Childhood vaccine uptake, particularly among US kindergarteners, has seen a concerning decline, plummeting to less than 93% in the 2023-24 school year from 95% just a few years prior. This trend raises alarms as vaccination rates for essential immunizations, such as the MMR vaccine, dip below critical thresholds necessary for herd immunity. Concurrently, vaccine exemptions have surged to an unprecedented 3.3%, reflecting shifting attitudes towards vaccination. According to a recent CDC vaccination report, these changes in vaccine coverage could be linked to broader public hesitance stemming from debates around COVID-19 vaccinations. As more families opt for exemptions, the risk of infectious outbreaks looms, threatening the health and safety of children and communities alike.
The decrease in adolescent immunizations signals a pivotal moment in public health, highlighting the pressing need to address kindergarten vaccination trends. Vaccine compliance rates are not just figures; they represent the community’s commitment to safeguarding children against preventable diseases. With rising vaccine hesitancy and increasing exemption requests, many children are at risk of not receiving crucial immunizations like the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine. Consequently, public health initiatives must focus on maintaining school vaccination standards and educating parents about the broader implications of skewed vaccination practices. Ensuring all children are vaccinated on time is essential for preserving public health and preventing future epidemics.
Declining Childhood Vaccine Uptake Among Kindergarteners
The latest report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) indicates a concerning trend in childhood vaccine uptake among kindergarteners across the United States. For the 2023-24 school year, vaccination rates have dropped to below 93%, reflecting a decrease from 95% during the 2019-20 school year and 93% in the previous year. This decline is significant given the importance of maintaining high vaccination rates to prevent outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases. The Children’s vaccination rates not only impact individual health but also play a critical role in community immunity, safeguarding vulnerable populations who cannot be vaccinated.
Alongside the decline in vaccination rates, the data shows an alarming rise in exemptions, which have reached a record high of 3.3%. This increase in exemptions, combined with the drop in childhood vaccine uptake, poses a serious threat to the goal of achieving the Healthy People 2030 target of 95% vaccination coverage among kindergarteners. Without swift action to address these trends, we risk potential outbreaks of diseases that were previously under control, highlighting the urgency of addressing vaccination hesitancy and advocating for increased participation in vaccination programs.
Factors Contributing to Vaccine Uptake Decline
Several factors may be contributing to the declining vaccination rates among kindergarteners. One proposed explanation relates to changing attitudes towards vaccines, possibly influenced by hesitancy surrounding COVID-19 vaccination mandates that have been prevalent in recent years. Many parents who had reservations or strong objections to COVID-19 vaccines may transfer these sentiments to routine childhood vaccinations, resulting in increased exemptions and lower compliance. This interconnectedness suggests that efforts to improve vaccination rates must also include addressing misconceptions and building trust in the broader immunization system.
In addition, the rise in nonmedical exemptions, which now account for over 93% of all exemptions, indicates a shift in how parents perceive vaccination requirements. Exemptions for personal beliefs are rising in many states, and with 14 states reporting over 5% of kindergartners having exemptions for at least one vaccine, public health officials are facing a growing challenge. Education and awareness campaigns are increasingly essential to counteract misinformation and promote the proven benefits of vaccinations, emphasizing the safety and efficacy of vaccines in preventing serious diseases such as measles, mumps, and rubella.
Impact of Vaccine Exemptions on Public Health
The recent data showcasing the increase in vaccination exemptions is particularly troubling for public health authorities. With 4.0% of kindergarteners statewide remaining neither fully vaccinated nor exempt, the potential for outbreaks of diseases like measles is concerning. As vaccination coverage dips below necessary thresholds, communities risk losing herd immunity, which protects those who are most vulnerable, including infants too young to be vaccinated and individuals with compromised immune systems. Moreover, areas where exemptions exceed 5% are now unable to achieve the protected vaccination level even if all non-exempt children are vaccinated, a statistic that should alarm health stakeholders.
Furthermore, the long-term implications of lower vaccination rates and higher exemption rates can hinder progress made over years in preventing outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases. Public health officials must strategically approach this issue by enhancing communication with parents and communities about the importance of vaccinations. By leveraging school-based clinics and outreach programs, there is potential to reverse the upward trend in exemptions and enhance kindergarten vaccination compliance, which will bolster public health and safety.
Strategies to Increase Vaccination Rates
In order to address the decline in childhood vaccine uptake, various strategies can be implemented to bolster vaccination rates among kindergarteners. Research indicates that enforcing school vaccination requirements is one of the most effective measures. Schools can serve as vital resources by offering vaccination clinics that make it easier for parents to access needed vaccines. Additionally, using reminders and recalls can also nudge families toward ensuring their children are up-to-date with their immunizations. Health providers are encouraged to deliver strong recommendations about the importance of vaccinations, as parents often rely heavily on doctors for health-related decisions.
Education plays a critical role in increasing awareness about vaccination benefits as well. Healthcare providers should proactively address parents’ concerns about vaccine safety and misinformation regarding side effects or necessity. By emphasizing the long-term health benefits of vaccinations not just for the individual child, but for the broader community, providers can help foster a culture of compliance. Collaborative efforts between health departments and schools are vital in sharing vaccination data and working with families to mitigate challenges that lead to vaccine exemptions, ultimately connecting families with the vital resources they need.
