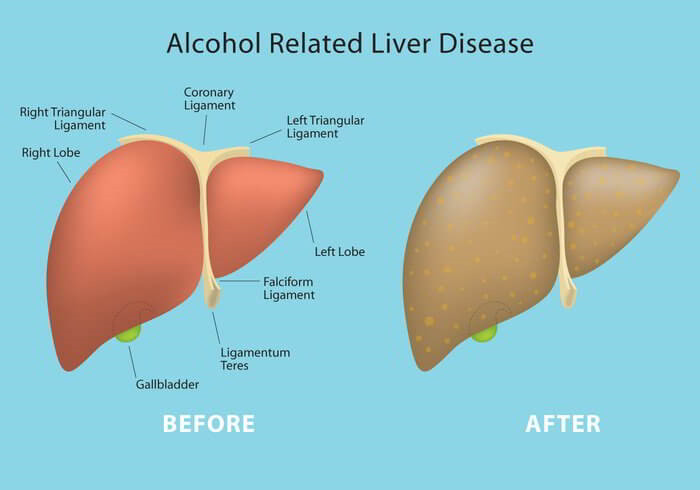
Alcohol-related liver disease (ARLD) has become a pressing concern in public health, particularly as its prevalence continues to rise among various age groups, including young adults. The impact of excessive alcohol consumption is not just a matter of social enjoyment; it poses severe risks to liver health that can lead to debilitating conditions. Understanding the symptoms of liver disease, such as fatigue and abdominal discomfort, is essential for early detection and intervention. Furthermore, awareness of the stages of liver disease—ranging from fatty liver to cirrhosis—can empower individuals to seek timely treatment for liver disease. With effective liver health management and support for those facing alcohol use disorder, we can combat the escalating crisis of ARLD and promote healthier lifestyles.
The issue of liver ailments linked to alcohol consumption has gained significant attention as a critical health challenge in modern society. Often referred to as alcoholic liver disease or liver injury due to alcohol, this condition manifests as a spectrum of disorders that can severely compromise liver function. Recognizing the early indicators of liver health deterioration is crucial, as these symptoms can often be mistaken for other health issues. With a comprehensive understanding of the various stages of liver disease and the available treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps toward recovery and prevention. Addressing alcohol dependency is not merely a personal challenge but a collective responsibility that necessitates awareness and education.
Understanding the Symptoms of Liver Disease
Recognizing the symptoms of liver disease is crucial for early intervention and effective treatment. Alcohol-related liver disease (ARLD) often presents with vague and subtle signs that many individuals might dismiss. Common symptoms include upper abdominal pain, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, and general malaise. Each of these symptoms can significantly impact daily life, and their presence should prompt individuals to seek medical advice to evaluate their liver health.
As liver disease progresses, symptoms can escalate to jaundice, swelling in the abdomen, and confusion due to liver dysfunction. Awareness of these signs is essential for those who engage in heavy alcohol consumption, as the liver can sustain considerable damage before symptoms become pronounced. Early recognition not only facilitates timely medical intervention but also allows for lifestyle adjustments that can mitigate further liver damage.
Stages of Alcohol-Related Liver Disease Explained
Alcohol-related liver disease progresses through distinct stages, each with its own implications for liver health. The first stage, steatosis or fatty liver, represents an early warning sign. At this stage, the liver becomes overloaded with fat due to excessive alcohol intake, but it can be reversed with lifestyle changes, such as abstaining from alcohol and adopting a healthier diet.
If left unaddressed, ARLD can advance to alcoholic hepatitis, characterized by inflammation and liver cell damage. This stage may require medical treatment to manage symptoms and prevent complications. The final stage, cirrhosis, is irreversible and leads to severe liver impairment, necessitating serious interventions such as liver transplantation. Understanding these stages can empower individuals to take proactive steps in liver health management.
Effective Treatment Options for Liver Disease
The treatment for alcohol-related liver disease hinges on the principle of addressing both the disease and its root causes. The most fundamental treatment option is to cease alcohol consumption entirely. This lifestyle change can lead to significant improvements in liver health and overall wellbeing. Nutritional support is also essential; a balanced diet rich in essential vitamins and minerals can help restore liver function.
