Bullous Pemphigoid vs Pemphigus Vulgaris represents two major autoimmune blistering diseases that, while sharing certain clinical symptoms, exhibit unique underlying mechanisms and patient demographics. Understanding the distinctions between Bullous Pemphigoid symptoms and Pemphigus Vulgaris diagnosis is essential for effective management and treatment. Both conditions involve the body’s immune system attacking its own skin, leading to painful blisters, but their treatment approaches significantly differ. Bullous Pemphigoid typically affects older adults and can often be managed with corticosteroids, while Pemphigus Vulgaris may necessitate more aggressive interventions due to its severe nature. We will explore key differences between these two conditions, shedding light on the specific treatment protocols used for Bullous Pemphigoid and the comprehensive management strategies for Pemphigus Vulgaris to enhance patient outcomes.
When comparing Bullous Pemphigoid and Pemphigus Vulgaris, it is important to consider these conditions as manifestations of autoimmune blistering skin diseases, each presenting with their own set of characteristics and treatment requirements. Bullous Pemphigoid, affecting primarily the older population, is marked by tense blisters that are more resistant to rupture, while Pemphigus Vulgaris tends to occur in younger adults, characterized by fragile blisters that can easily break. A critical aspect of understanding these disorders involves their diagnosis, where specific tests help distinguish between them and direct appropriate treatment. The management strategies vary significantly; for example, individuals with Bullous Pemphigoid may respond well to corticosteroid therapy, whereas those with Pemphigus Vulgaris might require intensive immunosuppressive treatments. In this article, we delve into the nuances that separate these two autoimmune conditions, focusing on their symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Understanding Autoimmune Blistering Diseases
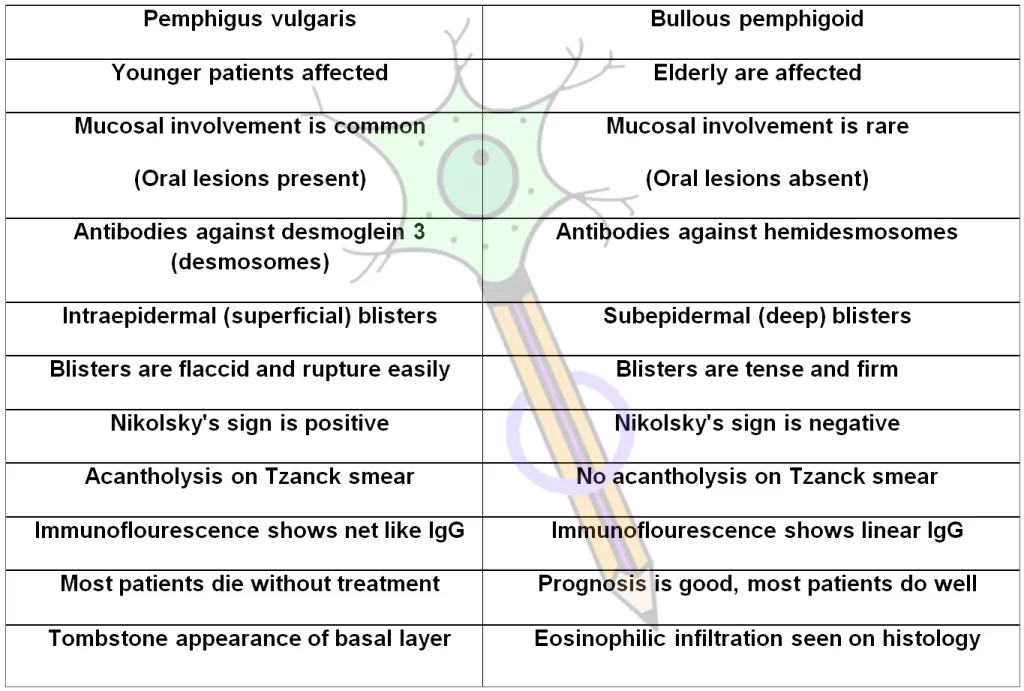
Autoimmune blistering diseases encompass a range of conditions where the body’s immune system erroneously attacks its own skin and mucous membranes, leading to blisters and lesions. Among these diseases, Bullous Pemphigoid (BP) and Pemphigus Vulgaris (PV) are two of the most prominent, each having a unique etiopathogenesis and clinical presentation. They primarily affect the epidermis, with BP typically causing subepithelial blisters below the basement membrane, whereas PV results from intraepithelial blister formation due to the disruption of desmosomes.
