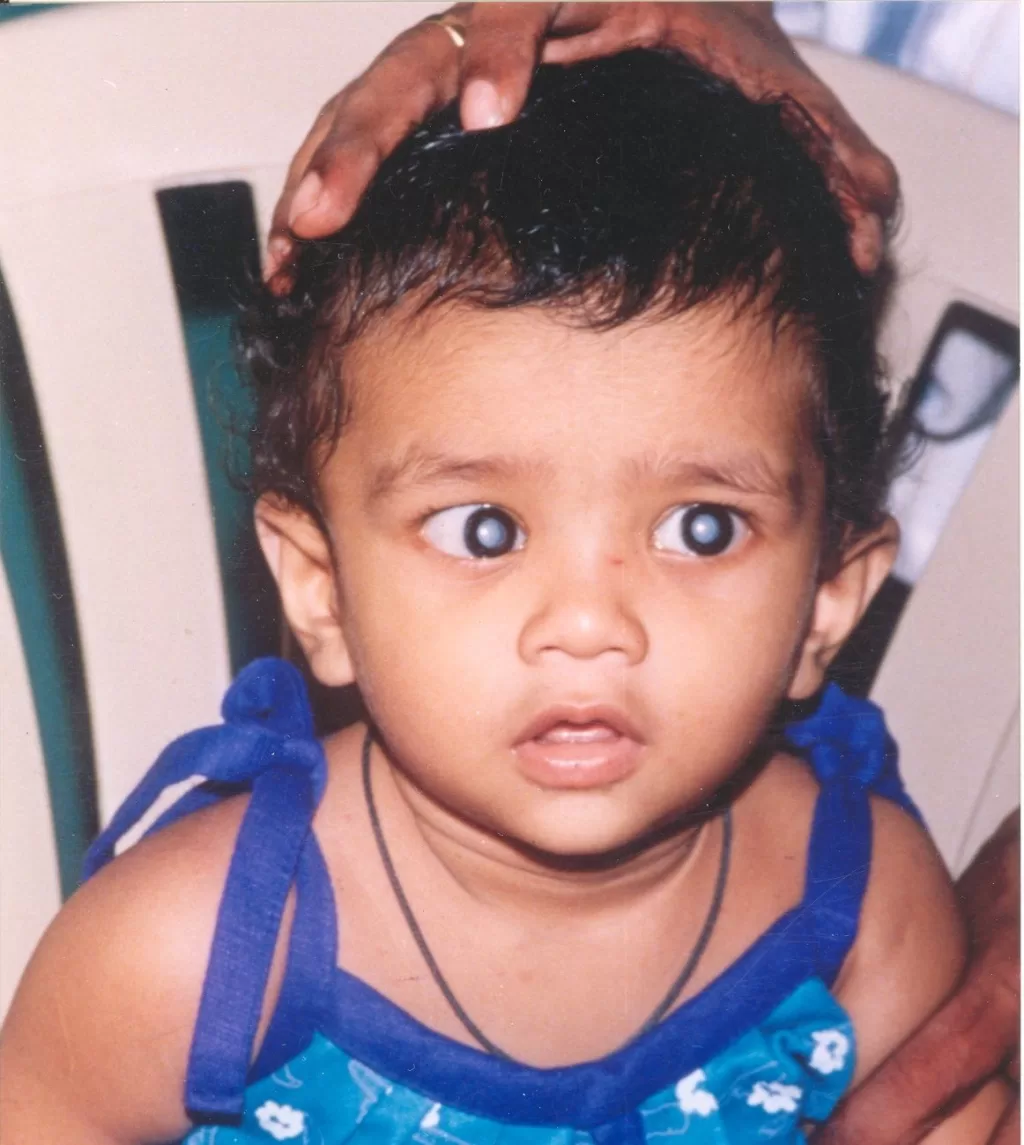
Childhood cataracts, a condition that can significantly impact a child’s visual development, deserve close attention from parents and caregivers. These cataracts can be congenital, meaning they are present at birth, or may develop within the first years of life. Addressing “Can childhood cataracts be cured?” reveals that surgical intervention is often necessary to ensure the best outcomes for young patients. In this article, we will delve into effective treatment for childhood cataracts, the critical importance of recognizing early signs of this condition, and the ongoing advancements contributing to pediatric eye health. By understanding the nuances of surgery for cataracts in children, families can better navigate the complexities of diagnosis and treatment.
When we discuss cataracts affecting young individuals, we are frequently referring to congenital cataracts, which can arise before or shortly after birth. Unlike typical cataracts that primarily affect older adults, these eye issues manifest in children and can lead to severe vision impairments if not promptly addressed. Parents are often left with questions about the various treatment options available, particularly the surgical methods involved, which can restore clear vision. As awareness grows regarding the early indicators of these eye conditions, such as cloudy vision and difficulty focusing, it becomes essential to prioritize pediatric eye health. By exploring these alternative terms, we can broaden the understanding of childhood cataracts and raise awareness about the urgent need for early diagnosis and intervention.
Early Signs of Childhood Cataracts: What to Look For
Detecting childhood cataracts early can be pivotal in ensuring proper treatment and maintaining a child’s vision. Parents and caregivers should be familiar with early signs such as cloudy or blurry vision, sensitivity to light, and difficulty seeing in dim lighting conditions. Other indicators include misalignment of the eyes (strabismus) and abnormal eye movements. Recognizing these signs promptly can facilitate timely medical intervention, making a substantial difference in treatment outcomes.
