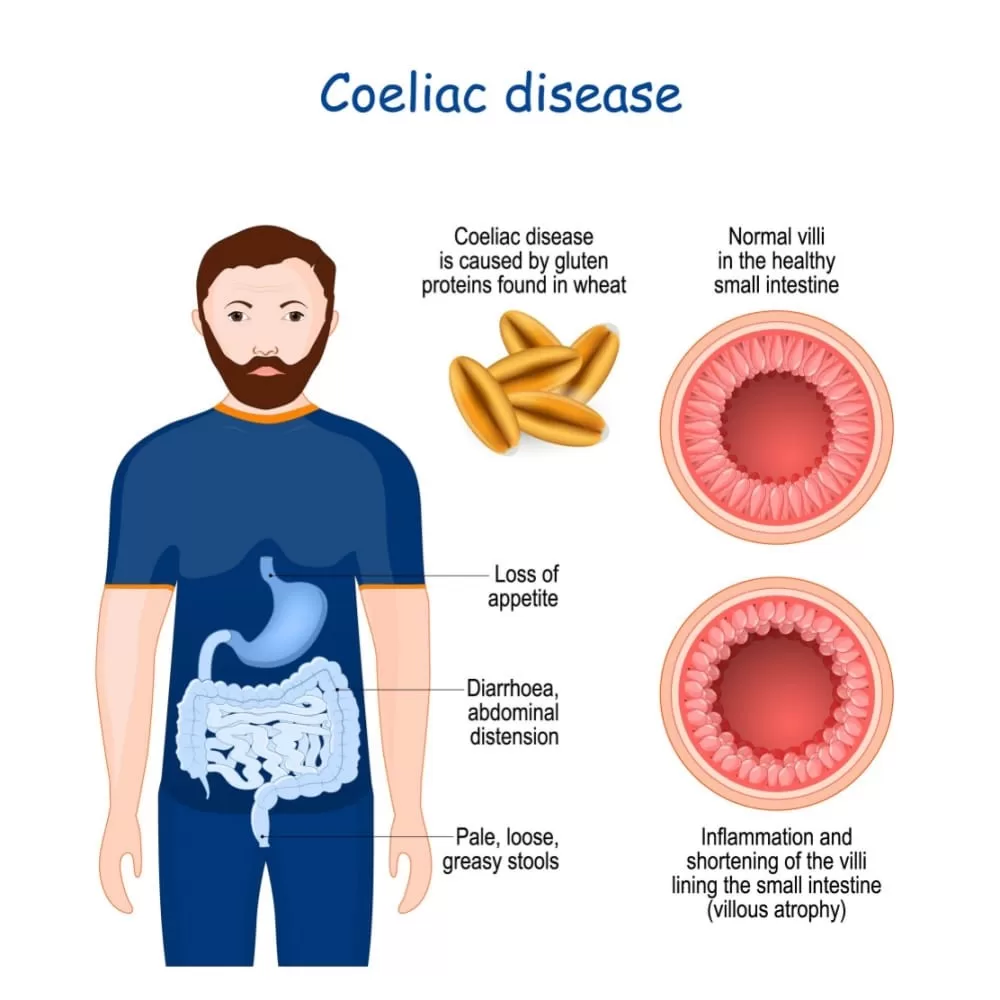
Coeliac disease is a serious autoimmune condition that arises in response to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. Individuals diagnosed with coeliac disease experience a range of symptoms that can severely impact their health, including chronic diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fatigue. Understanding the differences between coeliac disease and gluten sensitivity is crucial, as both conditions involve a negative reaction to gluten, but exhibit different health implications and management strategies. This condition requires a strict gluten-free diet to avoid further complications, making awareness of gluten intolerance all the more vital. In this article, we will delve into the symptoms of coeliac disease, compare it to gluten sensitivity, and explore the critical reasons for following a gluten-free lifestyle.
