Arthritis is a widespread condition that significantly impacts the lives of millions, particularly adults over the age of 50. This chronic disease is characterized by joint pain, stiffness, and inflammation, which can hinder daily activities and reduce overall quality of life. Understanding the various **arthritis types**, each with its unique **arthritis symptoms**, is essential for effective management. For some individuals, when conservative **arthritis treatments** fail to relieve pain, more advanced options like **joint replacement surgery** may be necessary. It’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider who can help individuals navigate the complexities of **managing arthritis pain** to maintain mobility and enhance their well-being.
Joint disorders manifest through various forms affecting the connectivity of bones and the functionality of the skeletal system. Conditions such as joint inflammation and degeneration can severely restrict movement and lead to discomfort. The most common manifestations include stiffness and pain, which may indicate underlying conditions that require medical attention. To effectively address these symptoms, it is important to explore therapeutic measures, preventative strategies, and surgical options that may arise in cases of severe joint deterioration. Anyone suffering from these symptoms should seek guidance from healthcare professionals to develop a suitable action plan for alleviating their condition.
Understanding the Different Types of Arthritis
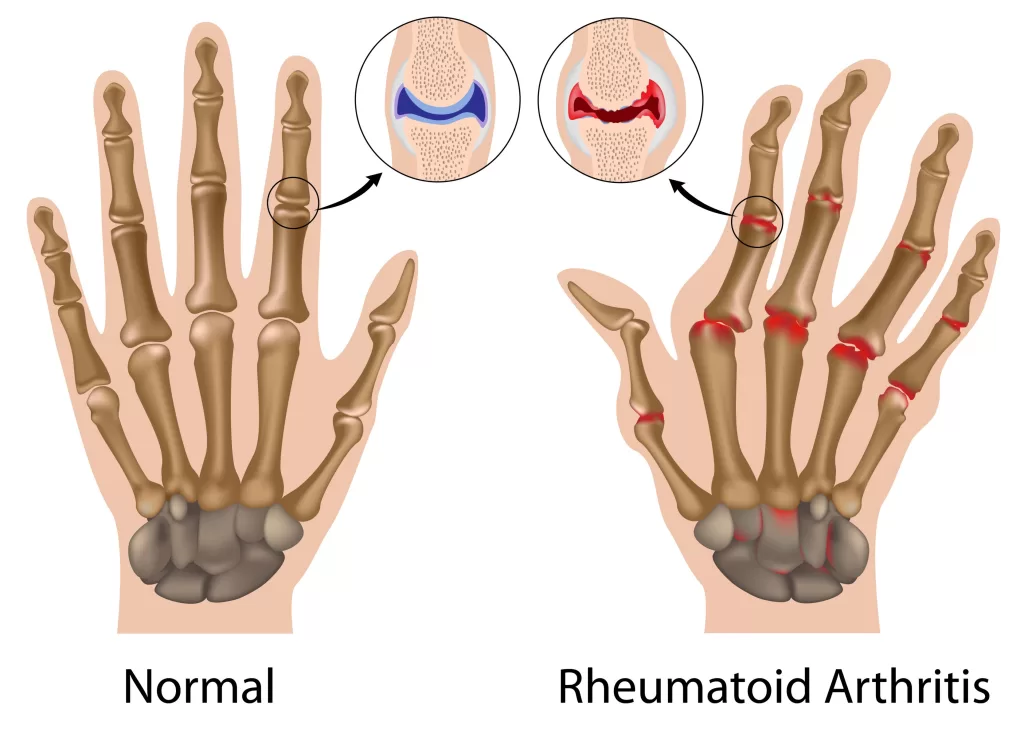
Arthritis encompasses a wide range of conditions that affect the joints, with over 100 distinct types recognized by medical professionals. The most prevalent include osteoarthritis, which typically results from the natural wear and tear on joints, and rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the joints. Both types exhibit varying symptoms, but common presentations include joint pain, stiffness, and inflammation, making it critical to identify the specific type for effective management.
Another significant type, gout, is characterized by sudden and severe pain due to the formation of sharp crystals in the joints, often causing intense discomfort and swelling. Diseases like ankylosing spondylitis primarily affect the lower back and pelvis, while psoriatic arthritis frequently co-occurs with psoriasis skin condition, resulting in joint issues among those affected. Understanding these diverse arthritis types is essential for developing tailored treatment strategies.