These diseases often share overlapping symptoms but require distinct diagnostic and treatment approaches due to their differing immune mechanisms. For instance, while both conditions involve the presence of autoantibodies, the specific targets differ greatly. Understanding the fundamental mechanisms behind these autoimmune conditions is crucial for the effective management of patients suffering from these debilitating diseases.
Key Differences in Clinical Presentation
The clinical presentation is one of the most significant distinguishing factors between Bullous Pemphigoid and Pemphigus Vulgaris. BP typically manifests as tense, fluid-filled blisters that are generally permissible and often appear on the lower abdomen, groin, and flexural areas of the skin. These lesions are more resistant to rupture compared to the fragile blisters associated with Pemphigus Vulgaris, which forms easily and can burst, leading to painful erosions. Oral lesions, often an early sign in PV, are rare in BP.
Furthermore, the itchiness associated with Bullous Pemphigoid can significantly impact the quality of life, while Pemphigus Vulgaris poses more serious complications due to pain from the erosions and the risk of secondary infections. Understanding these clinical distinctions is vital, as it aids in prompt and accurate diagnosis, allowing for timely intervention and optimal patient outcomes.
Diagnosis and Importance of Accurate Testing
Accurate diagnosis is paramount in differentiating between Bullous Pemphigoid and Pemphigus Vulgaris, as the management strategies differ vastly. For Bullous Pemphigoid, indirect immunofluorescence microscopy is a key diagnostic tool, revealing the presence of IgG and complement deposition at the basement membrane zone. This diagnostic method is essential in confirming the presence of specific autoantibodies and understanding the extent of disease involvement.
In contrast, Pemphigus Vulgaris is typically diagnosed through direct immunofluorescence, which highlights intercellular IgG binding to desmogleins within the desmosomes. This method is essential for accurate diagnosis, especially in cases where symptoms may overlap with other skin conditions. The ability to diagnose these conditions correctly not only aids in effective treatment planning but also significantly influences the management and prognosis for patients.
Treatment Approaches for Bullous Pemphigoid vs Pemphigus Vulgaris
Treatment strategies for both Bullous Pemphigoid and Pemphigus Vulgaris involve immunosuppressive therapies, yet they differ in intensity and complexity. In the case of Bullous Pemphigoid, first-line therapy typically includes topical and systemic corticosteroids to manage inflammation and blister formation. There is also growing evidence supporting the use of alternative immunosuppressive agents which may offer additional benefits without the side effects associated with prolonged steroid use.
Conversely, treatment for Pemphigus Vulgaris often necessitates higher doses of corticosteroids, along with additional immunosuppressive therapies such as azathioprine or rituximab for better disease control. Treatment regimens must often be tailored to the individual patient’s needs, considering the potential side effects of aggressive immunosuppression as well as the disease’s effects on the patient’s quality of life. The balance between controlling disease activity and minimizing adverse effects is crucial in effectively managing these challenging conditions.
The Implications of Recent Research on Autoimmune Conditions
Recent insights into the epidemiology and pathogenesis of autoimmune blistering diseases have significant implications for both diagnosis and treatment. The 2023 study by Rosi-Schumacher et al. highlights the multifactorial nature of Bullous Pemphigoid and Pemphigus Vulgaris, emphasizing environmental triggers and genetic predispositions. For instance, certain HLA alleles have been associated specifically with Bullous Pemphigoid, providing researchers and clinicians with valuable information that could shape future preventative and therapeutic strategies.
Moreover, the increasing understanding of the genetic complexity underlying both conditions may lead to the development of novel therapeutic targets. By pinpointing specific genetic markers and environmental factors that contribute to the onset of these autoimmune diseases, healthcare providers may enhance the accuracy of diagnosis and tailor individualized treatment plans, offering improved patient outcomes and a better quality of life for those affected.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main symptoms of Bullous Pemphigoid and how does it compare to Pemphigus Vulgaris symptoms?
