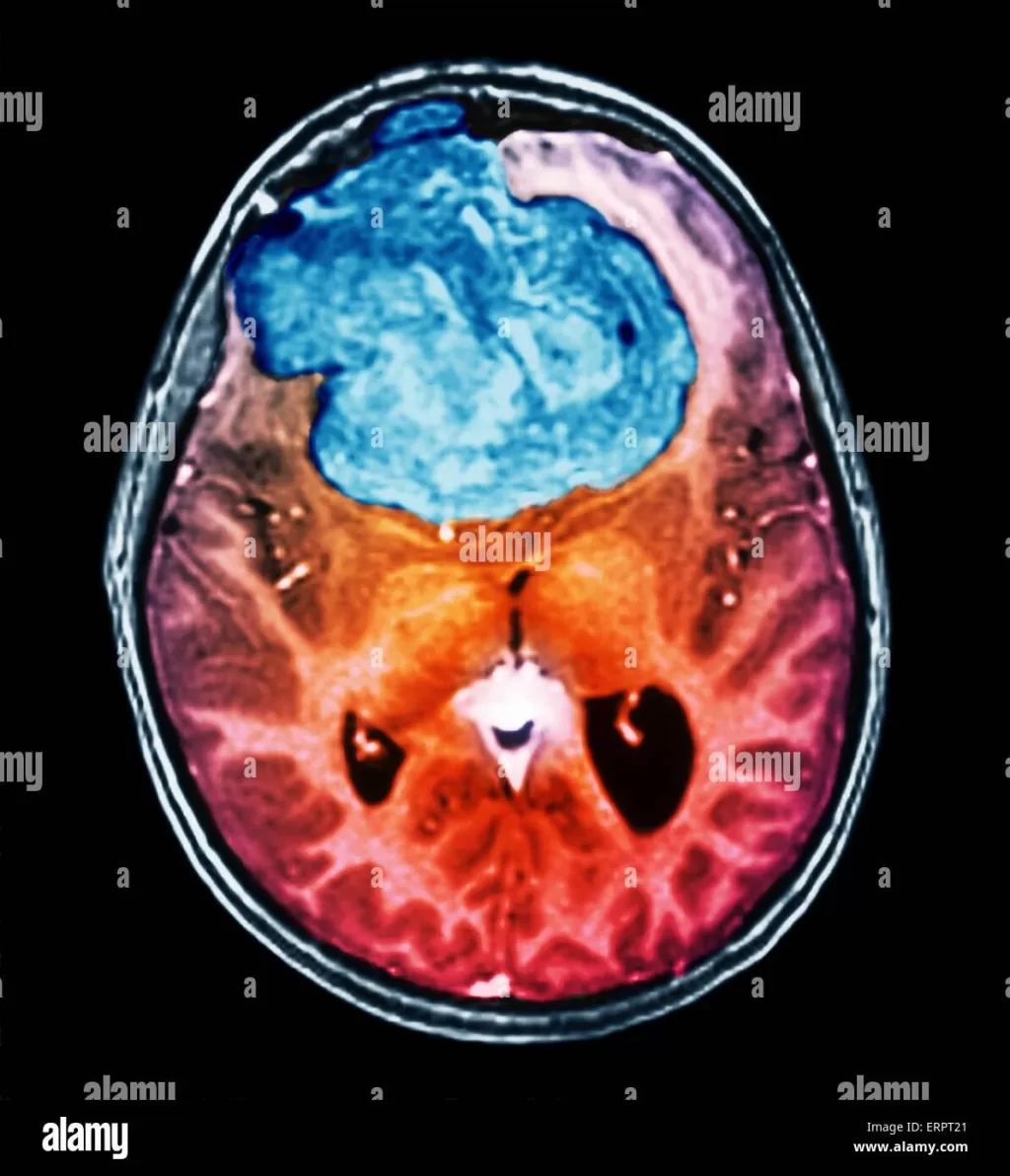
Benign brain tumors, also known as non-cancerous brain tumors, may not pose the same immediate threat as malignant tumors, but they still require careful attention due to their potential health implications. These tumors arise from abnormal cell growth within the brain and can lead to various brain tumor symptoms depending on their size and location. Understanding the different types of benign brain tumors, such as meningiomas and acoustic neuromas, is crucial for early detection and treatment. While the exact causes of brain tumors remain largely unknown, genetic predispositions and environmental factors may play a role in their development. Recognizing the risks of benign tumors is essential, as they can exert pressure on surrounding tissues, leading to significant health concerns.
Non-cancerous brain tumors, often referred to as benign brain tumors, represent a diverse group of growths that can impact individuals in various ways. Despite their benign classification, these tumors can still cause serious complications, making awareness of their symptoms and types vital for effective management. Various factors contribute to the development of these tumors, including genetic mutations and prior radiation exposure. The symptoms associated with benign tumors can range from mild headaches to severe neurological deficits, highlighting the need for prompt medical evaluation. Understanding the broader implications of benign brain tumors, including their risks and potential treatments, is essential for those affected and their healthcare providers.
Understanding Benign Brain Tumors: Definitions and Impact
Benign brain tumors, despite being classified as non-cancerous, hold significant implications for health and well-being. They arise from abnormal cell growth within the brain and often develop slowly, which can mask symptoms until they become pronounced. Recognizing that benign tumors can exert pressure on the surrounding brain tissues is crucial, as this pressure can lead to adverse neurological symptoms. Symptoms such as headaches, cognitive changes, and even seizures may arise, highlighting the importance of early detection and intervention.
