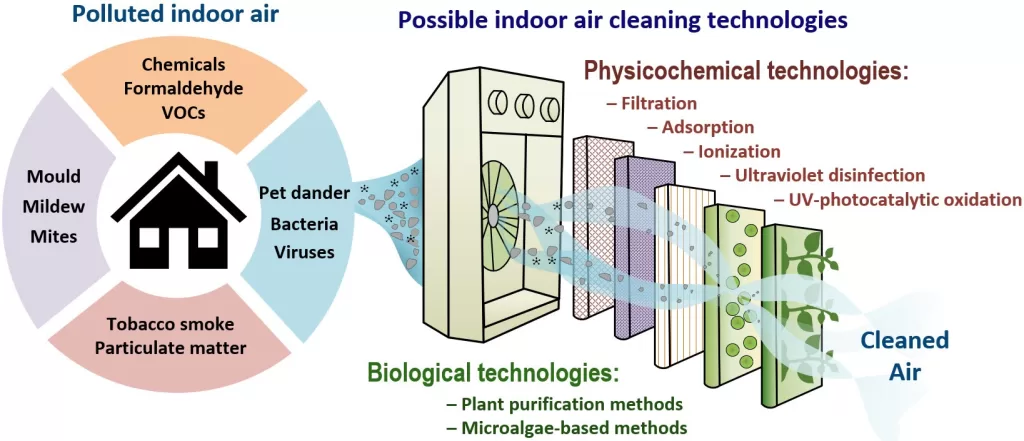
Air-cleaning technologies have garnered increasing attention in recent years due to their potential to enhance indoor air quality and curb the transmission of airborne viruses. With the COVID-19 pandemic highlighting the importance of effective air purification systems, many households and institutions are investing in solutions such as HEPA filters, UV lights, and ionizers to mitigate risks of respiratory infection. Despite the promise these technologies offer, recent reviews reveal a need for more comprehensive studies examining their real-world effectiveness and safety. Critical discussions around indoor virus transmission and the potential for harmful emissions have emerged, calling for a balance between innovation and public health. As individuals and businesses seek ways to improve indoor air quality, understanding the nuances of air-cleaning technologies is essential for making informed decisions that safeguard health and well-being.
The growing interest in improving indoor environments has led to a surge in advanced air purification methods aimed at enhancing living and working spaces. Commonly referred to as air filtration systems, these innovations use a variety of mechanisms—including high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters and germicidal ultraviolet (GUV) light—to mitigate the spread of diseases linked to airborne particles. However, discussions surrounding the effectiveness of these strategies in preventing respiratory infections highlight a critical need for empirical evidence supporting their claims. While the desire for cleaner air is universal, it is essential to critically assess the claims around these technologies to avoid misinformation and ensure informed choices. As the market for air-cleaning solutions expands, prioritizing rigorous scientific research will be key in navigating their implementation safely.
The Growing Interest in Air-Cleaning Technologies
The COVID-19 pandemic has rekindled significant interest in air-cleaning technologies as a solution to mitigate the spread of airborne viruses in various settings, including homes, schools, and healthcare facilities. With many individuals seeking ways to enhance the safety of their indoor environments, products like high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters and ultraviolet (UV) light systems have gained popularity. These technologies are marketed as effective means of filtering out harmful pathogens from the air, leading to a perception that they can greatly improve overall air quality.
However, despite their promising theoretical applications, the efficacy of these air-cleaning technologies in real-world scenarios remains a subject of debate among researchers. A recent review highlights the need for more comprehensive studies that not only assess the technological effectiveness in controlled conditions but also consider human health outcomes. As consumers invest in air purification systems, there is a critical need for transparent data and rigorous testing that examines the true impact these technologies have on respiratory infection prevention.
Challenges in Evaluating HEPA Filters Effectiveness
While HEPA filters have long been regarded as one of the most effective air-cleaning technologies available, their performance can vary significantly based on usage and context. The studies reviewed underscore a concerning trend: only a fraction of research includes actual human participants, leading to doubts about the real-world effectiveness of HEPA filters in preventing diseases like COVID-19. Limited empirical evidence means that many claims made by manufacturers about HEPA filters’ performance may not have the scientific backing needed to reassure consumers.