The Role of Healthcare Providers in Vaccination
Healthcare providers are essential in promoting childhood vaccines, particularly the critical vaccines required for school enrollment. Their role extends beyond just administering vaccines; they must also engage in dialogue with parents about the importance of vaccination. Evidence shows that strong provider recommendations significantly influence a parent’s decision to vaccinate their child. Therefore, educating healthcare professionals on how to effectively communicate vaccine safety and efficacy to parents can have a lasting impact on vaccine uptake.
Moreover, providers can conduct follow-ups with under-vaccinated families, reminding them of the health risks associated with incomplete vaccination schedules. Offering additional resources or support can ease any parental concerns a parent may have. Collaborating with local health departments, providers can help implement community-specific solutions to vaccine hesitancy and ultimately drive higher vaccination rates among populations that may otherwise remain at risk.
Review of Kindergarten Vaccination Trends
Analyzing trends over recent years, it is evident that kindergarten vaccination rates have experienced notable fluctuations. Reports have consistently indicated a downward trend in childhood vaccine uptake; from a high of 95% coverage in 2019-20 to a concerning low of under 93% for the current school year. This is a stark reminder of the fragility of established immunization programs and the work still needed to maintain public trust in vaccines as a critical component of children’s health.
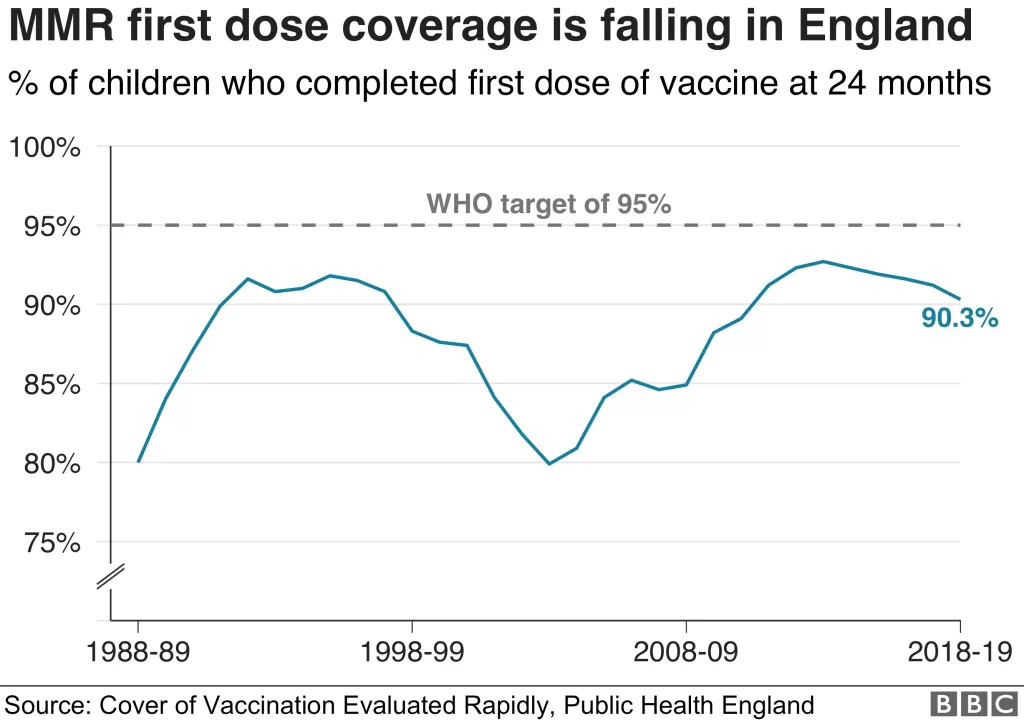
Additionally, data reveals that MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella) vaccine uptake fell particularly short in the past year, averaging only 92.7%, with states ranging from as low as 79.6% to as high as 98.3%. Such disparities showcase the importance of local insights into vaccination trends ensuring targeted interventions. Continuous monitoring and reporting, similar to the CDC vaccination report, are essential tools for public health strategies aimed at elevating overall kindergarten vaccination rates and preventing possible disease outbreaks.
Challenges in Achieving Pediatric Vaccine Coverage
For the public health community, maintaining or increasing pediatric vaccine coverage can be quite challenging. With the data revealing decreases in vaccination rates, public health campaigns must work to understand the underlying causes of hesitancy and resistance. One major obstacle includes the perception of vaccine safety and effectiveness, particularly stemming from the misinformation that has thrived online. Educating the public on the rigorous testing and monitoring of vaccine safety is a major priority.
Moreover, navigating the landscape of vaccine exemptions is equally challenging. As the rise in exemptions indicates a shift in public sentiment, strategies must be tailored to address the specific concerns behind these exemptions effectively. This may involve varying approaches based on geographic and demographic factors to resonate with varying communities, thus closing the gaps in knowledge and health access related to vaccination.