Additionally, pediatricians often perform routine eye exams during regular check-ups, which can help in identifying any potential issues before they become severe. Parents should advocate for comprehensive eye evaluations if they suspect any irregularities in their child’s vision. Early diagnosis and open communication with healthcare providers can lead to more favorable outcomes, emphasizing the critical role of awareness in pediatric eye health.
Surgical Treatment Options for Childhood Cataracts
The primary surgical intervention for childhood cataracts involves the removal of the cloudy lens to restore clear vision. Post-surgery, many cases require the implantation of an artificial intraocular lens, which can help improve visual clarity and development. The timing of the surgery is crucial; research indicates that early intervention can significantly reduce the risk of complications such as amblyopia, which can arise if treatment is delayed.
After the surgery, regular follow-ups with an ophthalmologist are essential to monitor the child’s recovery and address any potential issues. This includes checking for the proper positioning of the lens implant and assessing visual acuity. Parents are encouraged to stay educated on the various surgical techniques and potential outcomes, ensuring they make informed choices about their child’s eye health.
The Role of Education in Pediatric Eye Health
Education is a cornerstone in managing childhood cataracts and ensuring a healthy future for affected children. Parents should be informed about the condition and its implications. Community health programs can bolster this knowledge, teaching families about the signs and symptoms of cataracts and the importance of early detection. Workshops and seminars can empower parents, enabling them to take proactive steps concerning their child’s eye health.
Moreover, schools play an important role in promoting awareness about pediatric eye conditions. Educators can be trained to recognize visual difficulties in children and to communicate effectively with parents about seeking timely medical advice. This collaborative approach enhances community awareness, ensuring that children receive the necessary care and attention as early as possible.
Future Directions in Non-Surgical Treatments for Childhood Cataracts
While current standard therapies for childhood cataracts predominantly involve surgery, ongoing research is opening the door to potential non-surgical treatment options. Scientists are investigating the underlying causes of congenital cataracts, aiming to develop preventive strategies and alternative therapeutic methods. If successful, these advancements could reduce reliance on surgical intervention and improve the overall treatment landscape for childhood cataracts.
For instance, early genetic research may pave the way for targeted treatments that can address specific types of cataracts directly. Although this is still in the exploratory stages, continued funding and interest in pediatric eye health can lead to breakthroughs that enhance outcomes for children with cataracts. As more data becomes available, new therapies could emerge, fundamentally changing the approach to managing this condition.
Navigating Treatment Options: Insights for Parents
Navigating the treatment options for childhood cataracts can be overwhelming for parents. Understanding the recommended surgical procedures, potential risks, and recovery processes is essential for making informed decisions. Communication with healthcare professionals about concerns and expectations can significantly alleviate anxiety and foster a supportive environment for the child during treatment.
Moreover, understanding the long-term implications of cataract surgery, including follow-up care and vision monitoring, prepares parents to advocate effectively for their child’s eye health. It is important for families to stay involved in discussions surrounding treatment strategies, as collaborative decision-making can enhance the overall care experience and ensure better outcomes for children experiencing this condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the early signs of childhood cataracts?
The early signs of childhood cataracts often include cloudy or blurry vision, unusual eye movements, and difficulty seeing in bright light. Parents should observe their child for any signs of visual impairment and seek medical advice if they notice such changes.
What treatments are available for childhood cataracts?
Treatment for childhood cataracts primarily involves surgical intervention to remove the cloudy lens and possibly implant an artificial lens. Early surgery is crucial to prevent long-term vision problems and ensure optimal visual development in children.
How effective is surgery for cataracts in children?
Surgery for cataracts in children is highly effective, especially when performed early. It can restore clear vision and significantly improve a child’s quality of life when the procedure is done promptly after diagnosis.
Can congenital cataracts be prevented?
Currently, there are no guaranteed preventive measures for congenital cataracts. However, ongoing research aims to better understand their causes and may eventually lead to preventive strategies or alternative treatments in the future.
Why is pediatric eye health important in managing childhood cataracts?
Pediatric eye health is vital in managing childhood cataracts because early detection and treatment are crucial for preventing permanent vision loss. Regular eye examinations can help identify cataracts and other eye conditions early, ensuring timely intervention.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| What are Childhood Cataracts? | Cataracts that are congenital or develop in infancy, leading to cloudy vision and developmental challenges. |
| Surgical Treatment | Surgery is the primary treatment and involves removing the cloudy lens with the option for an artificial lens. |
| Early Detection Importance | Early treatment is crucial as delaying can cause serious complications like amblyopia or strabismus. |
| Surgical Risks | Implanting lenses during infancy poses risks; careful consideration of each case is essential. |
| Research Directions | Future research may explore non-surgical treatments and preventive strategies for childhood cataracts. |
Summary
Childhood cataracts are a significant concern for many families, as they can lead to various visual impairments if not treated promptly. Early intervention through surgical methods is currently the most effective way to address this condition and preserve vision. Parents should be proactive in recognizing the signs of cataracts and seeking medical help. Continued research into alternative treatments may offer promising solutions for the future, enhancing the quality of care available for children affected by this condition.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.