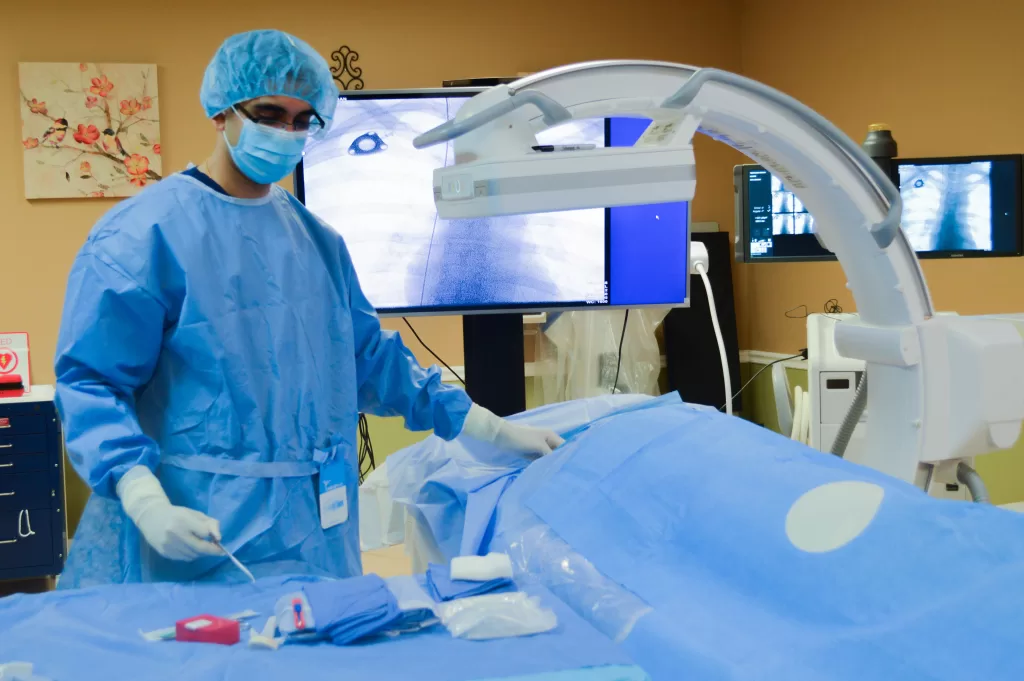
A **biopsy** is a pivotal medical procedure that involves the extraction of tissue or fluid from a living organism for diagnostic analysis. This essential technique is frequently employed when preliminary tests indicate potential abnormalities, particularly in identifying serious conditions such as cancer. Among the various **types of biopsies**, practitioners may recommend procedures like **endoscopic biopsy**, which utilizes a flexible tube to access internal organs, or the innovative **liquid biopsy**, which analyzes circulating tumor DNA from blood samples. These **biopsy procedures** not only aid in accurate disease diagnosis but also play a crucial role in shaping effective treatment strategies tailored to individual patient needs. As advancements continue to emerge in the field, understanding the implications and applications of biopsies is becoming increasingly vital for both healthcare professionals and patients alike.
In the realm of medical diagnostics, the term *tissue sampling* often surfaces as synonymous with what many recognize as a **biopsy**. This intricate process encompasses various methods, including **surgical sampling** and **blood tests** that facilitate the examination of cellular material. The growing prominence of *liquid biopsies* reflects a shift towards less invasive techniques, allowing clinicians to glean critical insights from a simple blood draw. Additionally, the use of *endoscopic techniques* has revolutionized how samples are obtained from within the body, enhancing diagnostic accuracy. By embracing a holistic view through the *biopsychosocial model*, healthcare providers can better understand the full spectrum of factors influencing patient health and outcomes.
Understanding the Different Types of Biopsies
Biopsies can be categorized into several types, each suited for different diagnostic needs and patient conditions. Needle biopsies, for instance, involve the use of a thin needle to extract tissue samples from a specific area. This method is particularly advantageous for patients as it is minimally invasive and can be performed on an outpatient basis. Another common type is the endoscopic biopsy, where a flexible tube is inserted into the body, allowing for direct access to internal organs like the lungs and gastrointestinal tract. This type of biopsy is essential for diagnosing conditions that are not easily accessible through other means.
Surgical biopsies, which involve the removal of larger tissue samples, are generally recommended when more extensive examination is necessary. While this procedure is more invasive, it often provides crucial information for accurate diagnosis. Additionally, liquid biopsies represent a revolutionary advancement in biopsy techniques, allowing for the analysis of circulating tumor DNA from blood samples. This non-invasive method not only facilitates early cancer detection but also assists in monitoring treatment effectiveness, showcasing the evolving landscape of biopsy procedures.
The Purpose and Importance of Biopsy Procedures
The primary purpose of a biopsy is to diagnose diseases, particularly cancers, by allowing medical professionals to examine tissue samples under a microscope. By identifying the cellular structure and any abnormalities present, doctors can determine the nature and severity of the disease. This information is critical in developing personalized treatment plans tailored to the specific type of cancer or condition diagnosed. Biopsy results inform decisions regarding the necessity of surgery, chemotherapy, or other forms of treatment, making them a cornerstone of modern diagnostic medicine.
Biopsies do not just play a role in diagnosis; they also provide insights into the progression of diseases. For instance, the results can indicate whether a tumor is benign or malignant, its grade, and potential response to certain therapies. This information is invaluable for oncologists who aim to provide the most effective treatment based on individual patient profiles. Therefore, understanding the implications of biopsy results is essential for both patients and healthcare providers in navigating the complexities of disease management.
