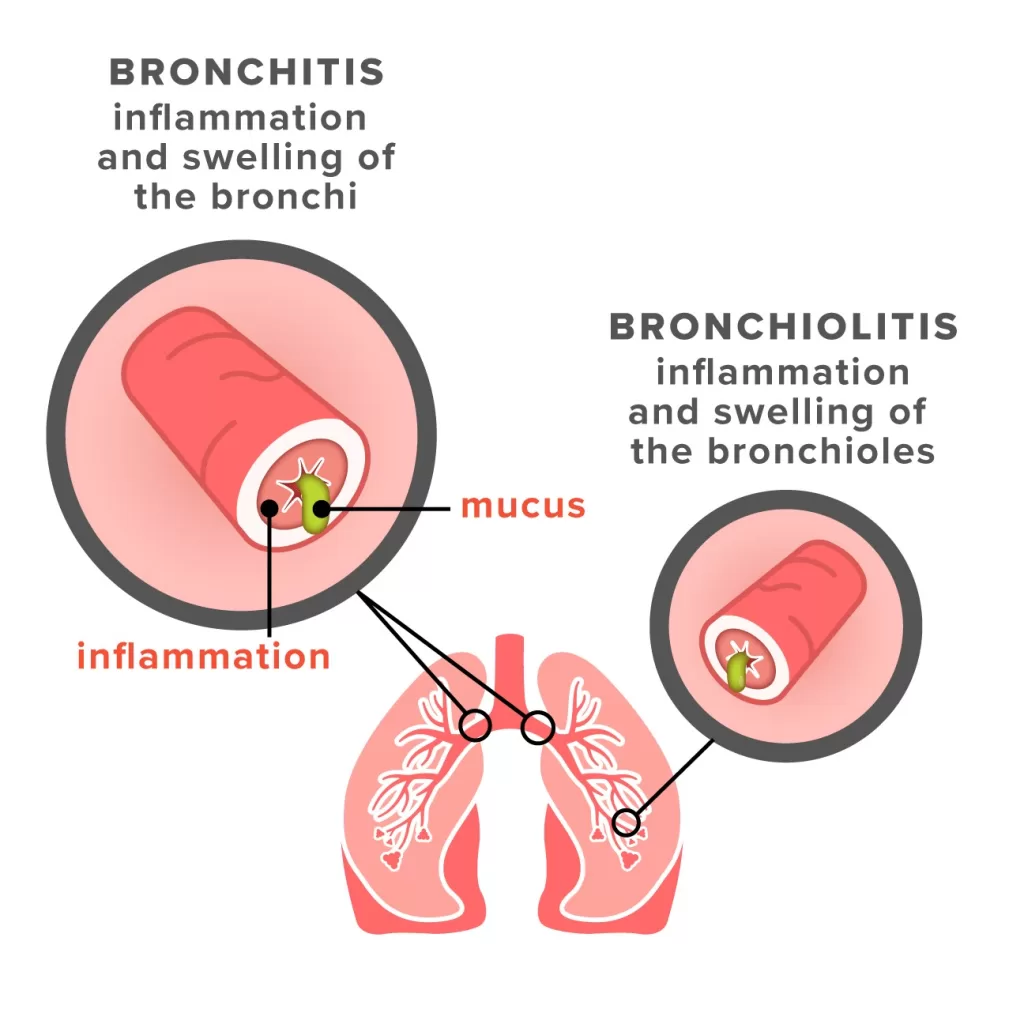
When it comes to understanding respiratory illnesses, the terms bronchiolitis and bronchitis often lead to confusion. While both conditions involve the airways, the differences between bronchiolitis and bronchitis are crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. Bronchiolitis typically affects infants and is primarily caused by viral infections, leading to symptoms like wheezing and difficulty breathing. Conversely, bronchitis can affect individuals of all ages and may stem from either viral or bacterial infections, with persistent cough and mucus production being its hallmarks. By highlighting the bronchiolitis symptoms and bronchitis treatment options, individuals can gain clarity on managing these distinct yet overlapping conditions effectively.
