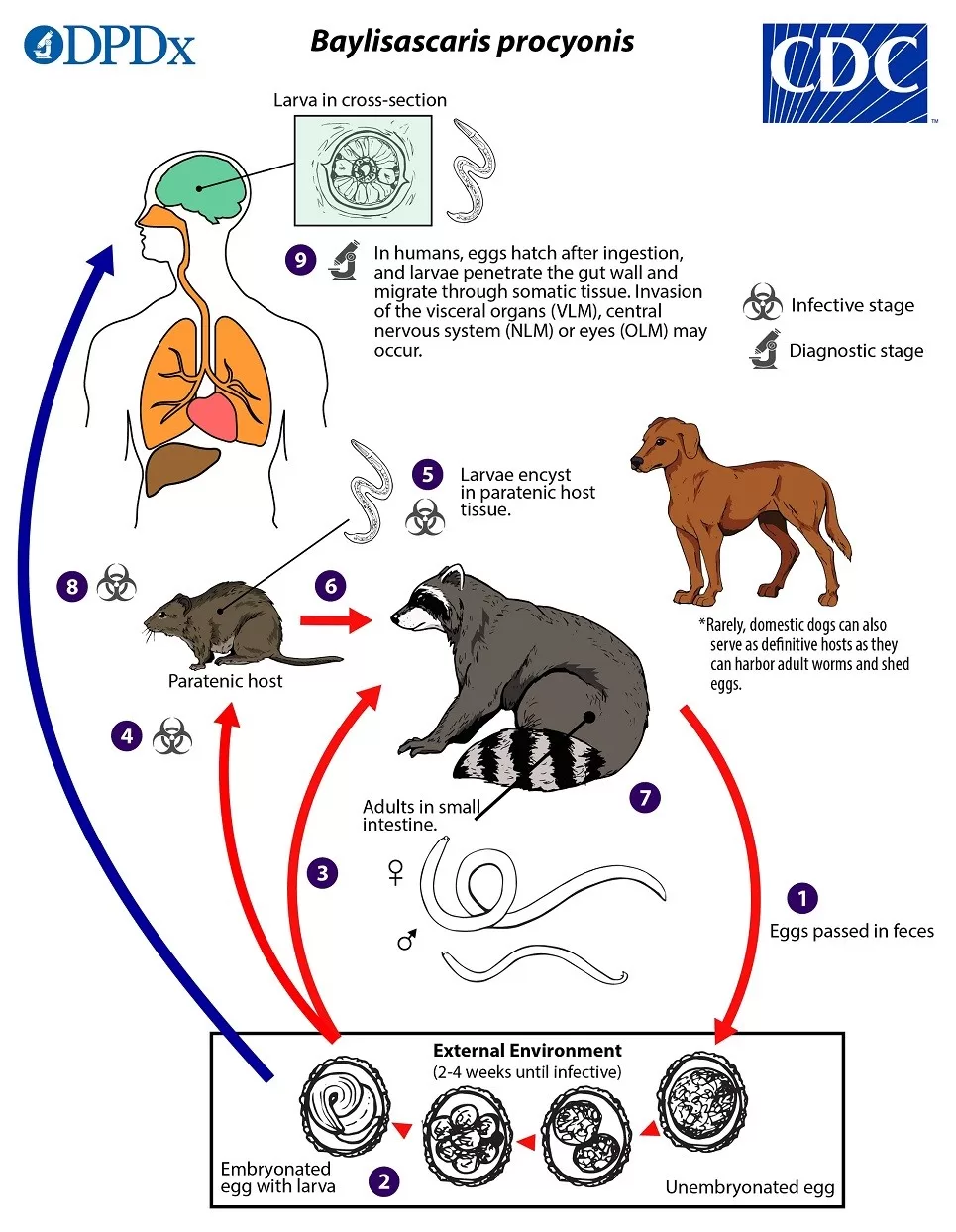
Baylisascaris procyonis, a concerning zoonotic nematode, has recently been identified in common raccoons, scientifically known as Procyon lotor, across Mexico. This roundworm poses significant health risks as it can lead to baylisascariasis, a parasitic infection that might affect humans, particularly in areas where these animals encroach upon urban environments. The alarming presence of Baylisascaris procyonis in these regions is raising awareness around the potential for human infections, especially among children who may come into contact with contaminated environments. As raccoons increasingly adapt to human-dominated areas, the threat of this parasite spreading further necessitates immediate attention in public health discussions. Enhanced understanding and surveillance are critical to mitigating the risks associated with this emerging zoonotic threat to human health.