Celiac disease, frequently known as gluten intolerance and often confused with gluten sensitivity, is an autoimmune disorder triggered by gluten consumption. While gluten sensitivity may cause discomfort and gastrointestinal issues, celiac disease leads to serious long-term health risks due to the body’s immune response against gluten. Distinguishing the difference between coeliac disease and gluten sensitivity is imperative for proper diagnosis and management. Symptoms can overlap, making it challenging for individuals to self-diagnose without professional help. This informative piece aims to clarify these terms and provide insight into effective dietary changes necessary for those affected.
Understanding the Differences Between Coeliac Disease and Gluten Sensitivity
Coeliac disease and non-coeliac gluten sensitivity (NCGS) are often confused due to their overlapping symptoms and shared trigger: gluten. However, understanding their distinctions is crucial for effective management. Coeliac disease is an autoimmune condition that leads to an damaging immune response against gluten, primarily found in grains such as wheat, barley, and rye. Conversely, gluten sensitivity lacks this autoimmune aspect; individuals experience discomfort and various symptoms without the immune response or intestinal damage characteristic of coeliac disease.
The primary difference lies in the body’s reaction to gluten. Coeliac disease leads to severe inflammation of the intestinal lining, resulting in malabsorption of nutrients, which can cause long-term health complications. On the other hand, gluten sensitivity, while uncomfortable, does not lead to chronic damage of the intestinal lining and can be managed through dietary adjustments without severe consequences. Identifying whether an individual has coeliac disease or gluten sensitivity begins with understanding these fundamental differences.
Symptoms of Coeliac Disease
Individuals with coeliac disease exhibit a wide range of symptoms, which can vary significantly from person to person. Common manifestations include gastrointestinal issues like chronic diarrhea or constipation, abdominal pain, and bloating. Additionally, coeliac disease may lead to systemic symptoms such as fatigue, anemia, and even skin disorders like dermatitis herpetiformis. These symptoms often become apparent after the consumption of gluten-containing foods, making it imperative to recognize the pattern.
In children, symptoms can also include delayed growth and development, which can result in serious health implications if coeliac disease goes undiagnosed. Due to the variability in symptoms and their overlap with other gastrointestinal disorders, it is crucial for individuals experiencing these signs to seek medical advice. A proper diagnosis through clinical testing and history assessment is essential to initiate the appropriate gluten-free diet for effective management.
Symptoms of Gluten Sensitivity
Gluten sensitivity presents with an array of symptoms that can often resemble those of coeliac disease but typically do not result in permanent intestinal damage. Individuals may experience bloating, gas, abdominal discomfort, fatigue, and even mood disturbances like brain fog. It’s worth noting that these symptoms can fluctuate in intensity and may vary based on the amount of gluten consumed, indicating a more subjective reaction compared to the autoimmune response seen in coeliac disease.
Additionally, gluten sensitivity is often characterized by the resolution of symptoms once gluten is eliminated from the diet. Unlike coeliac disease, where definitive testing can confirm the diagnosis, gluten sensitivity often hinges on the careful observation of symptom patterns during dietary changes. This makes the management of gluten sensitivity more reliant on personalized dietary approaches, which can lead to significant improvements in quality of life.
Diagnosis of Coeliac Disease vs Gluten Sensitivity
Diagnosing coeliac disease involves a systematic approach, typically starting with blood tests that check for specific autoantibodies like tissue transglutaminase antibodies. If these tests indicate coeliac disease, an endoscopy may be necessary to assess the extent of damage to the small intestine. This structured diagnostic process is critical to ensure that individuals receive the appropriate medical care and dietary guidelines.
In contrast, gluten sensitivity does not have a standardized testing protocol. Diagnosing this condition often requires a process of elimination, where coeliac disease and wheat allergies are ruled out. Once other conditions are excluded, the health care provider may recommend an elimination diet followed by a gradual reintroduction of gluten to monitor symptom resolution. The subjective nature of gluten sensitivity poses unique challenges for diagnosis, making a collaborative approach between patients and healthcare providers vital for effective management.
