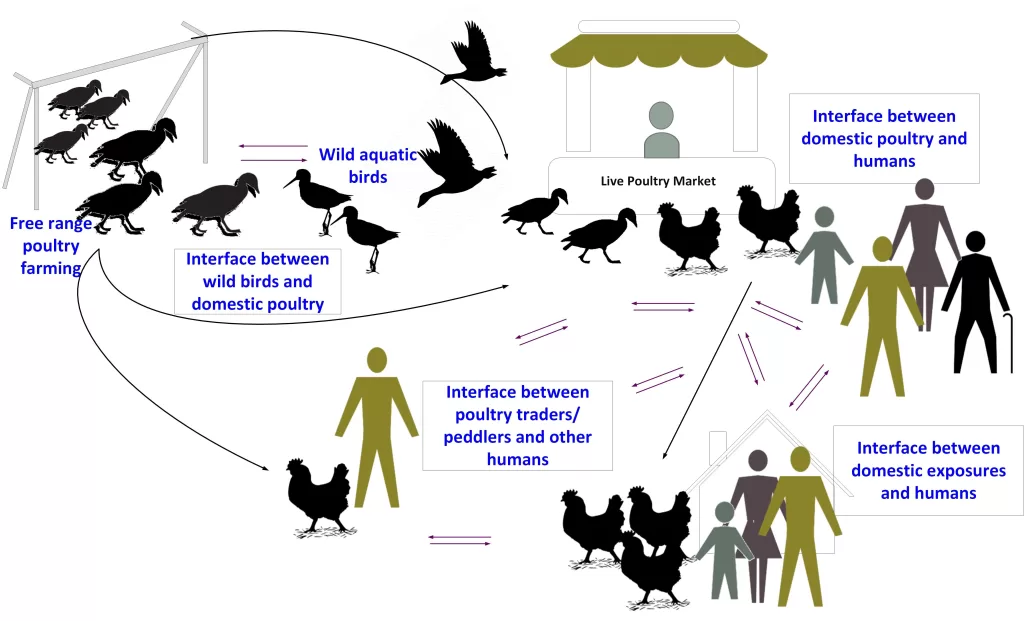
Bird flu transmission, driven primarily by the H5N1 virus, poses a looming threat to global health. This avian influenza strain has garnered attention due to its potential for human infection, with over 900 cases reported since 2003, many resulting in severe outcomes. Understanding how this virus transmits from birds to humans is crucial, as the consequences of widespread human infection could be devastating. Researchers emphasize the importance of disease prevention strategies while monitoring viral evolution to mitigate risks associated with this pathogen. As we face the threat of bird flu, implementing effective measures becomes essential to safeguard public health and curb its spread.
The transmission of avian influenza, particularly the H5N1 strain, highlights critical concerns in infectious disease management. Often referred to as bird flu, this illness is known for its capacity to leap from animals to humans, resulting in sporadic human cases with significant health implications. Scientists closely monitor these interactions, seeking to understand the evolution of the virus and its potential for widespread human-to-human transmission. The intricate dynamics of pathogen evolution underscore the importance of effective disease prevention methods. As we navigate the implications of such infectious agents, a comprehensive approach integrating public health measures and community awareness becomes imperative.
Understanding H5N1 and Human Infection Risks
The H5N1 virus, a subtype of avian influenza, has been the focus of public health discussions due to its sporadic transmission to humans. Although human infections remain relatively rare, the reported cases underscore a significant risk associated with close contact with infected animals, particularly poultry. Understanding how H5N1 can cause human infection is crucial to preventing potential outbreaks. Workers in poultry farms and those who handle infected birds are at a heightened risk, which raises concerns about the monitoring and management of animal health to mitigate these risks.
Epidemiologists categorize the stages of pathogen transmission, highlighting the importance of distinguishing between animal-to-human transfers and the potential for human-to-human spread. The rare occurrences of human infection with H5N1, while alarming, lead to a scenario where vigilance and preventive measures can be prioritized. By studying the patterns of H5N1 transmission, health authorities can devise strategies to minimize human interaction with infected birds and implement strict biosecurity measures to block virus spillover.
The Mechanism of Bird Flu Transmission
Bird flu transmission primarily hinges on a process called spillover, which refers to the pathogen’s evolution to infect new species. For the H5N1 virus, this means adapting to human cells after initially being suited for avian hosts. The molecular process requires the virus to acquire specific mutations that allow it to attach to human cells effectively. However, this mutation process is fraught with challenges, and the path from animal infection to human epidemic is highly complex. Therefore, understanding this mechanism is vital for identifying points where interventions can be applied.
Viral chatter, a term used in epidemiology, reflects the sporadic human cases of H5N1 without clear indications of sustained human transmission. It illustrates the need for close monitoring of these instances, as they may signal an emerging risk. Each case serves as a reminder that without careful observation and preventive action, the transition from isolated incidents to widespread human infection could occur, with devastating consequences.