The recent discovery of the Baylisascaris procyonis roundworm in the common raccoon, Procyon lotor, highlights important implications for both wildlife and public health. This particular zoonotic nematode is gaining notoriety due to its ability to infect a wide range of hosts, raising concerns about potential baylisascariasis outbreaks in human populations. The increasing interaction between raccoons and urban communities may heighten exposure to these harmful parasites, especially among vulnerable groups like children and pets. With situations evolving in Mexico, where this infection has been notably observed, it is vital to prioritize monitoring and education efforts to prevent future health complications. As we delve deeper into the life cycle and transmission dynamics of this roundworm, a proactive approach is essential to safeguard public health.
Understanding Baylisascaris procyonis: Zoonotic Threats from Raccoons
Baylisascaris procyonis is a parasitic roundworm predominantly found in common raccoons (Procyon lotor). This zoonotic nematode poses significant health risks to humans and other animals that inadvertently consume its eggs. The life cycle of this parasite involves raccoons as definitive hosts, where they harbor adult worms in their intestines, shedding eggs in their feces. Given their increased presence in urban and suburban areas, the risk of transmission to humans is elevated, particularly in places where children and pets might come into contact with contaminated soil or environments.
The public health implications of Baylisascaris procyonis are pressing, especially in regions like Mexico, where the raccoon population is expanding. Exposure to the eggs of this roundworm can lead to severe neurological conditions in humans, known as baylisascariasis. Efforts must be made to raise awareness and educate communities about the risks associated with raccoon encounters and proper hygiene practices to minimize infection chances. This includes avoiding direct contact with raccoon feces and ensuring that children do not play in potentially contaminated areas.
Baylisascaris procyonis in Urban Environments of Mexico
The increasing adaptation of the common raccoon (Procyon lotor) to urban environments in Mexico significantly impacts the transmission dynamics of Baylisascaris procyonis. As these animals thrive in urban settings, they come into closer contact with human populations, amplifying the risks associated with their parasitic infections. Studies have indicated that areas with higher raccoon populations are at greater risk for outbreaks of baylisascariasis, underscoring the need for enhanced monitoring and control measures in these urban ecosystems.
Moreover, the prevalence of Baylisascaris procyonis in raccoons is not just a concern for public health; it poses challenges for animal health as well. Domestic animals, particularly dogs, can become infected by ingesting the eggs present in the environment. This transmission pathway highlights how intertwined wildlife health and public health are, emphasizing the need for a One Health approach to address these issues holistically. Enhanced surveillance of raccoon populations and educational campaigns for pet owners are vital steps in preventing baylisascariasis and protecting both humans and domestic animals.
Consequences of Baylisascaris procyonis Infection in Humans
Infection with Baylisascaris procyonis can lead to severe health outcomes in humans, particularly in children who are more susceptible due to their exploration habits. Symptoms of baylisascariasis can manifest as serious neurological damage, including encephalitis, which may lead to lifelong disability or even death. Understanding the clinical features associated with this zoonotic nematode is crucial for providing timely medical intervention, which can be the difference between full recovery and irreversible damage.
Additionally, the moral and financial implications of an outbreak of baylisascariasis extend beyond individual victims. Public health systems may face overwhelming challenges, from rising healthcare costs to the necessity for community education and prevention programs. The importance of integrating baylisascariasis awareness into public health policies cannot be overstated, particularly in areas where encounters between humans and raccoons are frequent.
Surveillance Strategies for Baylisascaris procyonis
Effective surveillance for Baylisascaris procyonis is paramount in reducing the incidence of this zoonotic disease. This includes monitoring raccoon populations and their habitats, particularly in urban settings where potential human-raccoon interactions are prevalent. The implementation of regular fecal sampling from raccoon populations can help detect the presence of B. procyonis eggs, allowing for timely public health responses to mitigate risks.
