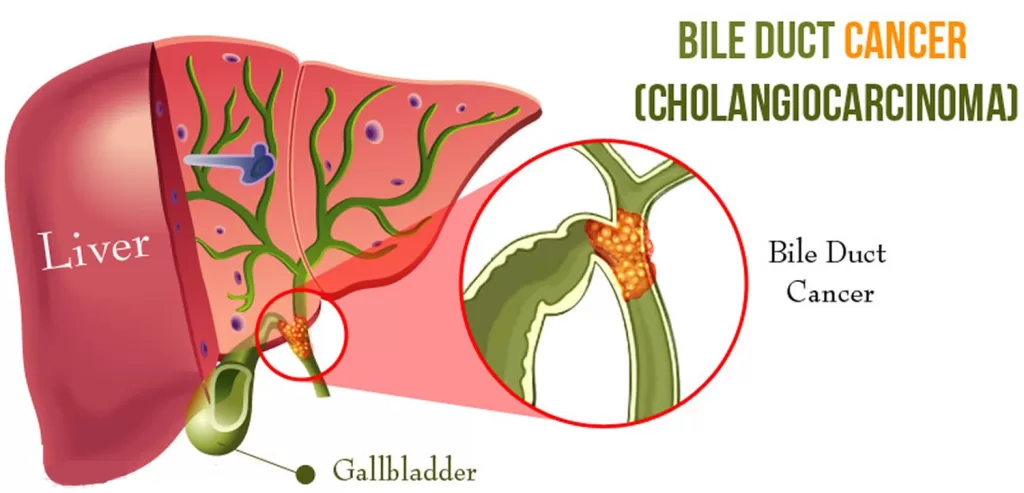
Cholangiocarcinoma, commonly referred to as bile duct cancer, presents a significant challenge in the field of oncology due to its aggressive nature and late-stage diagnosis. This rare malignancy originates in the bile ducts, which are crucial for transporting bile from the liver to the gallbladder. Patients often experience vague symptoms, making early detection difficult and contributing to a grim bile duct cancer prognosis. Current treatment options for cholangiocarcinoma vary greatly depending on the stage of the disease, highlighting the need for ongoing cholangiocarcinoma research to develop more effective therapies. By understanding cholangiocarcinoma symptoms and raising awareness, we can improve patient outcomes and encourage timely medical intervention.
Bile duct carcinoma, also known as cholangiocarcinoma, is a malignant tumor that arises within the biliary tract. This cancer primarily affects the ductal structures that transport bile, leading to significant complications if not diagnosed early. The disease can manifest in various forms, including intrahepatic and extrahepatic types, each presenting unique challenges for treatment. The pursuit of novel therapeutic strategies and a deeper understanding of cholangiocarcinoma biology remains critical as researchers strive to improve both survival rates and quality of life for affected individuals. Heightened awareness of bile duct cancer and its symptoms can play a pivotal role in facilitating earlier diagnosis and better treatment outcomes.
Understanding Cholangiocarcinoma: The Basics
Cholangiocarcinoma, or bile duct cancer, is a rare yet aggressive malignancy that arises in the bile ducts, which are essential for transporting bile from the liver. This cancer is categorized into three main types: intrahepatic, extrahepatic, and hilar cholangiocarcinoma, each differing in their location and implications for treatment. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma occurs within the liver, while extrahepatic types arise outside the liver. Hilar cholangiocarcinoma is particularly challenging due to its location at the convergence of the bile ducts, affecting surgical options and prognosis. Understanding these classifications is vital for patients and healthcare providers as they influence the treatment strategies employed and can significantly alter patient outcomes.
One of the major challenges in diagnosing cholangiocarcinoma is the absence of specific symptoms in its early stages. Patients often present with vague signs, such as fatigue, weight loss, and jaundice, which can be easily attributed to other conditions. This lack of clear symptoms leads to late-stage diagnoses, where treatment options may be limited and prognosis poor. Therefore, increasing awareness about the disease’s symptoms and risk factors is crucial for early detection and intervention.
Cholangiocarcinoma Symptoms: Recognizing the Red Flags
Identifying the symptoms of cholangiocarcinoma can be difficult, as many signs mimic other gastrointestinal disorders. Common symptoms include jaundice, which is characterized by yellowing of the skin and eyes, dark urine, clay-colored stools, and severe itching. Abdominal pain, particularly in the upper right quadrant, unexplained weight loss, and fatigue are also prevalent. Awareness of these symptoms is vital for prompt medical evaluation, as early detection can significantly improve treatment outcomes.
Moreover, because many patients are initially misdiagnosed with less serious conditions, it is imperative for healthcare providers to maintain a high index of suspicion when patients present with these symptoms, especially those with risk factors such as liver disease or a history of bile duct problems. Community education and advocacy efforts can play a key role in empowering patients to seek medical advice sooner, potentially leading to early-stage diagnoses and better survival rates.