Impact of Viral Evolution on Disease Outbreaks
The evolution of the H5N1 virus exemplifies how rapidly influenza viruses can change, particularly through genetic reassortment, which can lead to new strains capable of causing more severe human infections. As various strains of the influenza virus circulate among animals, the potential for recombination increases, making it essential to understand the evolutionary pathways these viruses may take. With H5N1 already infecting numerous species and the potential for cross-species transmission, the importance of monitoring and understanding viral evolution cannot be overstated.
Disease prevention strategies focus on two main fronts: monitoring viral changes and implementing effective vaccination programs. By enhancing surveillance of avian populations and understanding the evolutionary pressures on viruses, researchers can better predict and potentially inhibit the emergence of new infectious strains. Vaccination against seasonal influenza not only protects individuals but also reduces the chances of mixed infections that can lead to new variants, highlighting the interconnectedness of animal health and human disease prevention.
Strategies for Disease Prevention
Preventing the spread of H5N1 and mitigating the risks of potential human infection require coordinated efforts at both individual and societal levels. Basic hygiene practices, vaccination, and improved care of food animals are essential steps individuals can take to contribute to disease prevention. For example, ensuring proper handling and cooking of poultry can significantly reduce the risk of infection from H5N1, while public health campaigns can educate communities on the importance of biosecurity measures in preventing spillover events.
On a larger scale, government policies must support agriculture and public health initiatives that prioritize disease prevention. This includes enhancing biosecurity protocols in poultry farms and creating robust surveillance systems for avian influenza outbreaks. By addressing the factors contributing to the evolution of H5N1 and promoting international cooperation, we can reshape the trajectory of this virus and reduce the incidence of human infections and potential pandemics.
Long-term Perspective on Avian Influenza
Approaching the threat of H5N1 and other avian influenza viruses requires a long-term perspective that takes into account human behaviors over centuries. Throughout history, our interactions with animal populations have influenced the emergence and spread of infectious diseases. The patterns of modern agricultural practices, urbanization, and climate change all play roles in shaping the environment in which viruses adapt and spread. Recognizing these factors helps us understand how to manage risks effectively.
Furthermore, as we learn from pandemic events in the past, a proactive approach to avian influenza is necessary. Investments in research and public health infrastructure must be prioritized to ensure readiness for future outbreaks. By understanding the intricacies of viral evolution and the socio-anthropological factors at play, we can implement resilient strategies to curb disease transmission and enhance global health security.
Global Collaboration for Health Security
Global health security requires the collaboration of nations to monitor and control diseases like H5N1. Countries must cooperate to share data on outbreaks and best practices for disease prevention, as the implications of a pandemic extend beyond borders. International organizations play a vital role in coordinating these efforts, offering technical support and resources to countries with high risks of zoonotic infections.
Efforts to enhance food safety, animal health, and public awareness are essential components of this collaboration. By providing training for farmers and animal handlers on biosecurity measures and the risks of avian influenza, we can reduce potential threats. Additionally, countries can work together to fund research initiatives that explore viral evolution and transmission dynamics, ensuring a coordinated response to emerging infectious diseases.
The Role of Nutrition and Sanitation in Disease Resistance
Improving nutrition and sanitation in vulnerable communities is integral to enhancing resistance to infections, including avian influenza. Historical data illustrate a correlation between increased nutritional standards and reduced susceptibility to infectious diseases. Especially in poorer regions where resources are scarce, addressing health disparities can bolster overall public health and reduce the likelihood of outbreaks.
Moreover, enhancing sanitation measures decreases the likelihood of pathogen exposure from contaminated environments. As many pathogens rely on human and animal interactions to spread, effective sanitation reduces the risk by limiting potential contact. Investments in health infrastructure that focus on both nutrition and sanitation are essential for strengthening communities against the threat posed by H5N1 and other infectious diseases.
Monitoring and Research in Viral Evolution
Continuous monitoring and research into viral evolution are paramount for controlling outbreaks of H5N1 and assessing public health risks. Epidemiologists and virologists must actively study patterns of infection, mutation rates, and the genetic shifts that occur within avian influenza viruses. These data can inform public health interventions and enable timely responses to any emerging threats posed by the H5N1 virus.
Incorporating advanced technologies, such as genomic sequencing and bioinformatics, into surveillance programs can enhance the ability to track viral evolution. By understanding the specific mutations that facilitate spillover and human infection, researchers can develop targeted vaccine strategies and effective preventive measures. A dedicated research focus can ultimately contribute to global efforts to prevent potential pandemics caused by H5N1 and other zoonotic viruses.
