Bladder stones, medically known as vesical calculi, are hardened mineral deposits that can cause significant discomfort and health complications if left untreated. These stones can develop from various causes, including urinary retention and dehydration, leading to symptoms such as frequent urination, abdominal pain, and even visible blood in urine. Understanding the causes and symptoms of bladder stones is essential for effective treatment and prevention strategies. This overview will explore the latest insights into bladder stones treatment options and their impact on both humans and pets. By recognizing the differences between bladder stones and kidney stones, individuals can better navigate their health concerns and seek timely medical attention.
When discussing bladder stones, one might also encounter terms like urinary calculi or vesical stones. These solid formations develop in the urinary bladder and can lead to various health issues if not addressed promptly. The formation of these stones can occur due to several factors, including improper fluid intake and underlying medical conditions. Recognizing the symptoms of these urinary blockages is crucial for timely intervention. This guide aims to provide a thorough understanding of the condition, including its causes, potential treatments, and the similarities and differences between bladder stones and other types of urinary stones.
Understanding Bladder Stones: Causes and Risk Factors
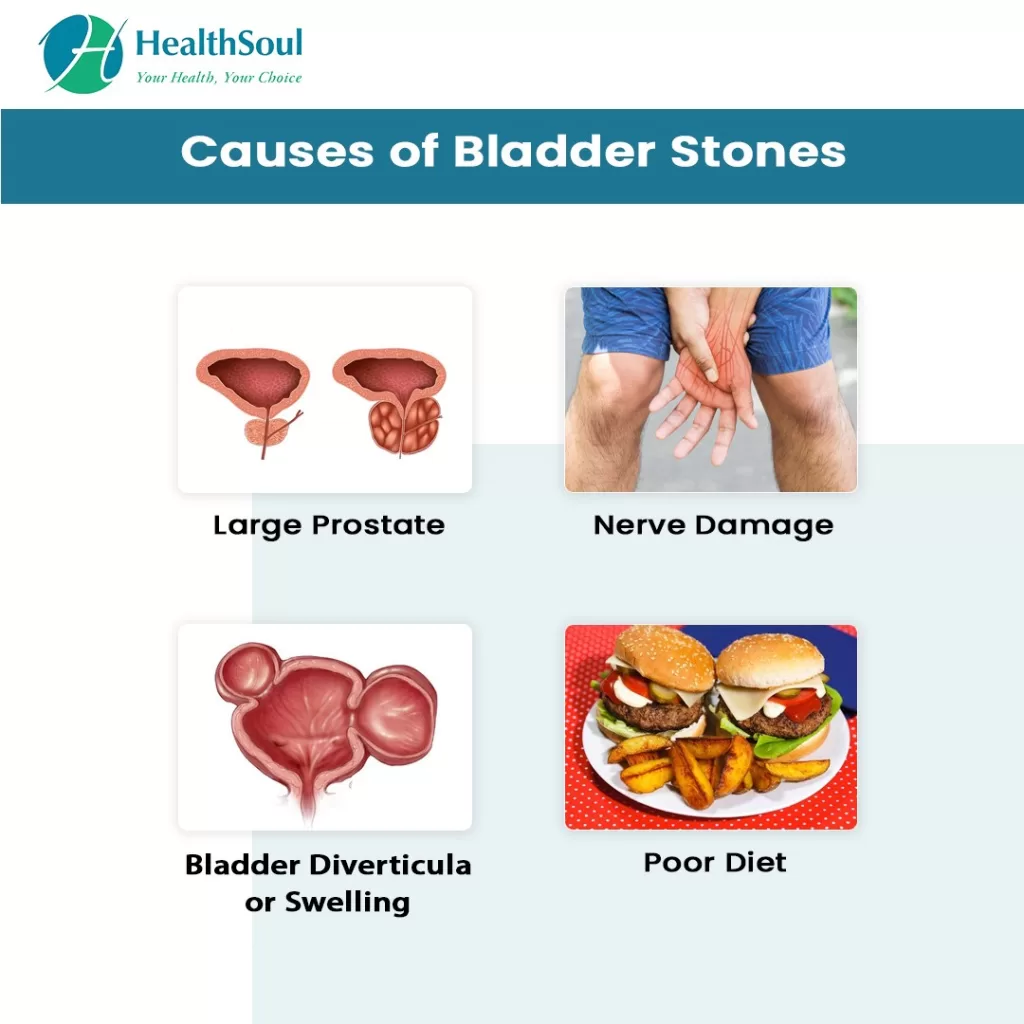
Bladder stones, or vesical calculi, can develop due to various underlying causes, with the most common being urine retention. When the bladder fails to empty completely, minerals in the urine can crystallize and form stones. Conditions like urinary tract infections (UTIs), diabetes, and certain anatomical abnormalities can significantly increase the risk of developing bladder stones. Additionally, age and gender play crucial roles, as older men are more prone to these stones, often due to an enlarged prostate that obstructs urine flow.
Diet is another critical factor influencing the formation of bladder stones. High levels of certain minerals, such as calcium and oxalate, in the diet can contribute to stone formation. Furthermore, inadequate hydration leads to concentrated urine, which is a conducive environment for crystal formation. Understanding these causes can help individuals take preventive measures, such as increasing fluid intake and managing underlying health conditions, to mitigate the risk of developing bladder stones.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common causes of bladder stones?
Bladder stones are often caused by urine retention, which can occur due to conditions like an enlarged prostate or bladder dysfunction. Other contributing factors include dehydration, urinary tract infections (UTIs), and certain dietary factors. Understanding these bladder stones causes is essential for prevention.
What symptoms indicate the presence of bladder stones?
Common symptoms of bladder stones include frequent urination, pain during urination, sharp abdominal pain, and visible blood in urine. If you experience these bladder stones symptoms, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly to avoid complications.
What treatment options are available for bladder stones?
Treatment for bladder stones varies with size. Small stones may pass naturally with increased water intake, while larger stones might require surgical removal or lithotripsy, a procedure that breaks them into smaller pieces. Medications may also be prescribed to manage pain or dissolve stones.
Can pets get bladder stones, and what are the symptoms?
Yes, bladder stones can affect pets such as dogs and cats. Symptoms in pets include difficulty urinating, blood in urine, and lethargy. Treatment may involve dietary changes, medications to dissolve the stones, or surgery in severe cases. Regular veterinary check-ups are essential for prevention.
How do bladder stones differ from kidney stones?
Bladder stones and kidney stones are both types of urolithiasis but differ in location. Bladder stones typically form due to urine retention, while kidney stones can arise from various factors including diet and hydration. Treatment methods also differ, with kidney stones sometimes requiring different surgical techniques.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Bladder stones, or vesical calculi, are solid mineral masses formed in the bladder. |
| Causes | Often caused by incomplete urine evacuation, urinary tract infections, or underlying health issues. |
| Symptoms | Frequent urination, pain during urination, abdominal pain, and visible blood in urine. |
| Treatment Options | Varies based on size: small stones may pass naturally; larger stones may require surgical removal, lithotripsy, or medications. |
| Bladder Stones in Pets | Similar symptoms in pets; treatment may include dietary changes, medications, or surgery. |
| Comparison with Kidney Stones | Bladder stones are caused by urine retention, while kidney stones arise from different factors. Treatment varies. |
Summary
Bladder stones are a serious health concern that can lead to significant discomfort and complications. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for effective management. Regular health check-ups and proper hydration are essential in preventing their formation. Awareness of the condition is key, as timely intervention can lead to better health outcomes for both humans and pets affected by bladder stones. By staying informed and proactive, individuals can effectively manage their health and mitigate the risks associated with this condition.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.