Identifying Symptoms and Causes of Arthritis
Recognizing the symptoms of arthritis is the first step towards effective management. Common symptoms include persistent joint pain, decreased range of motion, swelling, and skin discoloration. These manifestations can vary significantly depending on the type of arthritis one may have. For instance, osteoarthritis might lead to a gradual decline in mobility due to accumulated wear on the joints, whereas rheumatoid arthritis might present sudden flare-ups of pain and inflammation due to autoimmune activity.
The causes of arthritis are multifaceted and depend on the type of condition. While osteoarthritis is primarily age-related, other forms such as gout arise from lifestyle factors, particularly diet high in purines leading to elevated uric acid levels. Rheumatoid arthritis is linked to genetic predisposition and environmental triggers, highlighting the complexity of these conditions. Early recognition of symptoms and their respective causes can significantly enhance treatment outcomes.
Diagnosis and Testing for Arthritis
Diagnosing arthritis typically begins with a comprehensive physical examination where healthcare providers assess joint functionality and tenderness. Following this assessment, a variety of imaging tests play a crucial role in identifying the condition. X-rays can reveal joint damage associated with arthritis, while MRI and CT scans provide detailed images of soft tissues, essential for diagnosing conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
In addition to imaging, blood tests are instrumental in diagnosing specific types of arthritis. For instance, tests measuring uric acid levels are paramount for confirming gout. Also, health professionals may test for the presence of rheumatoid factor or anti-CCP antibodies as indicators of rheumatoid arthritis. Incremental testing and careful evaluation can aid in establishing a precise diagnosis, allowing for timely and effective treatment.
Managing and Treating Arthritis Pain
Effective management of arthritis pain is pivotal for enhancing quality of life. While there’s no definitive cure for arthritis, a range of treatments can help alleviate symptoms. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly used to reduce inflammation and provide pain relief, while corticosteroids can address severe symptoms and flare-ups. Integrating physical therapy can also empower patients, improving mobility and strength.
In cases where conservative treatments do not suffice, healthcare providers may consider more advanced options like disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) for rheumatoid arthritis. For individuals with irreparable joint damage, surgical interventions such as joint replacement surgery can dramatically improve functionality and reduce pain. Each treatment strategy should be personalized based on the type of arthritis and individual patient circumstances.
Exploring Surgical Options for Severe Arthritis
When conservative treatments fail to provide relief for severe arthritis patients, joint replacement surgery may become a viable option. This surgical intervention involves removing damaged parts of a joint and replacing them with artificial components, often leading to significant pain reduction and improved mobility post-recovery. Conditions such as osteoarthritis, where joint degradation is prevalent, are commonly addressed with this approach.
Patients considering joint replacement should engage in thorough discussions with their healthcare providers, weighing the benefits of the procedure against potential risks and complications. Factors such as age, overall health, and lifestyle will influence the decision-making process. Joint replacement can be life-changing, allowing individuals to regain normalcy in their daily activities and hobbies.
Lifestyle Tips for Arthritis Prevention
Preventing arthritis is not always possible, especially given genetic predispositions, but adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly lower your risk. A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, combined with regular physical activity, strengthens joints and may prevent the onset of some arthritis types. Low-impact exercises like swimming, cycling, or walking can keep joints mobile while minimizing stress on them.
Moreover, avoiding tobacco products can improve overall health and reduce the risk of developing certain types of arthritis. Staying hydrated and maintaining a healthy weight can also significantly impact joint health. By incorporating these preventive strategies, you enable your body to withstand joint stress better, ultimately reducing the likelihood of arthritis development.
Understanding the Long-term Outlook for Arthritis Patients
Living with arthritis can present ongoing challenges, necessitating a robust management plan tailored to individual needs. Many patients may experience fluctuating symptoms, worsening as they age. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are essential for monitoring disease progression and adjusting treatment plans. Staying informed and advocating for oneself are crucial elements in effectively managing arthritis.
Patients should also seek supportive resources, including community groups and educational seminars, to enhance their understanding of arthritis and share experiences with others facing similar challenges. Empowering oneself through knowledge reinforces a proactive approach to living with arthritis, facilitating better symptom management and a higher quality of life.
Common Questions about Arthritis Treatment
Patients frequently have numerous questions regarding their arthritis treatment options. Common inquiries include the effectiveness of over-the-counter medications for arthritis pain relief and whether lifestyle changes can potentiate treatment outcomes. Engaging with healthcare providers about lifestyle modifications like exercise routines and dietary adjustments can provide patients with supportive strategies to manage their condition better.
