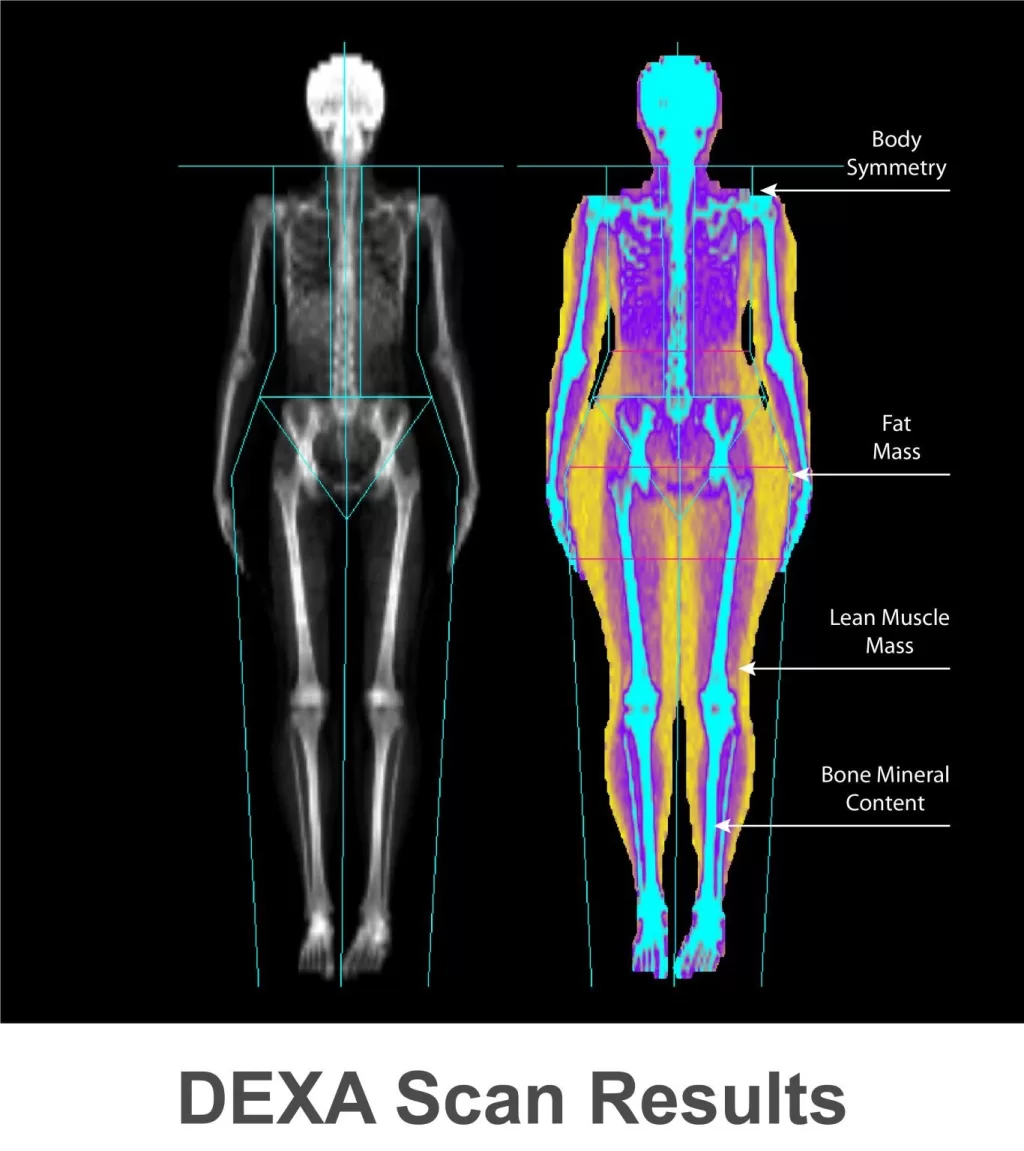
Bone density scans, often referred to as DEXA scans, are essential diagnostic tools used to evaluate bone health and assess the risk of osteoporosis. These scans measure bone mineral density (BMD) and help in the early detection of conditions like osteopenia, which can lead to osteoporosis if not addressed. By providing a precise measurement of bone density, DEXA scans play a critical role in osteoporosis diagnosis, helping to identify individuals at high risk for fractures. The results, expressed through a T-score, offer valuable insights into one’s bone health relative to that of a healthy young adult. Regular monitoring through bone density scans is vital for anyone concerned about their bone health, especially those with risk factors for bone density loss.
