Alkaptonuria, often referred to as “black urine disease,” is a rare genetic disorder that results from the body’s inability to break down homogentisic acid. This accumulation leads to distinctive symptoms such as dark urine and joint pain, significantly affecting the quality of life for those affected. As the homogentisic acid builds up, it can also cause serious complications like osteoarthritis, making early diagnosis and management crucial. Recent developments in treatment options, including the use of Nitisinone, show promise in reducing the harmful effects of this condition. Understanding alkaptonuria is essential not only for those diagnosed but also for raising awareness about this unique and challenging metabolic disorder.
Alkaptonuria, commonly known as black urine disease, is characterized by the accumulation of homogentisic acid, leading to various health complications. This metabolic condition, a hereditary genetic disorder, manifests through symptoms like darkened urine and joint deterioration, primarily due to the buildup of pigment in connective tissues. Individuals with alkaptonuria are at a heightened risk for developing osteoarthritis as the disease progresses. Management strategies often include lifestyle modifications and medications such as Nitisinone, which aim to mitigate the adverse effects associated with this disorder. By exploring alternative terms and related concepts, we can enhance understanding and promote awareness about this rare but impactful condition.
Understanding Alkaptonuria: A Deep Dive into Black Urine Disease
Alkaptonuria, commonly referred to as black urine disease, is an intriguing genetic disorder that affects the body’s ability to metabolize certain substances. This condition is primarily caused by a deficiency in the enzyme homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase, which is crucial for breaking down homogentisic acid (HGA). When HGA accumulates in the body, it is excreted in the urine, which upon exposure to air turns a dark black color. This striking symptom not only serves as a diagnostic marker but also highlights the underlying metabolic dysfunction that characterizes the disorder.
The impact of alkaptonuria extends far beyond discolored urine. As HGA deposits accumulate in connective tissues, patients often experience debilitating joint pain and early-onset osteoarthritis. These symptoms can drastically reduce mobility and quality of life, making it essential for affected individuals to seek effective management strategies. Understanding the intricate biology of alkaptonuria allows healthcare professionals to provide better care and support to those dealing with this rare condition.
Symptoms of Alkaptonuria and Their Impact on Daily Life
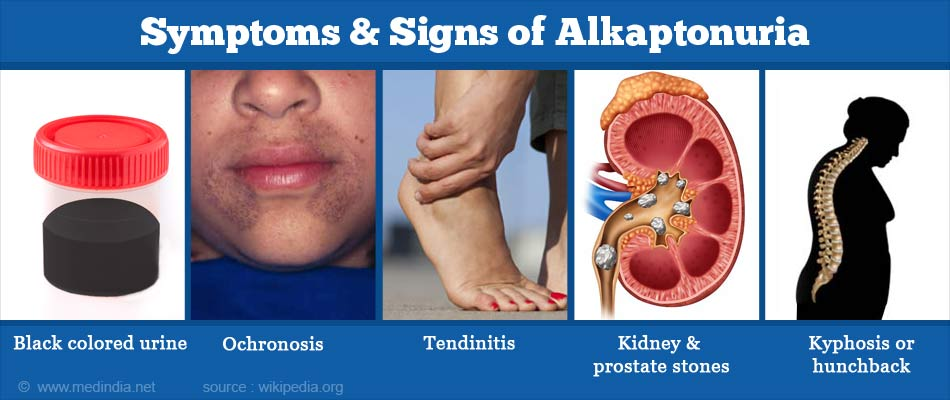
The symptoms of alkaptonuria can vary widely among individuals, but the most notable is the darkening of urine, which typically becomes black when exposed to air. This symptom often raises immediate concerns and leads to further investigation. In addition to dark urine, many patients report chronic joint pain due to the degenerative effects of osteoarthritis, which can develop as early as the second or third decade of life. The presence of these symptoms can significantly impair daily activities, leading to a diminished quality of life.
Moreover, the accumulation of homogentisic acid can result in a condition known as ochronosis, characterized by bluish-black discoloration of connective tissues, including skin and cartilage. This discoloration is not only a cosmetic concern but can also lead to psychological effects, as individuals may feel self-conscious about their appearance. For many, the combination of physical pain and emotional distress emphasizes the importance of ongoing research into better treatment options and support systems for those affected by alkaptonuria.
Genetic Factors and Inheritance Patterns of Alkaptonuria
Alkaptonuria is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, meaning that a child must inherit two copies of the mutated gene (one from each parent) to manifest the disorder. The specific gene responsible for this condition is the HGD gene, located on chromosome 3, which encodes the enzyme homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase. Understanding the genetic basis of alkaptonuria is crucial for genetic counseling, as it can inform families about the risks of passing the disorder to future generations.
