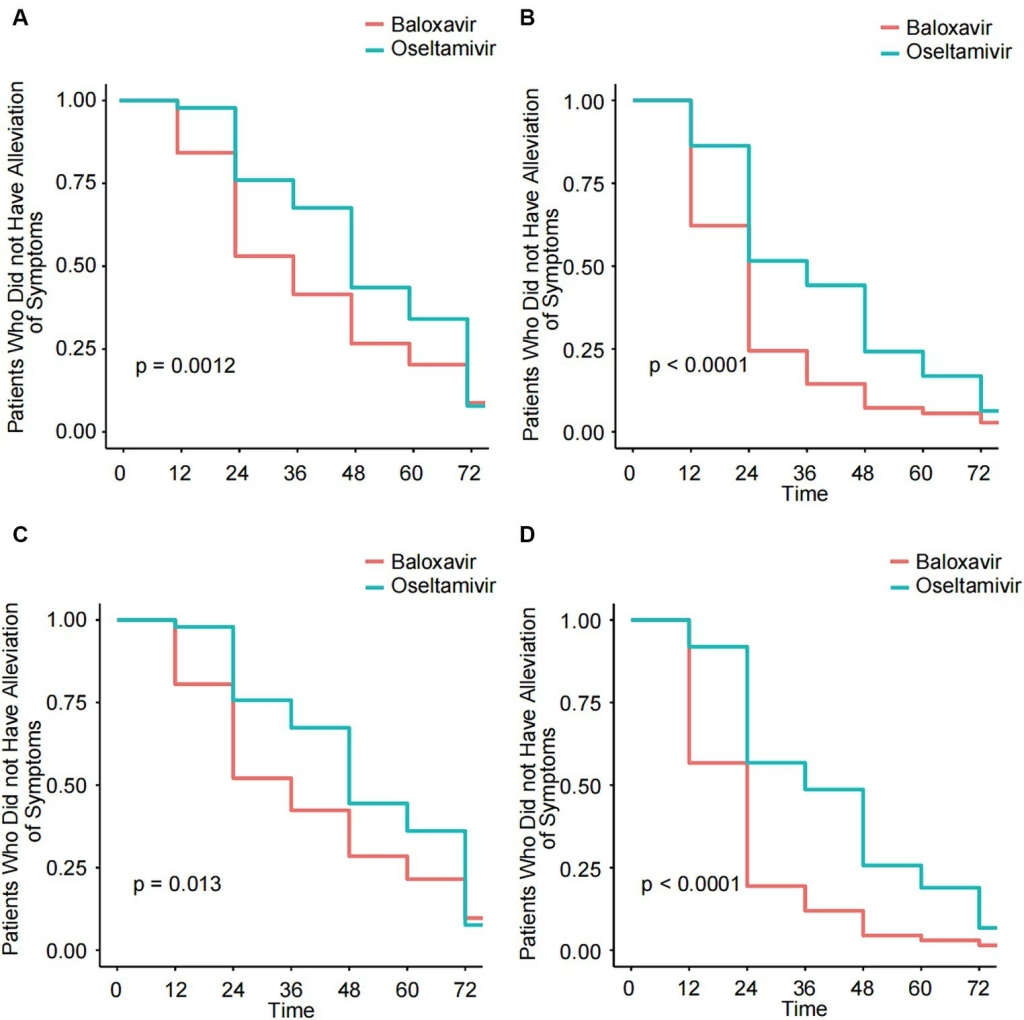
The effectiveness of baloxavir (Xofluza) in treating influenza has become a focal point of recent research, particularly when compared to traditional therapies like oseltamivir (Tamiflu). A comprehensive study utilizing electronic health records from over 75,000 patients highlights that baloxavir significantly reduces hospitalization and emergency department visits. Published in the _International Journal of Infectious Diseases_, this research indicates that baloxavir outperforms oseltamivir, suggesting a shift in how influenza treatment options may be viewed. Notably, the findings reveal that younger adults and females experienced better results with baloxavir, showcasing its potential benefits across demographics. As these insights unfold, the growing emphasis on antiviral drug comparisons furthers the dialogue surrounding optimal treatment choices for influenza.
