Beta blockers are a class of medications widely known for their effectiveness in managing various cardiovascular conditions. By blocking beta-adrenergic receptors, these agents help lower heart rate and blood pressure, making them essential for treating hypertension, heart failure, and arrhythmias. Surprisingly, beta blockers are also utilized in managing anxiety, particularly performance anxiety, where they help mitigate physical symptoms such as rapid heartbeat and tremors. However, understanding how do beta blockers work and their uses extends beyond just heart health; recent studies have highlighted potential beta blockers side effects that patients should be aware of. As interest grows in natural alternatives to beta blockers, it’s important to explore both the benefits and risks associated with this medication class.
Often referred to as beta-adrenergic blocking agents, these medications serve a vital role in medical treatment, particularly for heart-related issues. Their primary function is to inhibit the effects of adrenaline, which can lead to a decrease in stress-induced symptoms, making them beneficial for individuals experiencing anxiety. While the most common applications of these agents include managing hypertension and heart diseases, they have also gained traction for their use in alleviating symptoms of performance anxiety. As more patients seek information about the various options available, it’s crucial to consider both the established uses of beta blockers and the emerging interest in natural therapies that can provide similar effects without the associated risks.
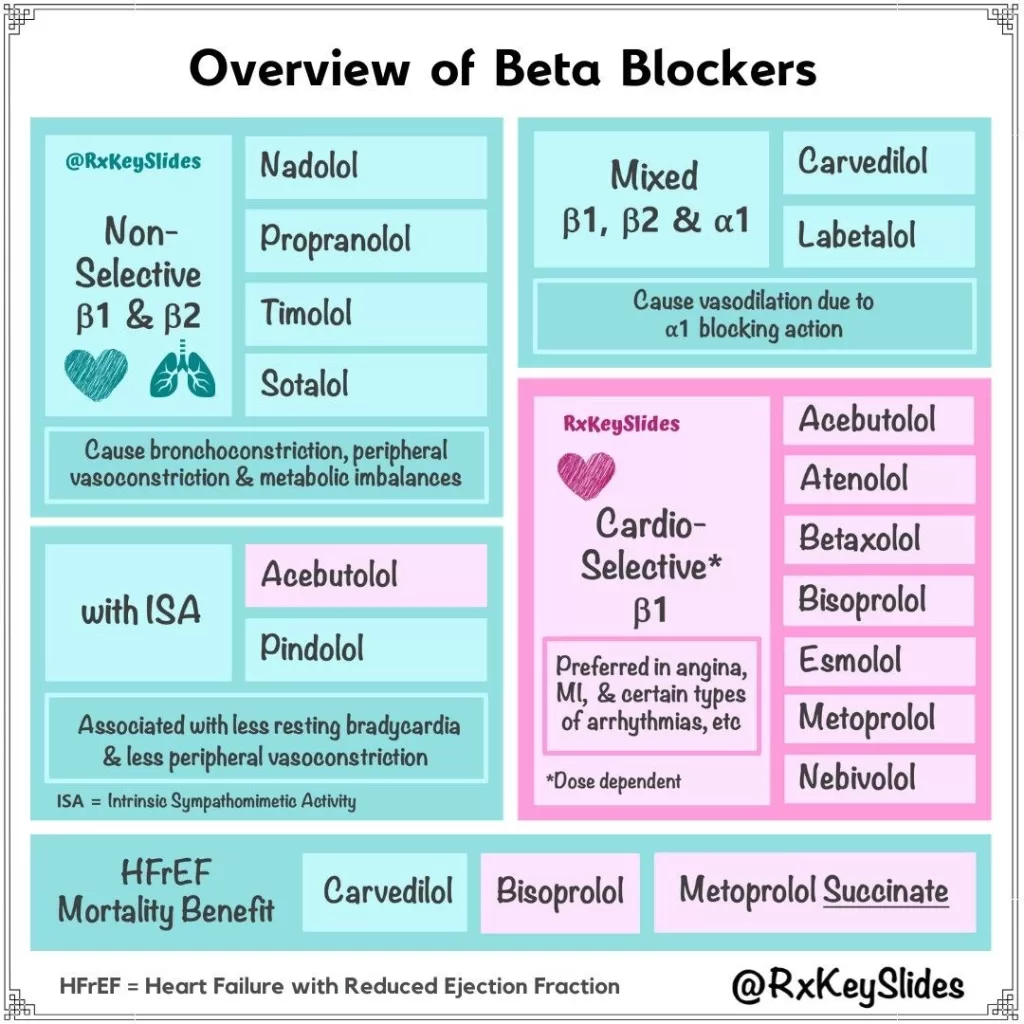
The Mechanism of Beta Blockers Explained
Beta blockers work primarily by blocking the action of neurotransmitters like norepinephrine and epinephrine at the beta-adrenergic receptors, which are found in various tissues throughout the body, including the heart. By doing so, they effectively reduce heart rate and myocardial contractility, leading to decreased cardiac output. This pharmacological action is particularly beneficial in treating conditions such as hypertension and heart failure, where lowering the heart’s workload is critical. Additionally, by dampening the body’s fight-or-flight response, beta blockers can alleviate the physical symptoms associated with anxiety.
When the body perceives a stressor, it releases catecholamines, which trigger an increase in heart rate and blood pressure. For individuals with performance anxiety or situational stress, this response can be overwhelming. Beta blockers mitigate these physiological reactions, making them particularly useful for those who experience anxiety during public speaking or other high-pressure situations. Understanding how beta blockers work is essential for recognizing their therapeutic potential and appropriate applications in both cardiovascular and psychological contexts.