In the realm of respiratory diseases, many individuals may struggle to differentiate between airways inflammation in infants, known as bronchiolitis, and the broader condition of bronchitis which affects various age groups. Bronchiolitis, a common viral infection predominantly affecting younger children, manifests as difficulty in breathing and wheezing, while bronchitis may occur as an acute or chronic condition, often linked to long-term irritants. Understanding the underlying causes of bronchiolitis and the different bronchitis types can guide effective treatment strategies tailored to the specific needs of the patient. By exploring the nuances between these respiratory ailments, we can better address and manage symptoms, ensuring optimal respiratory health for those affected.
Key Differences Between Bronchiolitis and Bronchitis
When comparing bronchiolitis and bronchitis, the primary distinction lies in the age group affected and the area of the respiratory system that is inflamed. Bronchiolitis predominantly affects infants and young children, leading to inflammation in the small airways (bronchioles). In contrast, bronchitis affects individuals of all ages, including adults, and targets the larger airways (bronchi). This difference in the affected population and airway size leads to variations in symptoms and severity, underscoring the importance of understanding bronchiolitis and bronchitis in the context of respiratory health.
Another key difference can be seen in the underlying causes. Bronchiolitis is typically instigated by viral infections, particularly the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), which poses a higher risk for infants. On the other hand, bronchitis can be triggered by a range of factors including viral, bacterial infections, and irritants like smoke or pollution. These factors not only differentiate the two conditions but also influence the treatment protocols, necessitating a proper diagnosis for effective management.
Understanding Bronchiolitis Symptoms and Treatment
The symptoms of bronchiolitis can be distressing, especially for young infants. Typical symptoms include coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing, often accompanied by a low-grade fever and increased respiratory effort. Caregivers should be attentive to these signs, especially in infants, as the condition can escalate quickly. Effective treatment for bronchiolitis primarily focuses on supportive care, with an emphasis on alleviating symptoms. In cases of severe respiratory distress, hospitalization may be required for close monitoring and oxygen support.
Managing bronchiolitis symptoms often involves encouraging hydration and maintaining humidity in the air to ease breathing. While antiviral medications are occasionally employed, they are rarely the first line of treatment as most cases resolve with time. Education for parents about the signs of worsening symptoms is paramount, as timely intervention can significantly improve outcomes for affected children.
Bronchitis Symptoms and Effective Treatment Options
Bronchitis manifests primarily through a persistent cough that may produce thick mucus, fatigue, and chest discomfort. Acute bronchitis is often triggered by infections, especially following a cold, while chronic bronchitis often arises from long-term exposure to irritants such as tobacco smoke. Patients experiencing these symptoms should seek medical evaluation to differentiate between acute and chronic forms and to initiate appropriate treatment.
Treatment for bronchitis often includes rest, fluids, and over-the-counter medications to alleviate cough and enhance comfort. For chronic bronchitis, a more comprehensive management plan may be necessary, involving bronchodilators and corticosteroids to reduce airway inflammation. Additionally, lifestyle changes including smoking cessation and avoiding environmental irritants are crucial for managing and curbing the progression of chronic bronchitis.
Complications of Bronchiolitis and Their Prognosis
Bronchiolitis, while common among infants, can lead to serious complications if not monitored closely. The potential for severe respiratory distress is especially high in infants under two, necessitating routine check-ups following initial treatment. Most cases resolve within one to two weeks; however, some cases may require hospitalization and follow-up assessment to ensure proper recovery and manage any residual symptoms.
Understanding the projection of bronchiolitis is vital for caregivers. It is reassuring that the prognosis for bronchiolitis is generally favorable with appropriate care, but awareness of the signs that necessitate emergency medical attention remains crucial. Parents and caregivers must stay informed about their child’s condition to support healthy recovery.
The Importance of Seeking Medical Advice for Symptoms
For both bronchiolitis and bronchitis, early recognition of symptoms can significantly alter the course of treatment. Parents and caregivers should not hesitate to seek medical attention if their child displays signs of respiratory distress. This proactive approach is essential in achieving better health outcomes, particularly with bronchiolitis, where delays in treatment can lead to complications.