The rarity of alkaptonuria can be attributed to the low prevalence of mutations in the HGD gene, and specific populations, particularly those with limited genetic diversity or higher rates of consanguinity, are at increased risk. By studying these genetic patterns, researchers can better understand the epidemiology of the disease and potentially identify new avenues for treatment and prevention. This genetic insight not only aids in diagnosis but also contributes to broader public health strategies aimed at managing this rare disorder.
Treatment Strategies for Alkaptonuria: Current Approaches and Future Directions
While there is currently no definitive cure for alkaptonuria, treatment strategies focus on managing symptoms and improving quality of life. One of the most promising developments in recent years is the use of Nitisinone, a drug that inhibits the production of homogentisic acid. Clinical studies have shown that Nitisinone can significantly reduce HGA levels in the body, potentially slowing the progression of symptoms and associated complications such as osteoarthritis.
In addition to pharmacological treatments, lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing alkaptonuria. Patients are encouraged to engage in regular physical activity, maintain a healthy diet, and seek physical therapy to alleviate joint pain. Ongoing research into gene therapy and other innovative treatments holds promise for the future, as scientists strive to find more effective ways to combat this challenging genetic disorder. Staying informed about the latest advancements is essential for individuals affected by alkaptonuria.
In conclusion, the management of alkaptonuria requires a comprehensive approach that combines medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and patient education. With ongoing research and support, individuals diagnosed with this rare condition can find hope and improve their quality of life.
Recent Research Developments in Alkaptonuria Treatment
Recent studies have shed light on the complexities of alkaptonuria and its management, emphasizing the need for continued research into effective treatments. Articles from reputable sources highlight the severe progression of osteoarthritis linked to the accumulation of homogentisic acid, which can significantly affect the lives of those diagnosed. As understanding of the disease increases, so does the potential for developing new therapeutic strategies that could alter the course of the disorder.
Additionally, innovative research is exploring the efficacy of Nitisinone not just in reducing homogentisic acid levels, but also in mitigating the long-term effects of the disease. Patient monitoring and longitudinal studies are crucial in assessing how these treatments influence the quality of life over time. As researchers work diligently to uncover more effective treatment options, individuals affected by alkaptonuria must remain engaged with their healthcare providers to discuss the latest advancements and tailored management plans.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes Alkaptonuria, also known as black urine disease?
Alkaptonuria, or black urine disease, is caused by a deficiency of the enzyme homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase, leading to the accumulation of homogentisic acid (HGA) in the body. This genetic disorder is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, requiring both parents to pass on the defective HGD gene for a child to develop the condition.
What are the symptoms of Alkaptonuria and how does it affect individuals?
Symptoms of Alkaptonuria include dark urine that turns black upon exposure to air, joint pain due to early-onset osteoarthritis, and discoloration of skin and eyes known as ochronosis. These symptoms can significantly impact quality of life, leading to mobility issues and chronic pain.
How is Nitisinone used in the treatment of Alkaptonuria?
Nitisinone is a medication that shows promise in treating Alkaptonuria by inhibiting the production of homogentisic acid. This helps reduce the harmful effects of this acid accumulation, potentially improving outcomes for patients suffering from this genetic disorder.
Why is regular monitoring important for individuals with Alkaptonuria?
Regular monitoring is crucial for individuals with Alkaptonuria to manage symptoms effectively and prevent complications, such as severe joint damage from osteoarthritis. Early detection of changes in health status can lead to timely interventions and better quality of life.
What support is available for those diagnosed with Alkaptonuria?
Individuals diagnosed with Alkaptonuria can benefit from support groups, medical consultations, and resources from organizations dedicated to rare genetic disorders. Staying informed about ongoing research and treatment options is essential for effective management of this condition.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Condition Description | Alkaptonuria (AKU) is a rare genetic disorder that causes accumulation of homogentisic acid, leading to various health issues. |
| Symptoms | Dark urine, joint pain, skin discoloration (Ochronosis), and potential heart ailments. |
| Causes | Caused by mutations in the HGD gene leading to enzyme deficiency; inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. |
| Recent Research Findings | Research emphasizes the severe impact of AKU on mobility and quality of life, along with management strategies. |
| Treatment Options | Currently, there is no cure; management includes Nitisinone to reduce homogentisic acid levels. |
| Importance of Awareness | Staying informed and connected with support resources is crucial for those affected by Alkaptonuria. |
Summary
Alkaptonuria is a rare genetic disorder that significantly impacts the metabolism of individuals, primarily causing joint pain and connective tissue complications due to the accumulation of homogentisic acid. Despite the absence of a definitive cure, advancements in treatment and management strategies are continually evolving. Individuals with Alkaptonuria can lead more manageable lives through awareness of their condition, lifestyle adjustments, and appropriate medical care. Engaging with healthcare specialists and support networks is essential for optimizing care and improving quality of life.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.