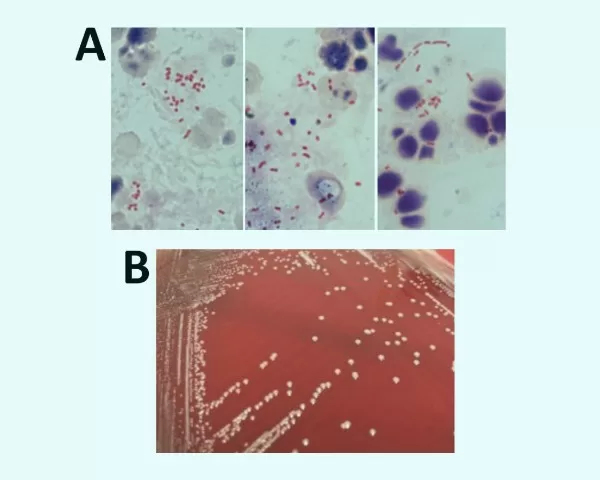
In 2024, the scientific community welcomed a significant addition to the taxonomy of gram-negative bacteria with the introduction of Emayella augustorita. This new bacterial species, part of the Pasteurellaceae family, was first identified by a team led by Sylvain Meyer from the University of Limoges in France. E. augustorita has been primarily recognized as a commensal bacterium residing in the oral cavities and upper respiratory tracts of common pets like cats and dogs. Notably, this novel bacterium gained attention after being isolated from blood cultures of a patient suffering from sepsis, highlighting its potential clinical implications. The discovery of Emayella augustorita not only opens new avenues for research into bacteria in cats and dogs but also emphasizes the crucial need for understanding the role of these organisms in health and disease.
Emayella augustorita represents an exciting breakthrough in the world of microbial research, particularly in the study of bacterial pathogens related to pets. This recently identified species is a gram-negative organism within the Pasteurellaceae family, highlighting its relevance in veterinary medicine and potential links to human health. The isolation of this bacterium from a case of sepsis underscores its significance, as it may play a role in infections that arise from animal interactions. As researchers delve deeper into the implications of this new bacterial species, it paves the way for advancements in our understanding of sepsis and its association with various bacterial strains prevalent in domestic animals. Furthermore, Emayella augustorita enriches our knowledge of oral microbiomes and the complex relationships between bacteria in cats and dogs and their potential impacts on human health.
Introduction to Emayella augustorita: A New Era in Bacterial Discovery
In 2024, the introduction of Emayella augustorita marked a significant milestone in microbiology, especially within the Pasteurellaceae family. This novel bacterial species represents not only a discovery of a new organism but also expands our understanding of gram-negative bacteria commonly found in the oral and respiratory tracts of pets like cats and dogs. The identification was spearheaded by Sylvain Meyer of the University of Limoges, emphasizing the importance of research in understanding the complexities of microbial life in domestic animals and humans alike.
The discovery of E. augustorita came from an insightful case where the bacterium was isolated from blood cultures of a patient who experienced sepsis, underscoring the potential health implications associated with this bacterial species. As healthcare professionals continue to address sepsis caused by various bacterial pathogens, understanding the role and behavior of newly identified organisms such as E. augustorita becomes crucial in developing effective treatments and preventative measures.
Significance of Gram-Negative Bacteria in Veterinary Medicine
Gram-negative bacteria are pivotal in veterinary medicine as they are often responsible for a variety of infections in companion animals. Species from the Pasteurellaceae family, like Emayella augustorita, can lead to significant health concerns in cats and dogs, making awareness and understanding of these organisms vital for veterinarians. Their presence as commensals in oral cavities often contrasts with their potential pathogenic roles under certain conditions, such as when the immune system is compromised or due to the introduction of foreign bodies.
E. augustorita’s classification as a gram-negative organism aligns it with other notable pathogens, highlighting the necessity for ongoing research and vigilance in clinical settings. Understanding the pathogenic potential of such bacterial species is essential, especially as they can be implicated in cases of sepsis, which is a severe medical condition requiring immediate attention. The knowledge gained from studying E. augustorita could lead to better preventative strategies and treatments for bacterial infections in pets.