Additionally, understanding the intricacies between bronchiolitis and bronchitis empowers patients to make informed health decisions. Knowledge of symptomatology and appropriate treatment options can help individuals to advocate for themselves or their children’s health effectively, ensuring they receive timely and accurate medical care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of bronchiolitis vs. bronchitis?
The symptoms of bronchiolitis primarily include coughing, wheezing, difficulty breathing, and a low-grade fever, affecting infants and young children. In contrast, bronchitis typically presents with a persistent cough that produces thick mucus, fatigue, slight fever, and chest discomfort. Recognizing these differences in symptoms can aid in timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
What are the key differences between bronchiolitis and bronchitis?
Bronchiolitis is an inflammation of the small airways (bronchioles) commonly seen in infants, primarily caused by viral infections like RSV. Bronchitis, however, is an inflammation of the larger airways (bronchi), and can be triggered by both viral and bacterial infections, as well as irritants such as smoke. This distinction is essential for understanding their respective treatments and risk factors.
What causes bronchiolitis and bronchitis?
The primary cause of bronchiolitis is viral infections, particularly the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), which predominantly affects younger children. Bronchitis, on the other hand, can be caused by both viral and bacterial infections. Chronic bronchitis is frequently the result of long-term exposure to irritants, especially tobacco smoke, making its causes multifactorial and manageable with lifestyle changes.
How is bronchitis treated compared to bronchiolitis?
For bronchiolitis, treatment focuses on supportive care, including symptom management and, in severe cases, hospitalization for oxygen therapy. Bronchitis treatment varies by type; acute bronchitis often requires rest, fluids, and OTC medications like cough suppressants, while chronic bronchitis may necessitate bronchodilators and corticosteroids, alongside lifestyle changes to avoid irritants.
What complications can arise from bronchiolitis vs. bronchitis?
Complications from bronchiolitis can include severe respiratory distress in young infants, requiring close monitoring. Most cases resolve in 1-2 weeks. Chronic bronchitis, however, is often linked to long-term health issues like Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), highlighting the importance of effective management to prevent deterioration of respiratory health.
| Aspect | Bronchiolitis | Bronchitis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inflammation of the small airways (bronchioles), affecting mainly infants and young children. | Inflammation of the larger airways (bronchi), can be acute or chronic, affecting all ages. |
| Affected Population | Primarily affects infants and young children under two years old. | Affects people of all ages, including adults. |
| Common Causes | Primarily viral infections, especially respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). | Can be caused by both viral and bacterial infections; often linked to irritants in chronic cases. |
| Symptoms | Coughing, wheezing, difficulty breathing, low-grade fever, increased respiratory effort. | Persistent cough with thick mucus, fatigue, slight fever, chest discomfort. |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, medical history, sometimes imaging tests like chest X-rays. | Similar diagnostic approach with focus on symptom history and chest X-ray if needed. |
| Treatment | Supportive care, possible hospitalization for severe cases, manage symptoms. | Rest, fluids, OTC medications for acute; long-term medications and lifestyle changes for chronic. |
| Complications | Severe respiratory distress in infants; typically resolves in 1-2 weeks but may need follow-up. | Can lead to long-term health issues if chronic bronchitis is not effectively managed. |
Summary
Bronchiolitis vs. Bronchitis are two respiratory conditions that are often confused due to their similar names and overlapping symptoms. Understanding the differences is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. Bronchiolitis primarily affects infants, causing inflammation in the small airways due to viral infections like RSV, while bronchitis affects individuals of all ages, inflaming the larger airways, often resulting from infections or irritants. Their symptoms, causes, and treatments vary significantly, as bronchiolitis tends to require supportive care, whereas bronchitis management may include both acute and chronic treatment strategies. Knowledge of these distinctions not only aids parents and caregivers in seeking timely medical intervention but also enhances health practices and informed choices regarding respiratory health.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.