When discussing flu medications, baloxavir emerges as a promising alternative to oseltamivir, showing impressive results in reducing severe outcomes such as hospitalizations. The latest virtual health records study adds clarity to influenza treatment options by providing compelling evidence that baloxavir may lead to fewer emergency visits and shorter recovery times. This research underscores the critical need for healthcare providers to consider newer antiviral medications amid rising hospitalization rates during flu seasons. As patients seek effective remedies, understanding the nuances of antiviral efficacy becomes increasingly vital. By analyzing patient data from various healthcare settings, the implications of these findings could reshape influenza management strategies.
Understanding Baloxavir’s Effectiveness in Influenza Treatment
Baloxavir, commercially known as Xofluza, has garnered attention in recent years as a potent treatment option for influenza. A recent study published in the International Journal of Infectious Diseases highlights its effectiveness, particularly in reducing hospitalization rates compared to oseltamivir, commonly referred to as Tamiflu. This evaluation of real-world healthcare data sheds light on how baloxavir can outperform its counterparts in clinical settings. Although both antiviral drugs are designed to fight influenza, patient outcomes suggest that baloxavir offers significant benefits in managing the symptoms and consequences of this viral infection.
In the analysis involving over 75,000 patients, researchers reported a stark difference in hospitalization rates: only 0.8% of those treated with baloxavir required hospital care after six months, compared to 5.3% of those receiving oseltamivir. This disparity could suggest that patients treated with baloxavir might experience not just faster symptom resolution but potentially lower rates of secondary complications that can lead to hospitalization. The findings underscore the need for clinicians to evaluate baloxavir as a favorable option in treating influenza, particularly among demographics that exhibit a higher susceptibility to severe illness.
Baloxavir vs Oseltamivir: A Comparative Analysis
Comparing the two antiviral agents, baloxavir and oseltamivir, reveals crucial insights into their respective efficacies in treating influenza. While oseltamivir has been a staple in influenza management for years, recent findings suggest that it may not be as effective in reducing emergency department visits and hospitalizations as baloxavir. In a study assessing the outcomes for patients treated between 2016 and 2023, researchers observed that those on baloxavir had lower rates of both ED visits and hospitalizations, particularly among females and younger adults. This poses a compelling case for clinicians to consider baloxavir as the first-line treatment, especially when treating populations most at risk for severe outcomes.
The differences in effectiveness between these two antivirals are significant, but it is important to consider the broader implications of these findings. With rising hospitalization rates during peak flu seasons, utilizing baloxavir could translate to considerable savings for healthcare systems. By potentially reducing the number of patients requiring inpatient care, healthcare providers might alleviate pressure on emergency services, making room for urgent medical situations when flu outbreaks become more severe. Thus, the baloxavir vs oseltamivir comparison not only informs clinical practice but also emphasizes the importance of effective influenza management strategies in public health.
The Impact of Influenza Treatment on Healthcare Utilization
The implications of effective influenza treatment extend beyond patient health outcomes; they significantly affect healthcare utilization patterns. With the increasing burden of influenza on healthcare systems globally, identifying treatments that minimize emergency department visits and hospitalizations is paramount. Baloxavir’s effectiveness at reducing hospitalizations, as evidenced by recent analyses, indicates a positive shift towards improved healthcare efficiency during flu seasons. This finding suggests that utilizing baloxavir not only benefits patients but also helps conserve clinical resources.
In a landscape where influenza treatments are essential for mitigating the impact of seasonal flu outbreaks, understanding treatment patterns through electronic health records helps illuminate the trends in healthcare utilization. The reported decrease in ED visits among baloxavir recipients is an essential part of this larger narrative. As healthcare organizations aim to innovate patient care pathways, embracing treatments that streamline care while enhancing patient recovery timelines becomes crucial for optimizing healthcare delivery.
Examining Patient Demographics in Influenza Outcomes
Patient demographics play a crucial role in evaluating treatment outcomes for influenza. The recent study revealed that baloxavir showed significant effectiveness particularly among females and younger adults, which is essential information for tailoring treatment strategies. The variance in response to antiviral medications based on age and gender underlines the necessity for personalized healthcare approaches in managing influenza. Understanding how different groups respond to treatments can better inform physicians about which patients may benefit most from baloxavir over oseltamivir.
This demographic focus is particularly important as healthcare systems seek to ensure equity in treatment access and outcomes. For younger patients and women, who may experience a disproportionate burden of flu severity, deploying effective treatments like baloxavir may significantly alter their clinical trajectory. Future research should further explore how demographic factors influence treatment efficacy, ensuring that all patient profiles are appropriately considered in clinical guidelines. Such knowledge is vital in refining treatment protocols for influenza and improving patient care.