Furthermore, training for healthcare providers to recognize the signs and symptoms of baylisascariasis is crucial. This awareness will facilitate prompt diagnoses and interventions, ultimately reducing morbidity and mortality associated with the infection. Integrating community involvement in surveillance efforts can also be beneficial, as local citizens can report unusual raccoon behaviors or increases in population density, leading to proactive measures against potential outbreaks.
Public Health Initiatives Against Baylisascaris procyonis
Public health initiatives focused on raising awareness about Baylisascaris procyonis are essential in preventing zoonotic infections. Local governments and health organizations should organize regular vaccination and deworming campaigns for domestic pets, coupled with educational programs that inform communities about the risks associated with raccoon interactions. Effective communication strategies that address the significance of avoiding contact with wildlife droppings can play a vital role in minimizing infection rates.
Additionally, collaboration with wildlife management authorities is necessary to establish safe raccoon population control measures that respect ecological balance while protecting human health. By fostering partnerships among public health officials, veterinarians, and ecologists, comprehensive strategies can be developed to monitor and manage the risks posed by Baylisascaris procyonis effectively.
The Ecological Role of Raccoons and Baylisascaris procyonis
Raccoons (Procyon lotor) are important ecological players within their environments, participating in seed dispersal and maintaining the health of their habitats. However, the role of these animals must be considered within the context of their association with Baylisascaris procyonis and the zoonotic threats they pose. While raccoons contribute to biodiversity, their ability to transmit zoonotic diseases can lead to significant public health challenges, particularly as they proliferate in human-dominated areas.
Balancing ecological preservation with public health initiatives regarding B. procyonis requires informed policy decisions. Studies into the ecological impacts of raccoon populations must be weighed alongside their potential health risks. Sustainable management practices can help maintain the ecological benefits while protecting communities from the hazards posed by this zoonotic nematode.
Complications Arising from Baylisascaris procyonis Infection
The ramifications of Baylisascaris procyonis infection in humans can be extensive, affecting not only individual health but also public health systems. In severe cases, the neurological damage caused by this zoonotic nematode can lead to complications such as vision loss, paralysis, or cognitive impairments. Understanding the spectrum of complications linked to B. procyonis is crucial for healthcare professionals to devise appropriate treatment plans.
Moreover, addressing the psychological effects of such a diagnosis on patients and families is equally important. The fear of infection and its potential consequences can lead to anxiety and stress, indicating the need for supportive mental health services in conjunction with medical treatment. Recognizing and managing these complications will enhance the overall care provided to affected individuals.
Environmental Factors Influencing Baylisascaris procyonis Transmission
Environmental factors significantly influence the transmission dynamics of Baylisascaris procyonis. Urbanization, land development, and changes in land use can disrupt raccoon habitats, pushing them closer to human dwellings. In addition, environmental conditions that favor the survival of B. procyonis eggs in the soil can heighten the risk of transmission to humans and pets. Factors such as temperature, moisture levels, and soil composition play crucial roles in the lifecycle of this zoonotic nematode.
Mitigating environmental risks requires understanding these ecological dynamics and implementing strategic urban planning. Landscape management that considers raccoon habitats and effectively limits their exposure to human populations could reduce infection rates significantly. Furthermore, maintaining clean environments around residential areas and educating communities about proper waste disposal can effectively minimize interactions between raccoons and humans.
Research Directions for Baylisascaris procyonis
Continued research is essential to better understand Baylisascaris procyonis and its implications for human and animal health. Future studies should focus on the genetic diversity of this roundworm and its various strains, which could provide insights into transmission patterns and pathogenicity. Investigating how environmental changes influence B. procyonis dynamics will also be pivotal in developing effective public health strategies to combat baylisascariasis.
Furthermore, interdisciplinary research that integrates veterinary science, wildlife ecology, and epidemiology could yield innovative approaches to manage and mitigate risks associated with this zoonotic nematode. Collaborating with international health organizations can also facilitate knowledge exchange and promote comprehensive strategies for monitoring and controlling B. procyonis worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Baylisascaris procyonis and where is it commonly found?
