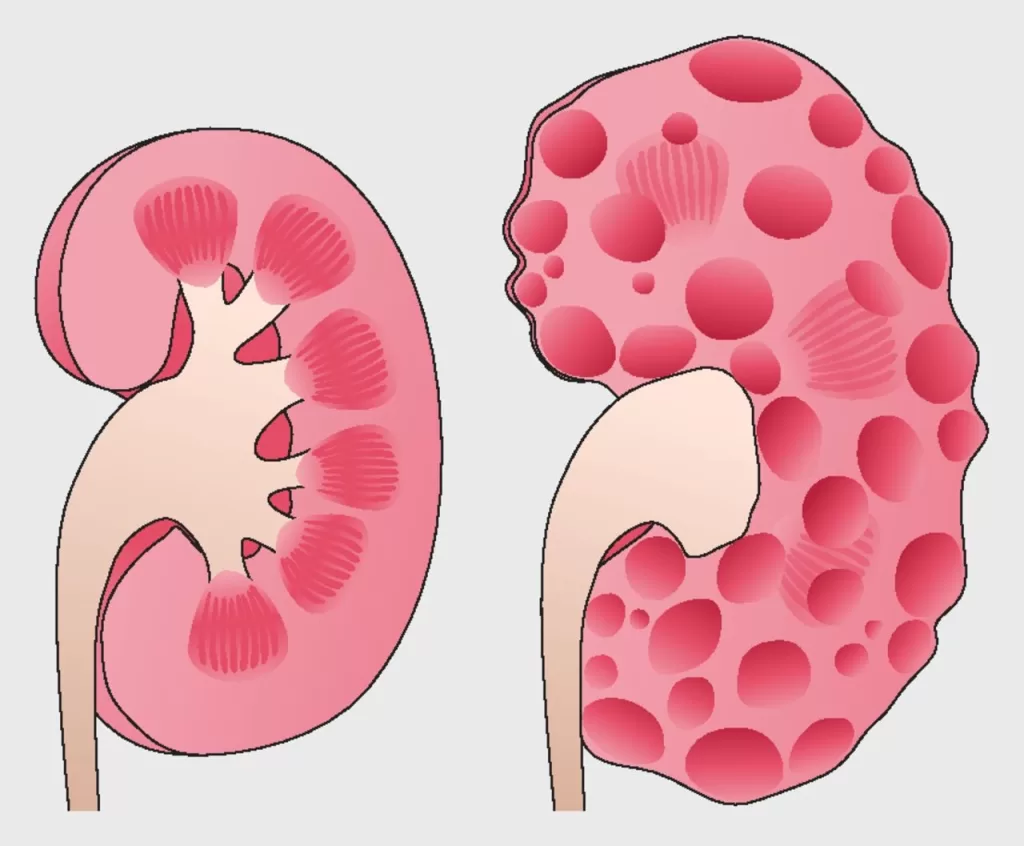
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD) is a hereditary condition that poses significant challenges to kidney health and overall well-being. This genetic disorder affects approximately 1 in every 400 to 1,000 individuals, often leading to debilitating symptoms such as abdominal pain, hypertension, and, in severe cases, kidney failure. Understanding the symptoms of ADPKD is essential for early diagnosis and management, as timely intervention can greatly improve patient outcomes. Recent research on ADPKD has unveiled promising treatment options aimed at slowing disease progression and addressing complications effectively. As awareness grows around the Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease overview, it is crucial for individuals and healthcare professionals to stay informed about the latest advancements in ADPKD treatment options and research discoveries.
Known for its impact on kidney function, Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease, often referred to as ADPKD, is a prevalent genetic disorder that causes the formation of numerous cysts in the kidneys. This condition not only affects renal health but can also lead to various complications, including hypertension and end-stage renal disease. Individuals with this genetic predisposition may experience a wide range of symptoms, making awareness and understanding of ADPKD vital for effective management. With ongoing research shedding light on new therapeutic strategies, patients can benefit from the most current ADPKD treatment options available. By recognizing the complexities of this condition, we can foster a better understanding of its implications and improve care for those affected.
Understanding Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD)
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD) is a genetic disorder that primarily affects the kidneys, leading to the growth of numerous cysts. These cysts can significantly impair kidney function and result in a variety of health complications. Due to its autosomal dominant inheritance pattern, only one copy of the mutated gene, either from the mother or father, is necessary for the disease to manifest. This means that individuals with a parent affected by the disease have a 50% chance of inheriting it themselves, thus emphasizing the importance of genetic counseling and awareness in families with a history of ADPKD.
The prevalence of ADPKD is notable, affecting approximately 1 in every 400 to 1,000 individuals, making it the most common hereditary kidney disorder. Symptoms often appear between the ages of 30 and 50, and they can range from mild discomfort to severe complications, such as hypertension and renal failure. Understanding the early signs and symptoms is crucial for timely diagnosis and management, which can significantly affect the quality of life and overall kidney health in affected individuals.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of ADPKD
The symptoms of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease can vary considerably among individuals. Commonly reported symptoms include abdominal pain due to the pressure from growing cysts, chronic hypertension, and back pain. In some cases, patients may also experience headaches and urinary tract infections. The variability in symptom severity means that not all individuals will face the same health challenges, which can complicate the diagnosis.