Real-World Effectiveness vs Clinical Trials: A Closer Look
Real-world effectiveness studies provide invaluable insights into how treatments perform outside the controlled environment of clinical trials. The recent findings corroborate earlier clinical trial results that suggested baloxavir might reduce viral load more rapidly than oseltamivir. Understanding the real-world context can often highlight potential advantages of a drug that might not surface in a clinical trial setting, especially when patient populations are considered. The comprehensive analysis of healthcare usage and outcomes in this large study reinforces the clinical relevance of baloxavir in treating influenza.
However, it is crucial to recognize the limitations inherent in real-world studies, such as potential biases and the absence of certain patient-reported outcomes. While the retrospective design of this specific study offers compelling evidence regarding baloxavir’s effectiveness, ongoing research must address these gaps to provide clearer insights. Future studies should also consider cost-effectiveness analyses of antiviral treatments, ensuring that healthcare providers can make informed decisions based on overall value to the healthcare system.
The Future of Influenza Treatment Strategies
The evolving landscape of influenza treatment strategies indicates a growing emphasis on novel antiviral agents like baloxavir. As healthcare systems increasingly prioritize patient outcomes and efficiency, adopting treatments that demonstrate superior effectiveness will become vital. The insights drawn from the recent electronic health record study not only advocate for baloxavir’s use but also highlight the changing paradigms in how influenza is treated in clinical practice. Moving forward, integrating innovative therapies could greatly enhance management protocols in the face of seasonal influenza outbreaks.
Moreover, with the importance of addressing influenza’s seasonal variability, healthcare practitioners should also consider including baloxavir in treatment guidelines to optimize patient care during peak flu seasons. As research continues to support its effectiveness, especially among vulnerable populations, embracing baloxavir may be instrumental in shaping future influenza treatment frameworks. Clearly defined protocols that incorporate evidence-based strategies will bolster public health responses to influenza, promoting timely and efficient healthcare interventions.
Monitoring the Safety Profile of Baloxavir
As baloxavir gains traction as a preferred treatment for influenza, understanding its safety profile remains a key concern for healthcare practitioners. Ongoing surveillance of adverse effects and patient outcomes is crucial for ensuring the holistic safety of this antiviral agent. The study cited earlier indicates low hospitalization rates and few recorded deaths within both the oseltamivir and baloxavir groups, suggesting a favorable safety outcome. Nonetheless, continuous monitoring beyond clinical trials is necessary to fully understand the implications of baloxavir use in diverse patient populations.
Moreover, adopting a vigilant approach to pharmacovigilance—especially within real-world settings—can aid in identifying any uncommon side effects that may not have surfaced during controlled trials. Tracking patient-reported outcomes in various demographics will contribute significantly to this knowledge base. As more healthcare providers incorporate baloxavir into their treatment regimens, ensuring patients are informed about potential risks will uphold high standards of patient safety and care.
The Role of Virtual Health Records in Influenza Research
Virtual health records have become an essential tool in modern healthcare research, particularly in tracking and analyzing treatment outcomes for conditions like influenza. The utilization of electronic health records in studying real-world data provides a vast and detailed framework for understanding how various antiviral therapies perform across different populations. The study discussed previously leveraged health record data from numerous organizations, illustrating how digital resources can illuminate patterns in healthcare utilization and patient outcomes. This method offers a unique advantage of reaching diverse patient populations, surpassing the limitations often found in traditional clinical trials.
In the context of influenza treatment, virtual health records allow for the continuous monitoring of antiviral drug efficacy and safety in real-time. This dynamic, data-driven approach not only aids researchers in drawing connections between treatment modalities like baloxavir and improved patient outcomes but also helps in identifying potential gaps in knowledge about treatment protocols across different demographics. The future of influenza research will undoubtedly rely increasingly on virtual health records, ensuring that healthcare providers can make informed decisions based on comprehensive data and trends.
Conclusion: Moving Towards Optimized Influenza Management
In conclusion, the emerging data on baloxavir’s effectiveness in treating influenza positions it as a valuable tool for optimizing patient management. With the ability to substantially reduce hospitalization rates and emergency department visits, baloxavir showcases a significant advancement in antiviral strategies relative to traditional treatments like oseltamivir. As healthcare systems continue to grapple with the implications of seasonal flu outbreaks, utilizing drugs that demonstrate lower rates of severe outcomes will be critical.