The Role of Pasteurellaceae Family in Infectious Diseases
The Pasteurellaceae family includes a variety of bacterial species known for their roles in infectious diseases in both animals and humans. Emayella augustorita adds to the diversity within this family, showcasing the complexity of interactions these bacteria have with their hosts. This family is typically associated with respiratory infections, soft tissue infections, and sometimes severe outcomes like sepsis, particularly in immunocompromised individuals or those with underlying health issues.
As practitioners and researchers continue to gain insights into the Pasteurellaceae family, understanding the epidemiology and pathogenic mechanisms of bacteria like E. augustorita is critical. The identification of these organisms not only assists in recognizing potential zoonotic threats but also emphasizes the need for integrated approaches in monitoring and managing infections crossed between pets and their human companions.
Isolating E. augustorita: Implications for Research and Healthcare
The isolation of Emayella augustorita from a blood culture poses significant implications for clinical microbiology, particularly in understanding sepsis and the role of previously unrecognized bacteria. Such discoveries compel healthcare practitioners to reassess diagnostic processes and treatment protocols for infected patients. The presence of a novel species like E. augustorita indicates that similar undetected organisms may exist, necessitating a robust laboratory capacity to identify and characterize these bacteria accurately.
The implications of isolating E. augustorita extend beyond infectious disease treatment; they provoke advancements in bacteriology, immunology, and antibiotic resistance research. As healthcare systems gear up to tackle complex infections, the emergence of novel bacterial species underscores the urgency for advancements in antibiotic stewardship and the search for new therapeutic strategies.
Understanding Sepsis and Its Association with Novel Bacterial Species
Sepsis represents a critical condition that arises when the body’s response to infection injures its tissues and organs. The discovery of Emayella augustorita as a causal agent of sepsis exemplifies the risks posed by emerging bacterial threats. Specifically, this gram-negative organism’s potential to cause severe bloodstream infections necessitates heightened awareness among clinicians and researchers alike. Early detection and identification of such pathogens are fundamental in improving patient outcomes in sepsis cases.
Research into how novel bacteria contribute to sepsis, which includes understanding their virulence factors and antibiotic susceptibility, will provide clinicians with better tools to treat such infections. The emergence of E. augustorita not only addresses existing gaps in medical knowledge but also emphasizes the importance of continuous surveillance in both veterinary and human health practices to prevent and manage severe infections.
Bacterial Identification and Its Importance in Clinical Settings
The identification of bacteria, such as the newly discovered Emayella augustorita, plays a critical role in clinical microbiology and infectious disease management. Accurate and timely identification can lead to improved treatment strategies and a better understanding of the disease mechanisms associated with various pathogens. Especially in the context of sepsis, where rapid intervention can be the difference between life and death, knowing the specific causative agent allows for targeted therapy.
Failure to identify emerging bacteria can result in misdiagnoses, inappropriate treatments, and worse patient outcomes. The case of E. augustorita emphasizes the significance of advancing diagnostic methods and maintaining a dedicated effort to catalog the microbial diversity that exists within our environment, including within domestic animals like cats and dogs.
Emayella augustus: A Connection to Local Heritage and Culture
The choice of name for Emayella augustorita reflects a deep connection to the cultural heritage of Limoges, France, where the bacterium was discovered. Named after the term for enamel, ‘Emayella’ serves as a reminder of the region’s artistic legacy that dates back to the Middle Ages. An understanding of local heritage enriches the scientific narrative surrounding bacterial discoveries and emphasizes the role of culture in shaping scientific endeavors.
Furthermore, the tribute paid to Emperor Augustus and the historical context surrounding the name add layers of significance to the bacterial identification. This aspect of naming not only embodies scientific progress but also maintains a link to the history and identity of the locale, reinforcing the idea that science and culture can intersect in meaningful ways.
Future Directions in Research on Emayella augustorita
The introduction of Emayella augustorita serves as a pivotal point for future research in microbiology and infectious disease. With this new bacterial species, scientists are presented with numerous avenues for investigation, including studying its metabolic pathways, virulence factors, and interactions with various hosts. Research on E. augustorita could lead to groundbreaking findings that may illustrate new pathways in the treatment of bacterial infections, particularly in susceptible populations.