Bullous Pemphigoid symptoms typically include tense, itchy blisters that mainly occur on the lower abdomen, groin, and flexural surfaces. These blisters are often more resistant to rupture than those seen in Pemphigus Vulgaris, which features fragile blisters that rupture easily, often leading to painful erosions and can involve the oral cavity early in the disease.
How is Pemphigus Vulgaris diagnosed and how does this differ from Bullous Pemphigoid diagnosis?
Pemphigus Vulgaris diagnosis is primarily conducted through direct immunofluorescence, which identifies IgG deposition on desmosomes. In contrast, Bullous Pemphigoid diagnosis utilizes indirect immunofluorescence microscopy to detect IgG at the basement membrane zone. Understanding these differences is key in differentiating these autoimmune blistering diseases.
What are the treatment options for Bullous Pemphigoid compared to Pemphigus Vulgaris management?
Treatment for Bullous Pemphigoid often begins with corticosteroids at lower doses, and may include immunosuppressants for effective management. Conversely, Pemphigus Vulgaris management frequently requires higher doses of steroids and may involve aggressive treatments such as rituximab or azathioprine to control symptoms.
What underlying mechanisms differentiate Bullous Pemphigoid from Pemphigus Vulgaris in autoimmune blistering diseases?
Bullous Pemphigoid involves autoantibodies against antigens at the basement membrane, specifically BP180 and BP230, leading to subepithelial blistering. In contrast, Pemphigus Vulgaris is characterized by autoantibodies targeting desmogleins, crucial for cell adhesion, resulting in intraepithelial blistering.
What demographic differences exist between Bullous Pemphigoid and Pemphigus Vulgaris?
Bullous Pemphigoid primarily affects older adults, typically after age 60, whereas Pemphigus Vulgaris more commonly occurs in younger adults between 40 to 60 years. This age-related difference highlights the varying epidemiological profiles of these autoimmune blistering diseases.
| Aspect | Bullous Pemphigoid (BP) | Pemphigus Vulgaris (PV) |
|---|---|---|
| Pathogenesis | Autoantibodies against BP180 and BP230 at the basement membrane causing subepithelial blistering. | Autoantibodies targeting desmogleins result in intraepithelial blistering. |
| Clinical Presentation | Tense, itchy blisters primarily on the abdomen and groin; resistant to rupture. | Fragile blisters that rupture easily, causing painful erosions, often starting in the oral cavity. |
| Demographics | Primarily affects older adults (avg. onset >60 years), often associated with neurological conditions. | Typically seen in younger adults (ages 40-60), with links to thymoma and certain drug reactions. |
| Diagnosis | Indirect immunofluorescence showing IgG and complement at the basement membrane; skin biopsies confirm diagnosis. | Direct immunofluorescence highlighting intercellular IgG and complement on desmosomes; crucial for early diagnosis. |
| Treatment | Initial treatment with corticosteroids; alternative immunosuppressants may be used. | Often requires higher doses of steroids and aggressive treatments like azathioprine or rituximab. |
Summary
Bullous Pemphigoid vs Pemphigus Vulgaris highlights important distinctions between these two autoimmune blistering diseases. While both conditions present with blister formation and share some clinical features, they differ significantly in their underlying mechanisms, symptoms, patient demographics, diagnostic processes, and treatment strategies. The pathogenesis of Bullous Pemphigoid is associated with autoantibodies against basement membrane proteins, resulting in subepithelial blisters, whereas Pemphigus Vulgaris is linked to autoantibodies affecting desmogleins, leading to intraepithelial blistering. Clinically, BP manifests as tense blisters in older adults, while PV typically occurs in younger individuals with more fragile blisters. Proper diagnosis is essential, given the differing treatment protocols, with BP often managed with lower doses of corticosteroids compared to the more intensive requirements for PV. Understanding these differences is vital for ensuring effective management and care for patients suffering from these serious conditions.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.