Uses of Beta Blockers in Medical Practice
Beta blockers are not only pivotal in managing cardiovascular diseases but also find applications in various other medical conditions. These medications are commonly prescribed for hypertension, where they help to stabilize blood pressure levels and reduce the risk of heart attacks. In patients with heart failure, beta blockers can improve heart function and reduce mortality rates. Furthermore, their use extends to managing certain types of arrhythmias, where they help maintain a regular heart rhythm, thus preventing complications associated with abnormal heartbeats.
Interestingly, beta blockers have also gained recognition for their off-label use in treating anxiety disorders, particularly performance anxiety. Medications like propranolol are often used to help individuals manage acute anxiety symptoms, such as tremors and palpitations, during stressful situations. While they are not FDA-approved for generalized anxiety disorder, their ability to reduce physiological responses to anxiety makes them a popular choice for those seeking relief from situational anxiety.
Potential Side Effects and Risks of Beta Blockers
While beta blockers are generally well-tolerated by many patients, they are associated with a range of possible side effects. Common issues include fatigue, cold extremities, and even mood changes such as depression. Patients may also experience decreased exercise tolerance due to the reduced heart rate, which can impact their overall physical activity levels. It is crucial for patients to discuss these potential side effects with their healthcare provider to determine if the benefits of beta blocker therapy outweigh the risks.
Moreover, interactions with other medications can pose additional risks. For instance, combining beta blockers with certain antidepressants may require careful monitoring and dosage adjustments to avoid adverse effects. Patients should provide their healthcare providers with a comprehensive list of all medications they are taking, as well as any pre-existing health conditions, to ensure safe and effective treatment. Awareness and communication about these side effects are essential for optimizing patient outcomes.
Recent Research Developments in Beta Blockers
Recent studies have highlighted both the therapeutic benefits and potential risks associated with beta blockers. For example, research published in early 2025 has shed light on the increased mortality risks linked to beta blocker use during hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. This finding suggests that while beta blockers can be effective in managing heart conditions, their role in specific medical procedures requires further scrutiny to understand the implications for patient recovery.
On a more positive note, ongoing research continues to affirm the role of beta blockers in treating various cardiovascular diseases. Clinical studies have demonstrated their effectiveness in reducing cardiac workload and stabilizing blood pressure, which is critical for patients with heart conditions. As the medical community gathers more data, it is important to balance the advantages of beta blockers against their potential drawbacks, ensuring that patients receive the most informed and effective treatment possible.
Exploring Natural Alternatives to Beta Blockers
As interest in holistic health and natural remedies grows, many patients are exploring alternatives to traditional medications like beta blockers. Some studies suggest that certain natural products, such as omega-3 fatty acids found in fish, and herbs like garlic, may offer benefits similar to those of beta blockers in managing heart stress and anxiety. These alternatives can potentially provide cardiovascular protection without the side effects associated with pharmaceutical interventions.
However, it is essential for patients to approach these natural alternatives with caution. While they may offer supplementary benefits, they should not replace prescribed beta blocker therapy without professional guidance. Consulting with healthcare providers can help individuals determine the best approach for their health needs, ensuring a well-rounded strategy that incorporates both conventional and natural options.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the uses of beta blockers in treating anxiety?
Beta blockers, particularly propranolol, are commonly used to manage performance anxiety. They help reduce physical symptoms such as rapid heart rate, sweating, and tremors, allowing individuals to perform in stressful situations with more ease. However, they are not FDA-approved for treating generalized anxiety disorder.
How do beta blockers work to alleviate symptoms of anxiety?
Beta blockers work by blocking the effects of norepinephrine and epinephrine on beta-adrenergic receptors. This action decreases heart rate and blood pressure, which can effectively mitigate the physical symptoms associated with anxiety, particularly during performance-related stress.
What are the common side effects of beta blockers?
Common side effects of beta blockers include fatigue, cold extremities, and potential mood changes such as depression. Understanding these side effects is essential for anyone considering beta blockers, especially for anxiety management.
Are there any natural alternatives to beta blockers for managing anxiety?
Yes, there are natural alternatives to beta blockers that may help manage anxiety symptoms. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, and herbal remedies like garlic are being researched for their potential benefits in mimicking the effects of beta blockers.
What should patients consider when using beta blockers for anxiety?
Patients should consult healthcare professionals before using beta blockers for anxiety. It’s important to discuss potential interactions with other medications, the nature of their anxiety, and to explore comprehensive treatment options that address underlying psychological issues.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Beta blockers are medications that block beta-adrenergic receptors, helping to lower heart rate and blood pressure. |
| Uses | Commonly prescribed for cardiovascular conditions like hypertension, heart failure, and anxiety disorders. |
| Mechanism of Action | They antagonize beta-1 and beta-2 adrenergic receptors, decreasing heart rate and myocardial contractility. |
| Recent Findings | 1. Increased mortality risk in stem cell transplantation. 2. Effective in managing heart diseases. 3. Interest in natural alternatives like omega-3 fatty acids. |
| Side Effects | May include fatigue, cold extremities, and potential mood changes. |
| Considerations | Important to consult healthcare professionals for appropriate use and risk assessment. |
Summary
Beta blockers are essential medications used in managing various cardiovascular conditions and certain types of anxiety. By blocking beta-adrenergic receptors, these drugs effectively lower heart rate and blood pressure, making them vital in treating ailments such as hypertension and heart failure. Recent research has highlighted both the efficacy and potential risks associated with beta blockers, particularly in scenarios like stem cell transplantation. While they can alleviate acute anxiety symptoms, patients should consult healthcare providers to ensure safe and effective use.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.