Recent Innovations in Biopsy Techniques
Recent advancements in biopsy procedures have significantly enhanced diagnostic accuracy and patient comfort. Liquid biopsies, for example, have emerged as a groundbreaking innovation in cancer detection. By analyzing circulating tumor DNA from blood samples, doctors can obtain critical information without the need for invasive surgical procedures. This method not only reduces patient discomfort but also allows for real-time monitoring of treatment responses, providing a more dynamic approach to managing cancer.
Moreover, technological innovations such as endobronchial ultrasound biopsy devices are transforming the landscape of biopsy techniques. These devices aid in the precise targeting of lung lesions, thereby improving the accuracy of diagnoses. Additionally, software advancements, like the contrast biopsy software recently approved by Hologic, enhance imaging capabilities during biopsy procedures. Such innovations reflect a shift towards more patient-centered care, where the emphasis is on reducing invasiveness and increasing the efficacy of diagnostic procedures.
Exploring Liquid Biopsies: A New Era in Diagnosis
Liquid biopsies signify a pivotal shift in how medical professionals approach disease diagnosis, particularly in oncology. By utilizing blood samples to detect circulating tumor DNA, liquid biopsies provide a non-invasive alternative to traditional tissue biopsies. This innovative method not only enables early detection of cancer but also allows for monitoring changes in tumor biology over time. As a result, healthcare providers can make timely decisions regarding treatment modifications, enhancing overall patient care.
The advantages of liquid biopsies extend beyond cancer diagnosis. They offer insights into genetic mutations and biomarkers that can guide personalized treatment strategies. For example, identifying specific mutations may help oncologists determine the most effective targeted therapies for individual patients. This ability to tailor treatment based on real-time genomic data represents a significant advancement in the biopsychosocial model of healthcare, where both biological and psychological aspects of patient care are considered.
The Biopsychosocial Model in Biopsy Procedures
The biopsychosocial model emphasizes the importance of considering biological, psychological, and social factors in patient care, particularly when it comes to procedures like biopsies. Understanding a patient’s mental and emotional state is crucial, as anxiety regarding diagnostic tests can significantly impact their overall well-being. By addressing these psychological aspects, healthcare providers can better prepare patients for the biopsy process, ensuring they feel supported and informed.
Furthermore, the social context surrounding a patient plays a vital role in their healthcare experience. Factors such as family support, access to healthcare resources, and community awareness can influence both the decision to undergo a biopsy and the subsequent management of health conditions. By integrating the biopsychosocial model into biopsy procedures, healthcare professionals can adopt a more holistic approach, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes and satisfaction.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the different types of biopsies available for diagnosing diseases?
There are several types of biopsies, including needle biopsies, surgical biopsies, endoscopic biopsies, and liquid biopsies. Needle biopsies use a thin needle to extract tissue, while endoscopic biopsies involve a flexible tube for sampling from internal organs. Surgical biopsies remove larger tissue samples during surgery. Liquid biopsies, a newer method, analyze circulating tumor DNA from blood, providing a non-invasive approach to detect diseases like cancer.
How does a liquid biopsy differ from traditional biopsy procedures?
Liquid biopsies differ from traditional biopsy procedures by analyzing circulating tumor DNA present in blood samples rather than removing tissue directly from the body. This minimally invasive method allows for early cancer detection and monitoring without the need for surgical intervention, making it a promising tool in oncology.
What role do endoscopic biopsies play in diagnosing gastrointestinal diseases?
Endoscopic biopsies are crucial for diagnosing gastrointestinal diseases as they allow healthcare providers to obtain tissue samples from inside the digestive tract using a flexible tube. This procedure is essential for identifying conditions such as cancers or inflammatory diseases, providing accurate diagnostic information essential for treatment planning.
Why is the biopsychosocial model important in understanding biopsy outcomes?
The biopsychosocial model is important in understanding biopsy outcomes as it integrates biological, psychological, and social factors that influence a patient’s health. This holistic approach considers not just the physical diagnosis from a biopsy but also the emotional well-being and support systems of the patient, leading to more comprehensive care and better overall health outcomes.
What advancements are being made in biopsy procedures to improve patient care?
Recent advancements in biopsy procedures include the development of liquid biopsies, which allow for non-invasive genomic profiling, and innovations in imaging technologies, such as contrast biopsy software. These improvements aim to enhance diagnostic accuracy while reducing invasiveness and discomfort for patients, ultimately leading to better treatment decisions and health outcomes.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition of Biopsy | A medical procedure to remove tissue, cells, or fluids for diagnostic examination. |
| Types of Biopsies | 1. Needle Biopsies: Using a needle to extract tissue. 2. Endoscopic Biopsies: Samples taken via a flexible tube. 3. Surgical Biopsies: Larger tissue samples removed surgically. 4. Liquid Biopsies: Analyzing circulating tumor DNA in blood samples. |
| Purpose of Biopsies | Critical for diagnosing diseases, determining severity, and guiding treatment decisions. |
| Recent Innovations | 1. Liquid Biopsies: Non-invasive blood tests like Labcorp Plasma Complete. 2. Market Growth: Endobronchial ultrasound biopsy devices projected to reach $925.2 million by 2030. 3. Technological Approvals: Hologic’s contrast biopsy software enhances accuracy. |
| Biopsychosocial Model | Integrates biological, psychological, and social factors in health assessments. |
Summary
Biopsy is a crucial medical procedure that plays an essential role in diagnosing various health conditions. By removing tissue, cells, or fluids for examination, biopsies provide valuable insights that help medical professionals determine the presence of diseases such as cancer. The advancement of biopsy techniques, including liquid biopsies and improved imaging technologies, reflects a significant evolution in medical diagnostics. With ongoing innovations, patients can anticipate more accurate, less invasive options that enhance health outcomes and support comprehensive patient care.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.