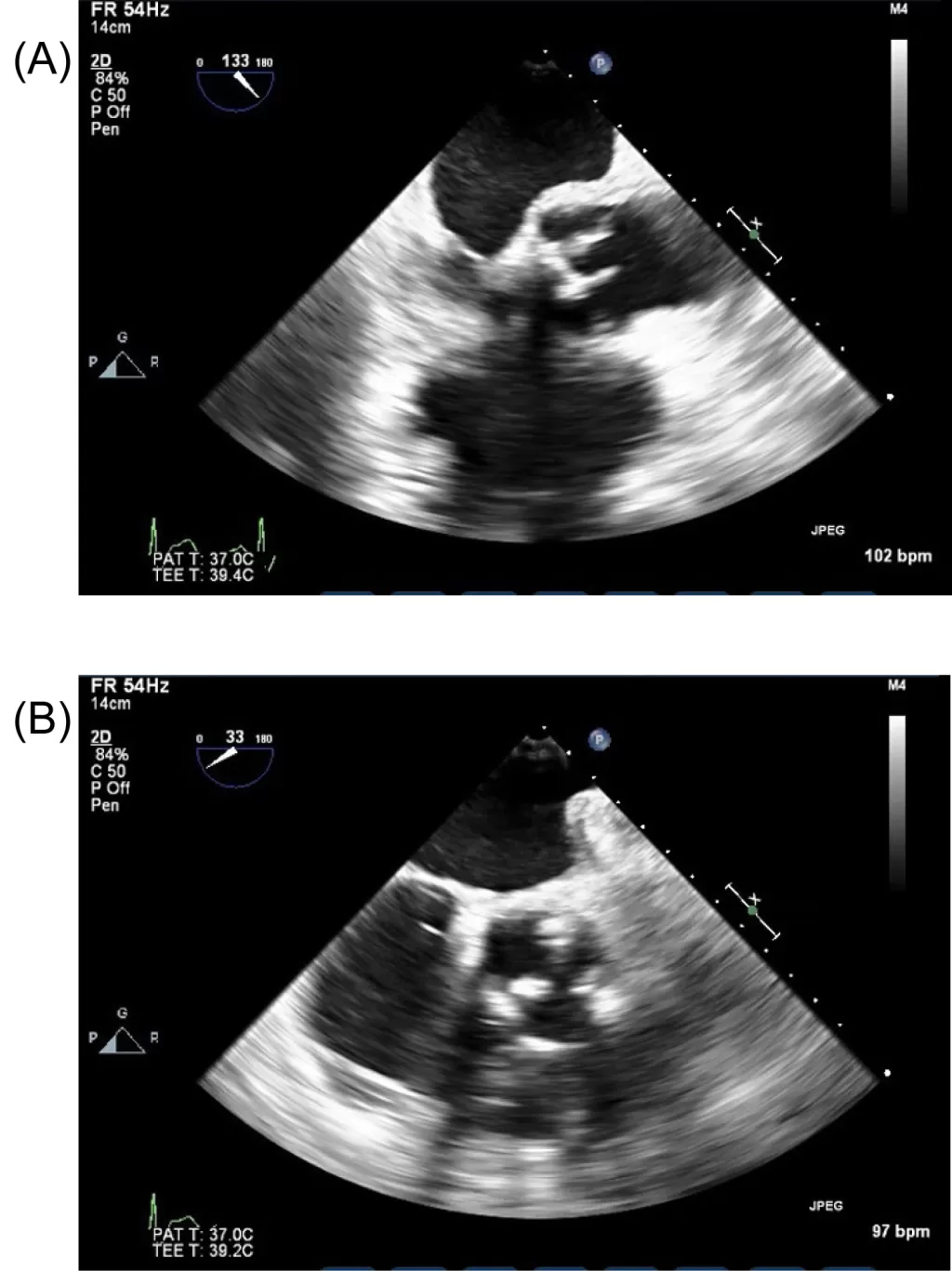
Aerococcus urinae endocarditis is an unusual yet critical condition that has garnered attention for its complex treatment scenarios. This case highlights the journey of a 61-year-old man who experienced recurrent Aerococcus urinae endocarditis, initially affecting his native tricuspid valve before leading to a bioprosthetic replacement. The significance of identifying and treating such infective endocarditis is underscored by the successful use of targeted antimicrobial therapy combined with surgical intervention. Treatment strategies, including tricuspid valve replacement, become essential to managing the complications of this rare infection. As occurrences of A. urinae endocarditis remain infrequent in medical literature, this case report serves to illuminate the challenges and potential solutions in handling this bacterial threat.