Cholangiocarcinoma Treatment Options: A Comprehensive Approach
The treatment landscape for cholangiocarcinoma is complex and varies significantly based on the cancer’s stage and location. Surgical resection remains the most effective treatment for early-stage cholangiocarcinoma, with the possibility of achieving long-term survival if the cancer is completely removed. For patients with advanced disease, chemotherapy and targeted therapies become crucial components of management. Chemotherapy is often used to control symptoms and prolong life when surgery is not an option.
In addition to traditional therapies, ongoing research into novel treatment modalities, including immunotherapy and personalized medicine based on genetic profiling, is showing promise. Clinical trials are increasingly exploring new combinations of existing drugs, aiming to overcome the cancer’s resistance to standard treatments. As research progresses, there is hope for improved therapeutic strategies and ultimately better outcomes for patients diagnosed with cholangiocarcinoma.
Prognosis for Cholangiocarcinoma: What Patients Need to Know
The prognosis for cholangiocarcinoma is often disheartening, with five-year survival rates typically below 20%. Factors influencing prognosis include the cancer’s stage at diagnosis, the patient’s overall health, and the presence of comorbid conditions. Unfortunately, most patients are diagnosed at an advanced stage, which severely limits treatment options and negatively impacts survival.
Understanding these statistics can help patients and their families make informed decisions regarding treatment options and palliative care. Engaging in discussions with healthcare providers about prognosis can also facilitate personalized care plans that align with patients’ values and goals. Additionally, support groups and counseling can play a vital role in helping patients cope with the emotional and psychological challenges of a cholangiocarcinoma diagnosis.
Advancements in Cholangiocarcinoma Research: The Path Forward
Recent advancements in cholangiocarcinoma research are paving the way for innovative treatment strategies and improved understanding of the disease’s biology. Researchers are focusing on identifying specific genetic mutations associated with cholangiocarcinoma, which may lead to targeted therapies that can significantly enhance treatment efficacy while reducing side effects. This personalized approach aims to tailor treatments based on individual patient profiles, moving beyond one-size-fits-all solutions.
Additionally, ongoing clinical trials are crucial for developing new drugs and combinations of existing therapies. These studies not only contribute to advancing treatment options but also provide hope for patients who currently have limited choices. Continued investment in cholangiocarcinoma research is essential to uncovering the complexities of this cancer and ultimately improving survival rates and quality of life for those affected.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of cholangiocarcinoma (bile duct cancer)?
Cholangiocarcinoma symptoms can be vague and non-specific, often leading to late diagnosis. Common symptoms include jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), dark urine, clay-colored stools, itching skin, abdominal pain or swelling, unexplained weight loss, and fatigue. Early recognition of these symptoms is crucial for timely intervention.
What treatment options are available for cholangiocarcinoma?
Cholangiocarcinoma treatment varies based on the cancer’s stage. Options include surgery, which is most effective for early-stage patients, chemotherapy for advanced cases, and targeted therapies tailored to specific genetic markers. Ongoing research aims to develop innovative treatments to improve efficacy and survival rates.
What is the prognosis for patients diagnosed with cholangiocarcinoma?
The prognosis for cholangiocarcinoma, or bile duct cancer, tends to be poor, with a five-year survival rate under 20%. This statistic highlights the challenges of late-stage diagnosis, emphasizing the importance of early detection and intervention for better outcomes.
How can awareness and education improve outcomes for cholangiocarcinoma patients?
Raising awareness about cholangiocarcinoma is vital because many patients experience vague symptoms until advanced stages. Education about common symptoms can lead to earlier diagnosis and treatment, ultimately improving survival rates. Community support and resources play a significant role in this effort.
What recent research developments are being made in cholangiocarcinoma?
Recent cholangiocarcinoma research focuses on innovative treatments and understanding the cancer’s biology. Clinical trials are investigating new drugs and combinations of therapies to combat the cancer’s resistance to standard treatments. These advancements are crucial for improving prognosis and patient quality of life.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) is bile duct cancer, characterized by its aggressive nature and complex diagnosis. |
| Types | 1. Intrahepatic – inside the liver. 2. Extrahepatic – outside the liver. 3. Hilar – at the bile duct junction. |
| Awareness | Personal stories, such as those of Sian Ashcroft and Dave Bundy, have heightened awareness and the need for early detection. |
| Prognosis | The five-year survival rate is below 20%, often due to late-stage diagnosis. |
| Treatment Options | 1. Surgery – best for early-stage. 2. Chemotherapy – for advanced stages or post-surgery. 3. Targeted therapies – based on genetic markers. |
| Symptoms | Common symptoms include jaundice, dark urine, abdominal pain, weight loss, and fatigue. |
Summary
Cholangiocarcinoma is a formidable form of bile duct cancer that poses significant challenges in early detection and treatment. This aggressive cancer often presents with vague symptoms, which can lead to late-stage diagnoses and a poor prognosis. Recent insights into the nature of cholangiocarcinoma highlight the importance of awareness and education, especially through personal stories that resonate deeply with communities. Efforts to raise awareness about cholangiocarcinoma are critical, as they can encourage individuals to seek medical advice sooner, ultimately improving survival rates. Continued research into innovative treatment options and better understanding of this disease remains essential for enhancing patient outcomes.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.