Baylisascaris procyonis is a zoonotic nematode, or roundworm, predominantly found in the common raccoon (*Procyon lotor*). This parasite is prevalent in North America and its geographic distribution has now extended into Mexico, as noted in recent studies. Its presence raises concerns for human health, particularly in environments where raccoons frequent.
How does Baylisascaris procyonis affect humans?
Infections from Baylisascaris procyonis can lead to serious health conditions in humans, particularly when individuals ingest fertile eggs from contaminated environments. The parasite can cause baylisascariasis, which may affect the nervous system and lead to severe neurological symptoms.
What is baylisascariasis and how is it transmitted?
Baylisascariasis is an infection caused by the Baylisascaris procyonis roundworm. It is transmitted through accidental ingestion of raccoon feces containing viable eggs, often occurring in contaminated soil or water. Increased interaction between raccoons and human populations, especially in urban settings, heightens the risk of transmission.
Why is the study of Baylisascaris procyonis in Mexico important?
Studying Baylisascaris procyonis in Mexico highlights the potential risks of human infection due to the expanding range of the common raccoon, especially in urban areas. Understanding its geographic spread and infection dynamics is crucial for public health measures aimed at preventing baylisascariasis in local populations.
What preventive measures are recommended against Baylisascaris procyonis?
Preventive measures against Baylisascaris procyonis include increasing public awareness about the risks associated with raccoon feces, promoting proper sanitation in areas where raccoons live, and encouraging healthcare providers to educate families, particularly those with children, about the dangers of potential exposure to this zoonotic nematode.
How is Baylisascaris procyonis linked to the common raccoon (Procyon lotor)?
Baylisascaris procyonis is specifically associated with the common raccoon (*Procyon lotor*), as this species serves as the primary host for the roundworm. The lifecycle of the parasite involves raccoons shedding eggs in their feces, which can contaminate surrounding environments and pose risks to other animals and humans.
What findings were reported regarding Baylisascaris procyonis in Mexican raccoons?
Recent findings indicate that Baylisascaris procyonis roundworms have been detected in common raccoons in Mexico, suggesting not only the presence of this zoonotic nematode but also a potential increase in human infection risks. This underscores the importance of ecosystem health and monitoring wildlife diseases.
Are there specific groups at higher risk for baylisascariasis?
Yes, children and other individuals who frequently play in or interact with environments where raccoons may have defecated are at higher risk for baylisascariasis. Additionally, pets that may scavenge or come into contact with raccoon feces can also pose indirect risks to their owners.
What is the significance of increased awareness of Baylisascaris procyonis?
Increased awareness of Baylisascaris procyonis is vital for public health, as it encourages preventive actions and educational initiatives aimed at reducing the risk of infection. Surveillance of raccoon populations and potential human engagement can help control and prevent the spread of this zoonotic nematode in urban areas.
How do environmental changes contribute to the spread of Baylisascaris procyonis?
Environmental changes, such as urbanization and habitat encroachment, facilitate the interaction between common raccoons (*Procyon lotor*) and humans. As raccoons expand into urban areas, the likelihood of contact increases, leading to a higher risk of humans encountering Baylisascaris procyonis eggs and potentially contracting baylisascariasis.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Research Letter | Study on *Baylisascaris procyonis* in raccoons in Mexico. |
| Authors | Ana Luisa Gómez-Sánchez and others from Instituto de Ecología-INECOL A.C. |
| Significance | Highlights the zoonotic risks posed by the roundworm, especially in urban areas. |
| Geographic Spread | Indicates a wider geographic distribution of the nematode in the Americas. |
| Prevention | Calls for increased surveillance and awareness among healthcare providers to prevent infections. |
Summary
Baylisascaris procyonis is a significant zoonotic nematode discovered in common raccoons in Mexico. This study shows that as raccoons expand into human habitats, the risks of human infections increase, particularly in urban settings where children and pets may encounter contaminated environments. Increased surveillance and education are critical to mitigate the risks associated with baylisascariasis, protecting public health in vulnerable populations.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.