Infective endocarditis, particularly caused by the unique pathogen known as Aerococcus urinae, presents a compelling challenge for healthcare professionals. This gram-positive, catalase-negative bacterium predominantly impacts the urinary tract but has recently drawn attention for its role in cardiac infections, notably affecting the tricuspid valve. Advanced microbiological techniques are pivotal in diagnosing such cases, ensuring appropriate antimicrobial therapy is administered. The complexity of tricuspid valve replacement in the context of A. urinae underscores the need for vigilance in patients with a history of urinary tract infections. This case narrative not only provides insight into a patient’s struggle with recurrent endocarditis but also emphasizes the importance of thorough understanding and recognition of this rare infectious agent.
Understanding Aerococcus urinae Endocarditis
Aerococcus urinae endocarditis is a rare but serious condition that primarily affects the heart valves, particularly in patients with preexisting health conditions. This gram-positive bacterium is often associated with urinary tract infections, yet its capability to cause infective endocarditis is frequently underestimated due to misidentification in standard culture tests. The clinical implications of A. urinae infections can be grave, particularly for patients with a history of heart issues, such as tricuspid valve replacement. Understanding the pathways of infection and the microbiological characteristics of A. urinae is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective treatment.
Historically, patients with Aerococcus urinae endocarditis often present with vague symptoms, making it challenging for healthcare professionals to consider this organism as a potential cause. In this context, advanced diagnostic methods, including molecular techniques, are necessary to enhance detection rates. This knowledge can aid in identifying patients at risk and tailoring a prompt and appropriate antimicrobial therapy that can mitigate the severity of the infection.
Clinical Presentation of Aerococcus urinae Endocarditis
The clinical presentation of Aerococcus urinae endocarditis can be quite nonspecific, often resembling more common infections. In the reported case, the patient experienced recurrent falls, weakness, and dyspnea, symptoms that could easily be attributed to other underlying conditions. This further complicates timely diagnosis, as many healthcare providers are not alert to the specific manifestation of endocarditis induced by A. urinae. The absence of classic symptoms such as fever or chills often delays intervention, putting patients at risk for more severe complications.
Furthermore, the patient’s previous medical history contributed significantly to his clinical picture. With a background of chronic kidney disease and diabetes, the immune response to infections can be compromised, thereby enhancing the potency of A. urinae. Close monitoring for patients with such risk factors is essential to catch the early signs of endocarditis and to start appropriate treatment before the disease progresses drastically.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Aerococcus urinae Endocarditis
Correct diagnosis of Aerococcus urinae endocarditis requires a multi-faceted approach, often involving advanced microbiological testing to overcome the traditional limitations of culture methods. In the case report, blood cultures were able to successfully isolate A. urinae, allowing for targeted treatment with antimicrobial therapy. It underscores the importance of highlighting this organism in differential diagnoses, particularly for patients presenting with symptoms of endocarditis and a history of urinary tract infections.
The treatment protocol in such cases typically includes the use of beta-lactam antibiotics, with ceftriaxone being a common choice due to its efficacy against gram-positive cocci. Transitioning to penicillin G based on susceptibility testing can provide additional assurance of effective treatment. Moreover, for cases accompanied by complications such as valve dehiscence, surgical intervention like a repeat tricuspid valve replacement may become necessary, as demonstrated in this case.
Prognosis Following Aerococcus urinae Endocarditis Treatment
The prognosis for patients undergoing treatment for Aerococcus urinae endocarditis largely depends on timely diagnosis and effective antimicrobial therapy. In the study presented, the patient showed notable improvement after properly directed treatment. Within weeks, both clinical symptoms and laboratory results indicated a resolution of infection, reflective of the effectiveness of the selected antimicrobial therapy combined with surgical intervention.