When discussing assessments of bone strength, the term “bone density scan” often comes to mind, but you might also hear about DEXA testing or dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. This imaging technique is pivotal in understanding bone mineral density, crucial for diagnosing conditions like osteoporosis and osteopenia. The results from such tests are typically conveyed using a T-score, which compares the patient’s bone density to that of a healthy young adult. Regular evaluations through these scans are recommended for individuals at risk, as they provide an accurate gauge of changes in bone health over time. Understanding these assessments can empower patients to take proactive steps in managing their skeletal well-being.
The Importance of Bone Density Scans in Osteoporosis Diagnosis
Bone density scans, particularly DEXA scans, play an essential role in the early detection and diagnosis of osteoporosis. Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by weakened bones, making individuals more susceptible to fractures. By measuring bone mineral density (BMD), DEXA scans provide a clear assessment of bone health, allowing healthcare providers to identify patients at risk for osteoporosis before serious complications arise. Understanding the significance of these scans is crucial for individuals, especially those with risk factors such as age, family history, or certain medical conditions.
In recent years, advancements in DEXA technology have enhanced the accuracy and reliability of bone density assessments. These scans utilize low-dose X-rays to measure BMD at key skeletal sites, such as the hip and spine, providing a comprehensive overview of bone health. The results are expressed as T-scores, which compare an individual’s bone density to that of a healthy young adult. This comparison not only aids in osteoporosis diagnosis but also helps in monitoring the effectiveness of treatment for bone density conditions.
How DEXA Scans Measure Bone Mineral Density
DEXA scans utilize a dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry technique to measure bone mineral density with remarkable precision. The process involves sending two different energy levels of X-rays through the bones, allowing for differentiation between bone and soft tissue. This advanced technique results in detailed images that reveal the density of bones, specifically targeting areas most vulnerable to osteoporosis and fractures. The accuracy of DEXA scans makes them the gold standard for assessing bone health, providing healthcare professionals with vital information for diagnosis and treatment.
The measurement obtained from a DEXA scan is usually reported as a T-score, which indicates how an individual’s bone mineral density compares to that of a healthy young adult. A T-score above -1 is considered normal, while scores between -1 and -2.5 indicate osteopenia, and scores below -2.5 signify osteoporosis. This clear classification helps doctors determine the best course of action for patients, whether it be lifestyle changes, medications, or further monitoring of bone health.
What to Expect During a DEXA Scan
Preparing for a DEXA scan is straightforward and typically requires minimal adjustments to your daily routine. Patients are advised to avoid calcium supplements for at least 24 hours prior to the scan, as these can artificially influence the results. Additionally, wearing loose-fitting clothing without metal fasteners is recommended to prevent any interference with the imaging process. The scan itself is quick, usually taking about 10-30 minutes, and involves lying on a table while the machine takes images of the bones.
During the procedure, patients may feel a sense of relaxation as the process is painless and non-invasive. It is important to inform the technologist about any medical conditions, such as pregnancy, that may affect the scan. Following the DEXA scan, patients typically receive their results within a few days, allowing them to discuss their bone health status and necessary next steps with their healthcare provider.
Interpreting T-Scores from Bone Density Scans
The T-score is a critical component of the results obtained from a bone density scan, as it provides a benchmark for assessing bone health. A T-score of 0 indicates normal bone density, while a score between -1 and -2.5 indicates osteopenia, a condition characterized by lower bone density but not yet classified as osteoporosis. Scores below -2.5 confirm a diagnosis of osteoporosis, highlighting the need for immediate attention and potential treatment to prevent fractures and other complications.