Diagnosis of ADPKD typically involves imaging tests such as ultrasounds or CT scans, which can visualize the cysts in the kidneys. Genetic testing is also a valuable tool, particularly for those with a family history of the disease. Identifying the presence of specific mutations can confirm the diagnosis and help guide treatment decisions. Early diagnosis is essential as it allows for better management of symptoms and can slow the progression of the disease.
Recent Research Developments in ADPKD
Recent research into Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease has unveiled significant insights that could change treatment approaches. For instance, studies conducted by Kalamazoo researchers have identified new genetic factors influencing cyst growth. This research holds promise for developing targeted therapies that could potentially halt or slow the progression of ADPKD, offering hope to millions affected by this condition.
Moreover, ongoing studies are exploring the impact of race and socioeconomic factors on the outcomes of patients with ADPKD. Understanding these disparities is crucial for ensuring that all patients have access to effective treatments and healthcare resources. As the medical community continues to investigate the complexities of ADPKD, findings from this research will play a vital role in shaping future treatment protocols and improving patient care.
Treatment Options for ADPKD
While there is currently no cure for Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease, several treatment options aim to alleviate symptoms and slow disease progression. One of the most promising treatments is Tolvaptan, a medication that has shown efficacy in slowing kidney enlargement and preserving kidney function. Clinical trials, such as the TEMPO trial, have provided substantial evidence supporting the use of this drug in managing ADPKD.
In addition to medication, managing hypertension through lifestyle modifications and pharmacological interventions is critical for patients with ADPKD. Maintaining optimal blood pressure can significantly reduce the risk of complications, including kidney damage. A multidisciplinary approach, involving nephrologists, dietitians, and other healthcare professionals, is recommended to provide comprehensive care tailored to the individual needs of ADPKD patients.
Complications Associated with ADPKD
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease can lead to a range of serious complications if left unmanaged. One of the most severe outcomes is the progression to End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD), which may require dialysis or kidney transplantation. This progression underscores the importance of regular monitoring and proactive management of the disease to mitigate its effects on kidney function.
In addition to renal complications, individuals with ADPKD may also develop liver cysts and face an increased risk of intracranial aneurysms. These complications can lead to significant health issues, including liver dysfunction and neurological problems. Awareness of these potential complications is crucial for patients and healthcare providers, as early intervention can improve outcomes and quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the symptoms of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD)?
The symptoms of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD) typically appear between the ages of 30 and 50 and may include abdominal pain, hypertension (high blood pressure), headaches, and back pain. Patients often experience discomfort due to fluid-filled cysts developing in the kidneys, which can also lead to serious complications like renal failure.
What are the recent treatment options for Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease?
Recent treatment options for Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD) include the medication Tolvaptan, which has shown effectiveness in slowing kidney enlargement. Additionally, managing hypertension through lifestyle changes and medications is crucial for delaying disease progression. A multidisciplinary approach involving nephrologists and dietitians can provide tailored care for patients.
What complications are associated with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD)?
Complications of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD) can be severe and include End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD), which may require dialysis or kidney transplantation. Other complications may involve liver cysts and a higher risk of intracranial aneurysms, which can lead to neurological issues.
How does recent research impact the understanding of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD)?
Recent research on Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD) has provided new genetic insights that may change treatment approaches for renal cyst development. Studies have also highlighted disparities in kidney transplant outcomes among different racial groups, which can inform equitable healthcare practices for ADPKD patients.
What is an overview of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD)?
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD) is a genetic disorder characterized by the formation of numerous fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys, affecting approximately 1 in every 400 to 1,000 individuals. It is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, leading to varying severity of symptoms and potential complications, including hypertension and kidney failure.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | ADPKD is a genetic disorder characterized by the formation of numerous fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys. |
| Prevalence | Affects 1 in every 400 to 1,000 people. |
| Symptoms | Includes abdominal pain, hypertension, headaches, and back pain. |
| Diagnosis | Confirmed through imaging tests like ultrasound or CT scans, as well as genetic testing. |
| Treatment Options | 1. Tolvaptan for slowing kidney enlargement. 2. Blood pressure management. 3. Multidisciplinary care approach. |
| Complications | May lead to end-stage renal disease, liver cysts, and intracranial aneurysms. |
| ICD-10 Codes | ADPKD is classified under codes Q61.1 and Q61.2. |
Summary
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD) is a crucial genetic disorder that significantly affects kidney function and overall health. Understanding ADPKD is vital not only for timely diagnosis but also for effective treatment strategies. With symptoms often appearing between the ages of 30 and 50, it’s essential for individuals to recognize the signs early on. Recent research continues to shed light on potential treatments and the complex nature of the disease, highlighting the importance of managing symptoms and complications effectively. By staying informed about the latest advancements and treatment options, patients and healthcare providers can work together to improve the quality of life for those affected by ADPKD.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.