In more severe cases, healthcare providers may recommend medications to alleviate inflammation or correct nutritional deficiencies. For individuals with advanced liver disease, surgical options, including liver transplants, may be necessary. As the incidence of ARLD continues to rise, understanding treatment options becomes critical for those at risk.
The Role of Alcohol Use Disorder in Liver Disease
Alcohol use disorder (AUD) is a significant risk factor for the development of alcohol-related liver disease. Individuals struggling with AUD often consume excessive amounts of alcohol over prolonged periods, leading to chronic liver damage. Early intervention for AUD can significantly reduce the risk of developing severe liver disease and improve overall health outcomes.
Addressing AUD involves a combination of counseling, support groups, and sometimes medication to help manage cravings and withdrawal symptoms. By treating the root cause of excessive alcohol consumption, individuals can improve their liver health and reduce the likelihood of progression to advanced liver disease stages, ultimately leading to a healthier lifestyle.
Promoting Liver Health Management
Promoting liver health management is essential in combating the rising tide of alcohol-related liver disease. Individuals can take proactive steps to improve their liver health by making informed lifestyle choices, such as regular exercise, maintaining a balanced diet, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption. Educational initiatives can raise awareness about the risks associated with heavy drinking, particularly among young adults.
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in liver health management by offering screenings for liver disease, providing resources for alcohol use disorder treatment, and guiding patients in lifestyle modifications. By fostering a culture of awareness and preventive care, society can significantly reduce the incidence of ARLD and promote healthier living.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of alcohol-related liver disease?
Symptoms of alcohol-related liver disease (ARLD) often develop gradually and can include upper abdominal pain, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, diarrhea, and general malaise. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for timely diagnosis and intervention.
What stages does alcohol-related liver disease progress through?
Alcohol-related liver disease progresses through three main stages: 1) Steatosis (Fatty Liver), which is often reversible; 2) Alcoholic Hepatitis, characterized by liver inflammation; and 3) Cirrhosis, which involves irreversible liver scarring and can lead to liver failure.
How is alcohol-related liver disease treated?
Treatment for alcohol-related liver disease focuses on restoring liver health by encouraging complete abstinence from alcohol, adopting a nutritious diet, managing inflammation with medications, and in severe cases, considering surgical interventions such as liver transplants.
Can alcohol-related liver disease be reversed?
In the early stage of alcohol-related liver disease, known as Steatosis (Fatty Liver), the condition can often be reversed through lifestyle changes, particularly by abstaining from alcohol and improving dietary habits.
What role does alcohol use disorder play in alcohol-related liver disease?
Alcohol use disorder is a significant risk factor for developing alcohol-related liver disease. It contributes to the progression of liver damage and complications, making early intervention and treatment essential for those who consume alcohol excessively.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Introduction | Alcohol-related liver disease (ARLD) is on the rise, especially among young adults, highlighting the need for awareness and proactive management. |
| Current Landscape | Statistics show an increase in liver transplants among young adults due to excessive drinking, necessitating public awareness. |
| Symptoms | Common symptoms include upper abdominal pain, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, and general malaise. |
| Stages | ARLD progresses through three stages: Steatosis (Fatty Liver), Alcoholic Hepatitis, and Cirrhosis. |
| Treatment Options | Treatment includes lifestyle changes, medications, and potentially liver transplantation for severe cases. |
Summary
Alcohol-related liver disease (ARLD) is a growing concern that demands immediate attention due to its rising prevalence, especially among young adults. The symptoms of ARLD often develop quietly, making early detection crucial for effective intervention. Understanding the stages of the disease, from fatty liver to cirrhosis, can empower individuals to seek timely medical help. Treatment options primarily focus on lifestyle changes, including abstaining from alcohol and adopting a healthy diet, along with medications for managing complications. Increased awareness, education, and proactive health measures are essential in combating the effects of alcohol-related liver disease, ultimately leading to better health outcomes.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.