The collective findings from today’s research, along with ongoing advancements in treatment protocols, call for a reevaluation of how influenza is managed in clinical practice. By placing emphasis on innovative treatments and integrating insights gathered from patient data, healthcare providers can enhance overall care for influenza patients. In doing so, the field will not only improve patient outcomes but will also ease the burden on healthcare infrastructure as we adapt to the ongoing challenges posed by influenza virus dynamics.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does baloxavir effectiveness compare to oseltamivir for influenza treatment?
Baloxavir has been found to reduce hospitalizations and emergency department visits more effectively than oseltamivir in patients treated for influenza. In a study published in the _International Journal of Infectious Diseases_, it was reported that only 0.8% of baloxavir users were hospitalized compared to 5.3% of those treated with oseltamivir at the six-month follow-up, indicating superior effectiveness of baloxavir.
What impact does baloxavir have on hospitalization rates for influenza patients?
The effectiveness of baloxavir in reducing hospitalization rates is significant. Data from a study showed that among influenza patients treated with baloxavir, only 0.8% were hospitalized at six months, compared to 5.3% for those receiving oseltamivir, highlighting baloxavir’s potential as a more effective antiviral drug in real-world settings.
Are there specific demographics for which baloxavir effectiveness is more pronounced?
Yes, baloxavir effectiveness appears to be particularly pronounced among females and younger adults. The study indicated that these groups experienced significantly fewer hospitalizations when treated with baloxavir compared to oseltamivir, suggesting that baloxavir may be a preferable choice for these demographics in influenza treatment.
What does the virtual health records study reveal about baloxavir’s effectiveness?
The virtual health records study provides real-world evidence supporting baloxavir’s effectiveness over oseltamivir in treating influenza. It analyzed data from over 75,000 patients and concluded that baloxavir was associated with fewer hospitalizations and emergency department visits, reinforcing its role as a strong option in influenza treatment.
Can baloxavir reduce emergency department visits compared to oseltamivir?
Yes, baloxavir has been shown to reduce emergency department visits more effectively than oseltamivir. In the mentioned study, 5.0% of baloxavir patients visited the ED after six months, compared to 7.2% of oseltamivir patients, showcasing baloxavir’s superior effectiveness in managing influenza symptoms.
How do baloxavir and oseltamivir compare in terms of rapid viral load reduction?
Baloxavir may offer a more rapid reduction in viral load compared to oseltamivir, as suggested by earlier trials and supported by the recent study findings. This quicker action could lead to faster symptom resolution, contributing to its overall effectiveness in treating influenza infections.
What are the limitations of the study comparing baloxavir and oseltamivir?
While the study highlighted important differences in the effectiveness of baloxavir and oseltamivir, it had limitations such as its retrospective design, a smaller number of baloxavir users, and a lack of racial diversity. The authors noted the need for further research to include diverse populations and patient-reported outcomes for a comprehensive understanding.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Overview | The study used electronic health record data from over 75,000 US patients comparing baloxavir and oseltamivir. |
| Hospitalization Rates | At six months, 5.3% of oseltamivir users were hospitalized vs. 0.8% of baloxavir users. |
| ED Visits | 7.2% of oseltamivir users visited the ED at six months compared to 5.0% for baloxavir users. |
| Effectiveness by Demographics | Baloxavir showed greater effectiveness in reducing hospitalizations and ED visits in females and adults under 50. |
| Previous Findings | Previous studies support baloxavir’s quicker reduction of viral load and better symptom resolution than oseltamivir. |
| Limitations | The study had a retrospective design, limited baloxavir sample size, and lacked patient-reported outcomes. |
Summary
Baloxavir effectiveness has been highlighted in a recent study which found that it may significantly reduce hospitalizations and emergency department visits compared to oseltamivir in patients treated for influenza. The data from over 75,000 patients indicate a clear advantage of baloxavir in both young and female populations, maintaining a trend of better outcomes as suggested by previous research. Given the critical role of antiviral treatments during severe flu seasons, further research is essential to explore diverse populations and patient outcomes to fully assess baloxavir’s potential in clinical practice.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.