Public Awareness and Education on Avian Influenza
Public awareness and education regarding avian influenza play a crucial role in preventing its spread. Effective communication strategies must be implemented to educate the general population about the risks associated with H5N1 and the importance of preventive measures. Campaigns targeting at-risk groups, such as poultry workers, can inform them about safe practices while interacting with animals and the significance of vaccination against seasonal flu.
Additionally, fostering a better understanding of the relationship between wildlife, agriculture, and human health can empower communities to engage in proactive measures. Public health initiatives that emphasize the interconnectedness of our actions and their impact on disease outbreaks will enhance overall vigilance in preventing bird flu transmission. Engaging communities in these discussions is vital for building resilience against future avian influenza threats.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is bird flu transmission and how does it relate to the H5N1 virus?
Bird flu transmission primarily refers to how the avian influenza virus, particularly the H5N1 strain, spreads among birds and potentially to humans. The H5N1 virus can infect various bird species, and in rare cases, spillover occurs when it transmits to humans, usually through direct contact with infected birds or contaminated environments.
How does human infection occur through bird flu transmission?
Human infection through bird flu transmission typically occurs when individuals come into close contact with infected birds or their droppings. Workers in poultry farms, for instance, are at higher risk. Though human cases are rare, the potential for transmission exists if the virus mutates and acquires the ability to spread between people.
What are the stages of bird flu transmission from animals to humans?
Bird flu transmission occurs in three stages: In Stage 1, the virus only infects nonhuman animals. Stage 2 occurs when the virus can infect humans, but cannot yet transmit between them. Finally, in Stage 3, the virus is capable of sustained human-to-human transmission, which poses a significant public health risk.
What role does viral evolution play in bird flu transmission?
Viral evolution plays a critical role in bird flu transmission as the H5N1 virus can mutate over time, potentially gaining the ability to infect humans more effectively. Each mutation gives the virus new capabilities, which may eventually lead to increased transmissibility among humans, highlighting the need for monitoring and controlling outbreaks.
What measures can be taken for disease prevention regarding bird flu transmission?
To prevent bird flu transmission and reduce the risk of outbreaks, individuals can improve animal care in agriculture, vaccinate against seasonal influenza, and enhance nutrition and sanitation in communities. These practices can help limit the chances of H5N1 evolving into a form that spreads easily among humans.
Can vaccination help reduce bird flu transmission risk?
Yes, vaccination against common seasonal influenza can help mitigate bird flu transmission risks. By preventing infections in humans, vaccination reduces opportunities for the avian strains to mix with human viruses, which is essential for preventing the emergence of new, more transmissible strains.
How does the H5N1 virus’s spillover process work regarding bird flu transmission?
The spillover process involves the H5N1 virus adapting from birds to humans, requiring specific mutations to infect human cells. This process is often inefficient, as the virus must create compatible ‘keys’ to unlock human cell mechanisms. Successful human infections might occur sporadically, with potential for further evolution towards human-to-human transmission.
What is viral chatter and its significance in bird flu transmission?
Viral chatter refers to sporadic human cases of bird flu that may signal potential for wider outbreaks. It indicates that while human-to-human transmission has not been fully established, the presence of H5N1 in humans could evolve into greater transmission possibilities, necessitating vigilant monitoring and preparedness.
Why is it crucial to monitor avian influenza and bird flu transmission?
Monitoring avian influenza and bird flu transmission is crucial because the H5N1 virus can pose significant health threats if it mutates to allow efficient human-to-human transmission. Understanding its patterns helps prevent potential pandemics and informs public health responses to protect populations globally.
How does the global poultry industry impact bird flu transmission?
The global poultry industry significantly impacts bird flu transmission, as large-scale poultry housing and international trade can facilitate the spread of H5N1 among birds, increasing the risk of spillover to humans. Reducing these practices may help limit outbreaks and viral evolution.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Rising Threat of Bird Flu | Bird flu, particularly the H5N1 subtype, poses significant risks to global health, with a high mortality rate in humans. |
| Transmission Risk | Workers in contact with infected animals are at high risk, and sporadic human cases suggest potential for human-to-human transmission. |
| Stages of Transmission | Pathogens go through three stages: 1) animal-to-animal transmission, 2) infection of humans without human transmission, 3) full human-to-human transmission. |
| Viral Evolution | Influenza viruses evolve rapidly due to genetic reshuffling between different strains. |
| Preventative Measures | Individual measures include improving animal care, vaccination against flu, and societal collaboration for better nutrition and sanitation. |
Summary
Bird flu transmission remains a pressing concern as the H5N1 subtype shows potential to evolve and infect humans more frequently. Understanding the stages of transmission and the factors influencing viral evolution can help us implement effective preventative measures. Enhanced animal care, vaccinations, and improved public health strategies are crucial to mitigating the risks associated with bird flu and preventing possible pandemics.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.