In addition to efficacy, the potential harmful emissions from some air-cleaning devices warrant investigation. Technologies like ionizers, which can generate ozone, may inadvertently compromise indoor air quality and pose health risks, particularly for vulnerable populations. This highlights the importance of evaluating not just the benefits but also the risks associated with air-cleaning technologies. Consumers should be aware of these nuances to make informed decisions that prioritize their health and well-being.
Impact of Indoor Virus Transmission on Public Health
Indoor virus transmission continues to pose significant public health challenges, especially in densely populated areas or enclosed environments where air exchange is limited. According to health experts, understanding how respiratory viruses spread indoors is essential for implementing effective prevention strategies. As individuals and organizations increasingly adopt air-cleaning technologies, it is crucial to assess their role in curbing indoor virus transmission.
Research has shown that improved air quality can indeed reduce the incidence of respiratory infections. However, reliance solely on air-cleaning technologies without proper ventilation and cleaning measures may not yield the desired protective outcomes against viruses. Public health initiatives must therefore encompass a holistic approach that combines various interventions—such as promoting regular air exchanges, improving ventilation systems, and incorporating air-cleaning technologies to create safer indoor environments.
Real-World Studies: A Call for Better Research
The need for robust, real-world studies that evaluate the impact of air-cleaning technologies on human health outcomes has never been clearer. Researchers have identified critical gaps in existing research, particularly in understanding the direct effects of air-cleaning systems on rates of respiratory infections. Current studies predominantly rely on indirect measures, like environmental air quality assessments, failing to capture the nuanced interactions between air quality and health outcomes.
To guide public health policies effectively, future studies must prioritize direct measurements of human exposure to pathogens in conjunction with air-cleaning interventions. This includes considering diverse environments and populations to provide a more comprehensive understanding of how air-cleaning technologies function in real-life settings.
Potential Health Risks from Air-Cleaning Devices
While air-cleaning technologies are marketed as solutions for improving indoor air quality, they can also pose potential health risks. Some units, particularly older models or poorly designed systems, may emit ozone and other volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which can irritate the lungs and exacerbate respiratory conditions. This necessitates consumer awareness regarding both the benefits and hazards associated with specific air purification systems.
Moreover, demographic groups such as children and individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions can be particularly susceptible to the adverse effects of indoor air pollutants. It’s vital that manufacturers provide clear information about potential emissions and guidelines on usage to ensure safe operation. As more people turn to air-cleaning devices in a bid to protect their families, understanding these risks is essential for making informed choices.
Economic Considerations in Air Quality Improvement
The economic implications of acquiring and maintaining air-cleaning technologies cannot be overlooked. As households and businesses consider investing in these devices, evaluating their cost-effectiveness in improving indoor air quality is vital. While some systems may have high upfront costs, they could potentially reduce healthcare expenses related to respiratory infections in the long term.
Additionally, understanding the operational costs associated with air-cleaning technologies is essential for consumers and public institutions. Maintenance requirements, energy consumption, and replacing filters can add to the lifetime cost of these systems. Therefore, conducting comprehensive economic analyses can help guide decisions about which technologies are worthwhile investments for improving indoor air quality and ensuring respiratory health.
Establishing Standards for Air-Cleaning Technologies
The variability in air-cleaning technologies poses a challenge to consumers and policymakers alike. Establishing standardized testing protocols and health-related outcome measures can pave the way for more transparent and comparable research results. This would not only assist consumers in making informed choices but also guide manufacturers in improving the design and efficiency of their systems.
Standardized evaluations can also help clarify which technologies are most effective, aiding public health frameworks in making evidence-based recommendations. With growing investment in air-cleaning technologies, a clear set of criteria for assessing their performance will be crucial for ensuring that they contribute positively to public health initiatives aimed at reducing respiratory infections.
Community Awareness and Action
Raising awareness within communities about air quality and its impact on health is crucial as indoor air pollution becomes more recognized as a public health concern. Informing individuals about the importance of proper ventilation, regular cleaning, and the potential benefits and drawbacks of air-cleaning technologies can empower them to make better choices in managing their indoor environments.
Additionally, community initiatives that promote indoor air quality improvement, including educational programs about respiratory infection prevention and guidelines on the safe use of air-cleaning devices, can foster a culture of health awareness. This collective action is essential not only in addressing current challenges posed by airborne viruses but also in ensuring long-term improvement in public health outcomes.