Moreover, the emotional and psychological impact of being diagnosed with a benign brain tumor should not be overlooked. Individuals may grapple with fear and uncertainty about their health, despite the non-malignant nature of their condition. Understanding the implications and potential complications of benign tumors helps in fostering a proactive approach to treatment and management, ensuring that individuals receive the support and care they need.
Types of Benign Brain Tumors: A Closer Look
Benign brain tumors can be categorized into several types, each exhibiting unique characteristics and potential risks. Meningiomas, for instance, originate from the meninges, the protective membranes surrounding the brain. They are typically slow-growing but can lead to significant symptoms as they press against brain structures. Acoustic neuromas, another type, affect the vestibular nerve, commonly resulting in balance issues and hearing loss. Understanding these types is essential for recognizing the specific symptoms and treatment options available.
Pituitary adenomas and craniopharyngiomas are also significant types of benign brain tumors. Pituitary adenomas can disrupt hormonal balance, leading to varied symptoms such as vision issues and weight changes, while craniopharyngiomas often affect younger populations and can lead to hormonal production challenges. Each type’s distinct nature necessitates tailored approaches for diagnosis and treatment, emphasizing the need for comprehensive medical evaluations for those exhibiting symptoms.
Identifying Symptoms of Benign Brain Tumors
Identifying the symptoms associated with benign brain tumors is critical for early diagnosis and treatment. Common symptoms include persistent headaches, seizures, and changes in vision or hearing. These symptoms can vary significantly based on the tumor’s size and location within the brain. For example, headaches may intensify due to increased intracranial pressure, while seizures can occur suddenly, even in those with no prior history of seizure disorders.
Moreover, personality changes and cognitive difficulties can arise as benign tumors affect brain areas responsible for these functions. Nausea and vomiting may also manifest due to pressure on specific brain regions. Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to timely medical consultation, enabling healthcare providers to conduct appropriate diagnostic tests and potentially initiate treatment that can prevent further complications.
Exploring the Causes of Benign Brain Tumors
The exact causes of benign brain tumors remain largely elusive; however, several factors have been identified as contributors. Genetic predispositions play a significant role, particularly in conditions such as neurofibromatosis type 2, which dramatically increases the likelihood of developing these tumors. Additionally, individuals who have received radiation therapy to the head for previous cancers may have an elevated risk of benign tumor formation.
Environmental factors are also under scrutiny, with ongoing research investigating how exposure to certain chemicals or viruses may influence tumor development. While these connections are not fully understood, understanding the potential causes of benign tumors can help guide preventative measures and inform individuals about their risk factors, ultimately facilitating early intervention when symptoms arise.
Assessing the Risks and Concerns of Benign Brain Tumors
Although benign brain tumors are non-cancerous, they can pose significant health risks that warrant serious attention. One of the primary concerns is the increased intracranial pressure that can result from tumor growth. This pressure can lead to severe neurological complications, affecting motor functions, cognition, and overall quality of life. Thus, labeling benign tumors as harmless can lead to detrimental outcomes if they are not properly managed.
Additionally, the location of a benign tumor can exacerbate its risks. For instance, tumors near critical areas of the brain may result in profound deficits or changes in behavior and personality. Therefore, understanding the risks associated with benign tumors is essential for patients and healthcare providers alike, ensuring that appropriate monitoring and treatment strategies are implemented to mitigate potential complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of benign brain tumors?
Benign brain tumors can cause a variety of symptoms depending on their size and location. Common symptoms include persistent headaches, seizures, vision or hearing problems, nausea, vomiting, and personality changes. Recognizing these brain tumor symptoms is essential for early detection.
What types of benign brain tumors are there?
There are several types of benign brain tumors, including meningiomas, which grow on the protective membranes of the brain, acoustic neuromas that affect hearing and balance, pituitary adenomas that can disrupt hormonal function, and craniopharyngiomas often found in children. Each type has distinct characteristics and potential complications.
What causes benign brain tumors?
The exact causes of benign brain tumors remain unclear, but several factors may contribute. Genetic predispositions, such as neurofibromatosis type 2, previous radiation exposure to the head, and certain environmental factors could increase the risk of developing these non-cancerous brain tumors.
Are benign brain tumors serious and what are the risks?
Although categorized as non-cancerous, benign brain tumors can pose serious health risks. They can lead to increased intracranial pressure and neurological deficits, affecting motor functions and cognitive abilities. Therefore, timely diagnosis and treatment are important to manage these risks.
How are benign brain tumors diagnosed and treated?
Diagnosis of benign brain tumors typically involves imaging tests such as MRI or CT scans to visualize the tumor. Treatment options may vary from monitoring the tumor to surgical removal, dependent on the tumor’s size, location, and symptoms. Early intervention can help prevent complications associated with these tumors.
| Key Points | Description |
|---|---|
| What is a Benign Brain Tumor? | A non-cancerous growth in the brain that can exert pressure on surrounding tissues, leading to neurological symptoms. |
| Key Types of Benign Brain Tumors | Includes meningiomas, acoustic neuromas, pituitary adenomas, and craniopharyngiomas, each with specific symptoms. |
| Symptoms | Common symptoms include headaches, seizures, vision/hearing problems, nausea, and personality changes. |
| Causes | Unknown, but factors include genetics, previous radiation exposure, and potential environmental influences. |
| Risks and Concerns | Can lead to increased intracranial pressure and neurological deficits, requiring medical attention. |
| Recent Developments | Personal stories and celebrity experiences raise awareness about the emotional impact of benign brain tumors. |
Summary
Benign brain tumors, despite their non-cancerous classification, can pose significant health risks and affect quality of life. Understanding these tumors, including their types, symptoms, and potential complications, is essential for early detection and treatment. Individuals experiencing symptoms associated with benign brain tumors should consult healthcare professionals for timely intervention to prevent severe consequences.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.