospitalizations affect healthcare systems?
Flu-related hospitalizations place a significant burden on healthcare systems, often leading to overcrowding and increased patient care demands. With hundreds of thousands affected yearly, understanding the flu burden is crucial for healthcare planning and resource allocation.
What does CDC surveillance reveal about flu illness trends?
CDC surveillance, including the Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network, helps track flu illness trends, showing weekly reports of patients seeking care for flu-like symptoms. This data aids in estimating the overall flu burden during flu seasons.
What challenges does the CDC face in accurately estimating influenza statistics?
Challenges in accurately estimating influenza statistics include under-reporting of cases, lack of widespread testing, and reporting inconsistencies across states. These issues complicate efforts to determine precise flu burden figures.
Are flu-related deaths in children reported differently than in adults?
Yes, flu-related deaths in children under 18 are nationally notifiable and reported to the CDC, while deaths in adults are less systematically tracked. This distinction aims to improve monitoring of pediatric flu mortality, though under-reporting remains a concern.
How does the seasonal flu impact productivity?
Seasonal flu leads to millions of illnesses, affecting school attendance and workplace productivity. Flu-related absenteeism can hinder both educational and economic outcomes, emphasizing the need for effective vaccination strategies.
What role does the CDC play in managing flu burden in the U.S.?
The CDC plays a vital role in managing flu burden through surveillance, public health recommendations, and promotion of vaccination to mitigate the impact of seasonal flu on public health.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Flu Illness | CDC estimates 9.3 to 41 million illnesses from seasonal flu annually in the U.S. (2010-2021). Participation in ILINet helps track flu-like symptoms. |
| Flu-related Hospitalizations | Annual estimates suggest 120,000 to 710,000 hospitalizations due to flu each year. Vaccination is crucial for prevention, especially for those at higher risk. |
| Flu-related Deaths | Between 6,300 to 52,000 flu-related deaths are estimated per year in the U.S. The actual numbers may be higher due to under-reporting challenges. |
| Changing Estimates | Flu death estimates may be revised as new data becomes available. CDC uses mathematical models and historical data to track flu-associated mortality. |
Summary
The flu burden refers to the significant impact influenza has on public health, with millions of illnesses and hundreds of thousands of hospitalizations occurring each year. Vaccination plays a crucial role in mitigating the flu burden, helping to prevent severe outcomes in vulnerable populations and reducing the strain on healthcare resources. Monitoring and accurate estimation of flu-related data are essential for effective public health responses.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.