The Importance of a Gluten-Free Diet
For individuals with either coeliac disease or gluten sensitivity, adhering to a gluten-free diet is paramount. In coeliac disease, even trace amounts of gluten can trigger severe immune reactions, leading to inflammation and intestinal damage. Thus, eliminating all gluten-containing foods from the diet is essential to prevent complications, including malnutrition and associated health risks such as osteoporosis and certain cancers.
On the other hand, for those with gluten sensitivity, while complete avoidance of gluten can lead to significant symptom relief and improved quality of life, some individuals may find they can tolerate small amounts without severe repercussions. Regardless, a gluten-free diet emphasizing whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, and proteins remains beneficial for both conditions. Learning to navigate food labels and seeking guidance from nutrition professionals can empower individuals to thrive on a gluten-free diet.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of coeliac disease?
The symptoms of coeliac disease can vary widely, but they often include chronic diarrhea, abdominal pain, bloating, fatigue, and weight loss. Skin rashes like dermatitis herpetiformis, anemia, and developmental delays in children are also common. If you suspect you have coeliac disease, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
What is the main difference between coeliac disease and gluten sensitivity?
Coeliac disease is an autoimmune disorder triggered by gluten that causes damage to the small intestine, whereas gluten sensitivity does not involve the immune system and typically does not cause lasting intestinal damage. Symptoms of both conditions can overlap, but they require different management approaches, predominantly a strict gluten-free diet for coeliac disease.
How is coeliac disease diagnosed compared to gluten sensitivity?
To diagnose coeliac disease, blood tests for specific antibodies followed by a small intestine biopsy are typically performed. In contrast, gluten sensitivity diagnosis is often based on the elimination of gluten from the diet and monitoring symptom improvement, as there are currently no standardized tests for gluten sensitivity.
Can a gluten-free diet help with symptoms of coeliac disease?
Yes, a strict gluten-free diet is crucial for managing coeliac disease, as even small amounts of gluten can trigger serious symptoms and intestinal damage. Following this diet allows individuals with coeliac disease to heal their intestines and prevents long-term health complications.
Is there a link between coeliac disease and gluten intolerance?
Yes, both coeliac disease and gluten intolerance involve adverse reactions to gluten. However, coeliac disease is characterized by an autoimmune response and potential damage to the intestines, while gluten intolerance (or sensitivity) does not cause such harm. It’s important to differentiate between them for appropriate treatment.
| Key Point | Coeliac Disease | Gluten Sensitivity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Chronic autoimmune disorder affecting the small intestine due to gluten intake | Non-autoimmune condition where symptoms arise after gluten consumption |
| Symptoms | Chronic diarrhea, bloating, weight loss, anemia, fatigue, skin rashes | Bloating, abdominal discomfort, fatigue, headaches, mood changes |
| Diagnosis | Blood tests for antibodies and intestinal biopsy for confirmation | Elimination diet after ruling out coeliac disease and wheat allergy |
| Long-term Complications | Increased risk of osteoporosis, infertility, certain cancers | Not associated with long-term health risks, but requires dietary management |
| Dietary Management | Strict gluten-free diet is essential; even small amounts can cause severe issues | Many can tolerate small amounts of gluten; a gluten-free diet alleviates symptoms |
Summary
Coeliac disease is a chronic autoimmune disorder that necessitates a complete avoidance of gluten due to severe health risks. Understanding coeliac disease is essential because it presents unique challenges in terms of diagnosis, symptoms, and dietary management compared to gluten sensitivity, which does not trigger the same autoimmune response or long-term health implications. Those affected by either condition should consult healthcare professionals for accurate diagnosis and dietary guidance. A gluten-free diet is the cornerstone in managing both conditions and can greatly enhance quality of life.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.