Future Implications for Childhood Vaccination Programs
The implications of declining vaccination rates and increasing exemptions for childhood vaccinations are significant and require urgent attention from stakeholders across the educational and health sectors. Failing to curb this downward trend may not only lead to outbreaks of preventable diseases but also undermine the overall health of future generations. Therefore, it is crucial to invest in proactive measures to enhance community education about the importance of vaccines, utilizing data and personal stories to humanize the issue.
Additionally, policymakers must consider legislative measures to support schools in enforcing immunization requirements while also addressing the underlying factors contributing to vaccine hesitancy. Strengthening partnerships between health departments, schools, and families could drive awareness campaigns that reiterate the necessity of vaccines for public health, ensuring children receive the protection they need to thrive in healthy environments.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the current trends in childhood vaccine uptake for kindergarteners in the US?
As of the 2023-24 school year, childhood vaccine uptake among US kindergarteners has declined to below 93%, sitting at approximately 92.7% for MMR, 92.3% for DTaP, and 92.6% for polio vaccines. This marks a decrease from 95% in 2019-20 and 93% in the previous year, indicating a concerning trend towards lower vaccination rates.
How do vaccination rates among kindergarteners affect public health?
The decline in vaccination rates among kindergarteners can jeopardize herd immunity, increasing the risk of outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases like measles. With 4.0% of kindergarteners neither fully vaccinated or exempt, these lowered rates threaten to hinder reaching the Healthy People 2030 target of 95% coverage.
What factors have contributed to the decline in childhood vaccine uptake?
The decline in childhood vaccine uptake may be linked to shifts in public attitudes towards vaccination stemming from hesitancy experienced during the COVID-19 pandemic. Additionally, the rise in vaccine exemptions from 3.0% to 3.3% indicates growing skepticism around vaccine requirements and overall public health policies.
Why are vaccine exemptions increasing among kindergarteners?
Vaccine exemptions have increased due to both medical and nonmedical reasons, with nonmedical exemptions accounting for the vast majority. In the 2023-24 school year, 3.1% of kindergartners had nonmedical exemptions, suggesting a growing reluctance among parents to adhere to vaccination requirements.
What role does the CDC play in monitoring childhood vaccine uptake?
The CDC is responsible for gathering and reporting national vaccination data, like the ones found in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR). Their reports indicate trends in childhood vaccine uptake and highlight states where vaccination rates are falling below recommended levels.
How can schools improve kindergarten vaccination rates?
Schools can improve kindergarten vaccination rates by enforcing vaccination requirements, hosting school-based vaccination clinics, and providing reminders to parents. Additionally, sharing vaccination and exemption data with parents and educating them about the importance of vaccination can further boost uptake.
What vaccines are routinely required for kindergarten entry?
Routine vaccines that are typically required for kindergarten entry include the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine, DTaP vaccine for diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis, the polio vaccine, and the varicella (chickenpox) vaccine.
How does the uptake of the MMR vaccine impact overall childhood vaccination rates?
The MMR vaccine uptake is critical to overall childhood vaccination rates, as it reflects the public’s compliance with key vaccine protocols. With current two-dose MMR coverage at 92.7%, any decline directly affects achieving broader public health goals and maintaining herd immunity against measles outbreaks.
What are the risks associated with delayed or incomplete vaccination in children?
Delayed or incomplete vaccination can leave children vulnerable to serious illnesses such as measles, which can lead to complications, hospitalization, or even death. It also poses community risks, as low vaccination rates increase the potential for disease outbreaks.
What strategies have been suggested to counteract the decline in vaccine uptake?
Strategies to counteract the decline in childhood vaccine uptake include robust enforcement of school vaccination requirements, establishing school-based vaccination clinics, enhancing provider communication about the safety and effectiveness of vaccines, and implementing follow-ups for undervaccinated students.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Decline in Vaccination Rates | Routine childhood vaccine uptake among kindergarteners dropped to less than 93% in 2023-24, down from 95% in 2019-20. |
| Increase in Exemptions | Exemptions rose to a record 3.3% in 2023-24, compared to 3.0% in 2022-23. |
| Major Vaccines Affecting Uptake | Vaccine uptake dropped across four main vaccines: MMR, DTaP, polio, and VAR, with coverage ranging between 92.3% and 92.7%. |
| Geographic Disparities | MMR coverage varied from 79.6% in Idaho to 98.3% in West Virginia, showing significant regional differences in vaccination rates. |
| Potential Risks | Approximately 280,000 kindergarteners were unvaccinated for MMR, putting them at risk for measles. |
| Strategies to Improve Uptake | Enforcement of school vaccination requirements, strong provider recommendations, and school-based clinics were suggested to improve vaccine uptake. |
Summary
Childhood vaccine uptake has faced a concerning decline, with rates falling below 93% among US kindergarteners in the 2023-24 school year. This trend highlights potential shifts in public attitudes toward vaccinations, influenced perhaps by recent hesitancies surrounding COVID-19 vaccines. Given the crucial role that routine immunizations play in protecting public health, it is imperative to address these declines effectively. By implementing strategies such as enforcing vaccination requirements and enhancing educational outreach on vaccine safety, we can improve childhood vaccine uptake and safeguard the health of our communities.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.