Understanding your T-score is crucial for making informed decisions about health management. For instance, individuals with osteopenia may benefit from lifestyle changes such as increased physical activity, dietary adjustments, and potentially medications to help preserve bone density. Conversely, those diagnosed with osteoporosis may require more intensive treatment strategies to mitigate the risk of fractures. By interpreting T-scores correctly, patients can engage in proactive discussions with their healthcare providers about the best approaches to maintain or improve bone health.
The Role of DEXA Scans in Monitoring Bone Health Over Time
Regular monitoring of bone density through DEXA scans is essential for individuals at risk of osteoporosis or those undergoing treatment for low bone density. Healthcare providers often recommend follow-up scans every one to two years to track changes in bone mineral density. This ongoing evaluation allows for timely adjustments to treatment plans based on individual responses to therapy, ensuring that patients are receiving the most effective care for their bone health.
In addition to tracking the effectiveness of osteoporosis treatments, DEXA scans can also help identify secondary causes of low bone density, such as nutritional deficiencies or hormonal imbalances. By analyzing changes in bone density over time, healthcare providers can gain insights into the overall health of a patient and tailor interventions accordingly. This personalized approach is vital for effective prevention and management of bone health issues, ultimately reducing the risk of fractures and improving quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of bone density scans (DEXA scans)?
Bone density scans, also known as DEXA scans, are used to measure bone mineral density (BMD) to assess bone health and diagnose conditions like osteoporosis and osteopenia. They help determine your risk of fractures and monitor the effectiveness of treatments for bone density issues.
How is the T-score calculated in a bone density scan?
The T-score in a bone density scan compares your bone mineral density to the average peak bone density of a healthy young adult. A T-score of -1.0 or higher is considered normal, while a score between -1.0 and -2.5 indicates osteopenia, and a score below -2.5 indicates osteoporosis.
What should I expect during a DEXA scan for osteoporosis diagnosis?
During a DEXA scan for osteoporosis diagnosis, you will lie on a padded table while a scanning arm passes over your body. The procedure is quick, painless, and involves minimal radiation exposure. The results will provide detailed information about your bone density and potential fracture risk.
How often should I get a bone density scan if I have osteopenia?
If you have been diagnosed with osteopenia, it is typically recommended to have a bone density scan every one to two years. This regular monitoring helps track changes in your bone mineral density and assess the effectiveness of any treatments you may be undergoing.
Can a DEXA scan detect conditions other than osteoporosis?
Yes, while DEXA scans are primarily used for osteoporosis diagnosis, they can also help identify other conditions related to low bone density, such as hormonal imbalances and nutritional deficiencies. Additionally, they provide insights into overall bone health, which can guide personalized treatment plans.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| What is a DEXA Scan? | A specialized imaging test measuring bone mineral density (BMD), identifying conditions like osteopenia and osteoporosis. |
| Key Differences | DEXA is a type of bone density scan using low-dose X-rays; results are expressed as T-scores comparing bone density to healthy young adults. |
| Significance | Assesses osteoporosis risk, monitors treatment effects, and provides personalized health insights. |
| Recent Findings | Forearm DEXA scans aid in osteoporosis detection; regular monitoring is recommended for at-risk individuals. |
| Preparation for DEXA Scan | Wear loose clothing without metal, avoid calcium supplements 24 hours prior, and inform the technician about pregnancy. |
Summary
Bone density scans (DEXA scans) are essential for evaluating bone health and diagnosing conditions like osteoporosis. These scans provide valuable insights into an individual’s bone mineral density, helping to assess fracture risk and monitor treatment efficacy. With advancements in technology and ongoing research, DEXA scans are becoming more precise, offering tailored health recommendations based on individual needs. Understanding the importance of these scans empowers patients to take proactive measures in managing their bone health effectively.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.