Moreover, as the microbial landscape becomes increasingly complex with the continual discovery of novel species, focus should be directed toward understanding how such bacteria evolve and adapt within their environments. Continued research efforts may support the development of innovative diagnostic technologies and therapeutic modalities, ensuring that emerging pathogens are met with effective countermeasures.
Implications of Emayella augustorita on Antibiotic Stewardship
The discovery of new bacterial species such as Emayella augustorita reinforces the critical need for effective antibiotic stewardship in both human and veterinary medicine. As gram-negative bacteria exhibit varying levels of resistance to existing antibiotics, understanding the characteristics of newly identified organisms is essential. This knowledge helps inform appropriate antibiotic selection and resistance management strategies.
Addressing the challenges posed by bacteria like E. augustorita will require concerted efforts in surveillance, research, and development of new antimicrobial agents. The rise of multidrug-resistant bacteria highlights the urgent need for a proactive approach in combating bacterial infections, ensuring that future healthcare practices are equipped to handle evolving microbial threats.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Emayella augustorita and how was it discovered?
Emayella augustorita is a newly classified species of gram-negative bacteria from the Pasteurellaceae family. Discovered in 2024 by Sylvain Meyer and his team, this novel bacterium was isolated from blood cultures of a female patient who developed sepsis due to an infected metallic biliary stent. It is often found in the oral cavities and upper respiratory tracts of cats and dogs as a commensal organism.
What role does Emayella augustorita play in animal health?
Emayella augustorita, being a gram-negative bacterium, is commonly found in cats and dogs. While it usually exists as a commensal organism, it can be associated with infections in case of compromised health. Understanding its role is crucial as it may also play a part in cases of sepsis when it enters the bloodstream.
Is Emayella augustorita harmful to humans or pets?
Emayella augustorita is primarily a commensal bacterium in cats and dogs. However, it can become pathogenic and lead to sepsis in humans when it infects the bloodstream, particularly in medically compromised individuals. Therefore, while it poses a risk, it largely depends on the health status of the affected individual.
What are the characteristics of Emayella augustorita?
Emayella augustorita is a rod-shaped, fermentative, gram-negative bacterium belonging to the Pasteurellaceae family. It exhibits typical characteristics of commensal bacteria found in the oral cavities of cats and dogs, but it can cause serious infections like sepsis if introduced into the bloodstream.
How does Emayella augustorita relate to sepsis in humans?
Emayella augustorita was identified in a human patient who developed sepsis, highlighting its potential as a pathogen under certain conditions. While typically non-pathogenic in cats and dogs, if it enters the bloodstream, it can contribute to severe infections and sepsis, particularly in individuals with weakened immune systems.
What does the name Emayella augustorita mean?
The genus name ‘Emayella’ refers to enamel in Latin, honoring Limoges’ rich artistic heritage in enamel-painted metalwork. The species name ‘augustorita’ pays tribute to Emperor Augustus and references the historical foundation of Limoges, emphasizing the cultural significance of the discovery.
Where was Emayella augustorita discovered?
Emayella augustorita was discovered in France by a team from the University of Limoges. The bacterium was isolated from blood cultures of a woman suffering from sepsis, showcasing its clinical relevance and potential impact on human health.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Introduction of Emayella augustorita | A new bacterial genus and species introduced in 2024 by Sylvain Meyer and his team at the University of Limoges. |
| Classification | Belongs to the Pasteurellaceae family, identified as a fermentative, gram-negative organism. |
| Natural Habitat | Found as a commensal in the oral cavities and upper respiratory tracts of cats and dogs. |
| Clinical Significance | Isolated from blood cultures in a case of sepsis linked to an infected metallic biliary stent. |
| Etymology | “Emayella” means enamel in Latin, reflecting Limoges’s heritage of enamel-painted metalwork. |
| Historical Context | The name honors Emperor Augustus and references the city’s historical significance dating back to Roman times. |
Summary
Emayella augustorita is an important new discovery in microbiology, representing a significant addition to the understanding of bacteria within the Pasteurellaceae family. This newly identified bacterium not only has clinical implications, particularly in cases of sepsis, but also connects deeply with the cultural and historical narrative of Limoges, France, enriching our appreciation for the interplay of science and heritage.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.