The Future of Indoor Air Quality Research
Looking ahead, the landscape of indoor air quality research must evolve to keep pace with emerging challenges posed by respiratory viruses. A concerted effort from researchers, health professionals, and policymakers is needed to develop and implement studies that more accurately reflect real-world exposures and health impacts associated with air-cleaning technologies. By adopting an interdisciplinary approach that includes engineering, public health, and environmental sciences, the field can advance significantly.
Encouraging collaboration between academic institutions, industry stakeholders, and government entities will be critical for fostering innovation and building public trust in air-cleaning technologies. As awareness of indoor air pollution grows, it is vital for future research efforts to prioritize transparency and accountability, ensuring that the public has access to reliable information that contributes to informed decision-making.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of air purification systems in preventing indoor virus transmission?
Air purification systems, particularly those utilizing technologies like HEPA filters, can help reduce the presence of airborne pathogens and improve overall air quality. However, while many studies suggest their effectiveness in preventing indoor virus transmission, more robust research is needed to assess their impact on actual human infections.
How effective are HEPA filters at improving air quality in residential settings?
HEPA filters are designed to trap tiny particles, including viruses and allergens, thus significantly improving indoor air quality. However, the effectiveness of HEPA filters can vary based on proper installation and maintenance. Real-world studies are needed to validate the claims surrounding their efficacy in various environments.
Can air-cleaning technologies really prevent respiratory infections like COVID-19?
While air-cleaning technologies show potential in laboratory settings, research into their effectiveness in real-world situations is limited. Only a small percentage of studies evaluate direct health outcomes related to respiratory infection prevention, indicating a need for further investigation.
What are the possible risks associated with air-cleaning technologies?
Some air-cleaning technologies, such as ionizers and certain UV systems, can produce ozone and other lung irritants that may adversely affect health, particularly for children and individuals with existing respiratory conditions. It is crucial to check manufacturers’ data for any harmful emissions and follow usage recommendations.
What should be considered when investing in air purification systems for schools and homes?
When considering air purification systems, look for independent research supporting their efficacy, potential health risks from emissions, and specific operational guidance from the manufacturer. Enhanced ventilation and regular cleaning practices should also be maintained for optimal indoor air quality.
Are there studies that measure the real-world effectiveness of air-cleaning technologies against respiratory viruses?
Currently, few studies measure the direct impact of air-cleaning technologies on human exposure to respiratory viruses. Most research focuses on environmental samples instead, emphasizing the need for studies that monitor actual health outcomes in typical indoor settings.
How can improving indoor air quality help reduce respiratory infections?
Improving indoor air quality, through measures like using air purification systems and increasing ventilation, can potentially lower the concentration of airborne pathogens, thereby reducing the risk of respiratory infections. Nonetheless, evidence from real-world studies is still necessary to evaluate this claim.
What are the challenges in validating the effectiveness of air-cleaning technologies?
Challenges include a lack of comprehensive studies that include human participants and direct health outcomes, the presence of potential conflicts of interest in research funding, and variations in how different technologies function in real-world settings.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Overview | Reviewed 672 studies about air-cleaning technologies from 1929 to 2024. |
| Main Findings | Most studies did not include human participants (only 8% did); many were conducted in laboratory settings. |
| Research Gaps | Need for studies that assess real-world health outcomes and potential harmful emissions. |
| Funding Concerns | A significant number of studies lacked clear funding and conflict of interest disclosures. |
| Public Health Implications | Call for more robust independent studies to guide public health policy regarding air-cleaning technologies. |
Summary
Air-cleaning technologies play a crucial role in indoor air quality and public health, especially following the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the recent scoping review highlights significant gaps in research surrounding their real-world effectiveness and safety. While many technologies claim to reduce airborne pathogens, the evidence primarily relies on laboratory studies rather than real-world scenarios, which raises concerns about their actual impact on health outcomes. Moreover, incomplete transparency regarding funding sources and potential harmful emissions further complicates the assessment of these technologies. As such, there is an urgent need for comprehensive, independent research that not only measures efficacy but also evaluates the safety and environmental impact of air-cleaning technologies. Only through such rigorous studies can we ensure that our indoor environments are genuinely safer for everyone.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.