Moreover, many seek information about how environmental factors, such as weather changes, can exacerbate arthritis symptoms. This understanding can help individuals prepare and plan for potential flare-ups, allowing them to implement their coping strategies effectively. Accessing trustworthy resources and maintaining open communication with healthcare providers can lead to personalized answers that cater to each patient’s unique journey with arthritis.
Empowering Individuals to Live with Arthritis
Living with arthritis requires resilience and adaptability, as it often necessitates adjustments in daily routines. Seeking individualized treatment from healthcare providers and continuously learning about the condition empowers patients to take charge of their health. Patients are encouraged to embrace community support networks, as connecting with others can facilitate emotional support and shared strategies for managing symptoms.
Additionally, maintaining an open dialogue with healthcare providers about new treatment options, symptom changes, and lifestyle adaptations enables patients to stay proactive in their management approach. Encouraging self-care practices, such as mindfulness and stress management techniques, can also enhance overall well-being, demonstrating that while arthritis is prevalent, it is manageable.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common arthritis symptoms?
The most common arthritis symptoms include joint pain, stiffness or decreased range of motion, swelling due to inflammation, skin discoloration, tenderness around joints, and sensations of heat near the affected areas. Understanding these arthritis symptoms can help in early diagnosis and management.
What are the different types of arthritis?
There are over 100 types of arthritis, with common ones including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, and juvenile arthritis. Each type has unique causes and symptoms, which a healthcare provider can help identify.
How can I manage arthritis pain effectively?
Managing arthritis pain effectively often involves using a combination of over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications, corticosteroids, and therapies such as physical or occupational therapy. Your healthcare provider can recommend a personalized plan to help alleviate arthritis pain.
What are the available treatments for arthritis?
Available arthritis treatments include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), physical therapy, and, in severe cases, joint replacement surgery. It’s essential to work with your healthcare provider to find the best treatment plan.
Can joint replacement surgery help with severe arthritis?
Yes, joint replacement surgery can significantly help those suffering from severe arthritis that does not respond to other treatments. It involves replacing the damaged joint with an artificial one to relieve pain and restore function, allowing individuals to return to daily activities.
What precautions can I take to prevent arthritis?
To prevent arthritis, maintain a healthy diet and exercise regime, avoid tobacco products, engage in low-impact exercises, and protect your joints during physical activities. These lifestyle choices can help reduce the risk of developing arthritis.
How does weather affect arthritis symptoms?
Many individuals with arthritis report that their symptoms can worsen in cold, damp weather or during sudden changes in humidity. It’s important to monitor your own body’s response to weather changes and discuss any significant shifts in symptoms with your healthcare provider.
What diagnostic tests are used for arthritis?
Diagnosing arthritis typically involves a physical examination, imaging tests such as X-rays, ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans, and blood tests to check for uric acid levels or signs of infections and autoimmune diseases. These tests help determine the type and extent of arthritis.
Is arthritis manageable for daily living?
Yes, while arthritis is a chronic condition, it is manageable. With the right treatment plan, individuals with arthritis can maintain their daily activities and quality of life. Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider are crucial for effective management.
What lifestyle changes can support arthritis management?
Lifestyle changes that can support arthritis management include maintaining a healthy weight, staying physically active, practicing joint protection strategies, and ensuring proper nutrition. Consultation with a healthcare provider can guide you in making effective changes.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Commonality | Arthritis is common, especially over the age of 50. |
| Symptoms | Joint pain, stiffness, inflammation, swelling, tenderness. |
| Types | Includes Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Gout, Ankylosing Spondylitis, Psoriatic Arthritis, Juvenile Arthritis. |
| Causes | Aging, joint injuries, immune system responses, elevated uric acid levels. |
| Diagnosis | Physical exams, X-rays, MRI, blood tests. |
| Management | NSAIDs, corticosteroids, DMARDs, physical therapy, surgery. |
| Prevention | Healthy lifestyle, low-impact exercises, joint protection. |
| Outlook | Chronic management may be required, regular check-ups are essential. |
| Living with Arthritis | Seek help for severe pain, stiffness, or flare-ups. |
Summary
Arthritis is a widespread health issue that affects millions, particularly those over the age of 50, causing significant discomfort and joint impairment. Despite its prevalence, there are effective management strategies available, allowing individuals to maintain their quality of life. With proper diagnosis, treatment, and a proactive approach to joint care, individuals with arthritis can effectively manage their symptoms and continue engaging in daily activities.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.