However, continuous follow-up is crucial as patients may experience lingering effects from prior infections or may be predisposed to future episodes. Careful monitoring ensures that any recurrent symptoms can be promptly addressed, and subsequent treatment regimens can be adapted as necessary. This holistic approach enhances long-term outcomes for patients recovering from A. urinae endocarditis.
The Role of Surgery in Aerococcus urinae Endocarditis Cases
Surgical intervention plays a critical role in managing infective endocarditis, particularly in cases complicated by valve dysfunction or large vegetations, as seen in tricuspid valve pathologies. In the reported case, the patient’s complicated condition warranted a repeat tricuspid valve replacement after multiple courses of antibiotic therapy. This illustrates the dual approach often necessary in effectively treating Aerococcus urinae endocarditis, combining antimicrobial therapy with surgical options to eliminate the infective source.
Surgery not only addresses the immediate threat posed to the heart by infected valve tissue but also provides an opportunity to further examine and ensure complete removal of infected material that may not respond to antibiotics alone. Successful outcomes hinge on the coordination of medical and surgical teams, aiming to optimize patient recovery and prevention of future complications.
Antimicrobial Therapy Approaches for Aerococcus urinae Endocarditis
Antimicrobial therapy is fundamental in treating Aerococcus urinae endocarditis, necessitating careful selection based on the organism’s susceptibility profiles. In many cases, empirical therapy is initiated with broad-spectrum antibiotics, transitioning to narrower options once specific susceptibilities are determined. The use of intravenous ceftriaxone followed by penicillin G, as seen in the patient’s documented treatment, emphasizes the importance of adapting therapy based on real-time microbiological data.
Moreover, understanding the underlying mechanisms of drug resistance when dealing with gram-positive bacteria is crucial for effective treatment. As the medical community becomes increasingly aware of A. urinae’s potential pathogenicity, so too must the approaches to antimicrobial therapy adapt, ensuring that practitioners remain vigilant in their treatment strategies to reduce the risk of complications associated with this infection.
Implications of Misidentifying Aerococcus urinae in Clinical Settings
Misidentification of Aerococcus urinae infections can lead to significant delays in appropriate treatment, underscoring the need for improved laboratory techniques in detecting such pathogens. Historical reliance on biochemical tests has often led to underreporting of A. urinae as a cause of infective endocarditis, particularly in patients with complicated medical histories or atypical presentations. The implications of such misdiagnosis can be severe, hindering effective patient management and increasing morbidity.
Enhancing healthcare professionals’ awareness of A. urinae’s clinical significance is essential for early recognition and intervention. Training sessions that update clinicians on the potential presentation and identification of this organism could enhance patient outcomes, ensuring that those at risk receive prompt and appropriate care. As research continues to pull A. urinae into the spotlight, evolving diagnostic criteria will ultimately improve patient management in cases of infective endocarditis.
The Importance of Long-Term Follow-Up After Endocarditis
Long-term follow-up care after Aerococcus urinae endocarditis is crucial for detecting any residual effects or complications arising from the infection or the treatment process. Monitoring helps identify early signs of reinfection or valve failure, allowing for prompt interventions that can significantly influence outcomes. Patients with a history of infective endocarditis benefit from regular cardiology assessments to ensure their heart health remains stable post-treatment.
Additionally, interdisciplinary collaboration among healthcare providers, including infectious disease specialists, cardiologists, and kidney specialists, can foster comprehensive care plans that address the multifaceted needs of these patients. Holistic follow-up improves not only short-term recovery but long-term survival and quality of life for individuals impacted by A. urinae endocarditis.
Future Directions in Managing Aerococcus urinae Infections
The management of Aerococcus urinae infections, particularly endocarditis, is evolving as our understanding of the organism’s epidemiology and virulence factors improves. Future research is needed to establish evidence-based treatment protocols and identify potential vaccine targets for A. urinae. Investigating the mechanisms of virulence may open new avenues for therapies that could decrease the burden of these infections.
Moreover, clinical studies focusing on the long-term outcomes of patients treated for Aerococcus urinae endocarditis are necessary to refine guidelines for managing similar cases. The advancement of laboratory techniques will further enhance our diagnostic capabilities, ensuring better identification and management of this and other rare pathogens.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Aerococcus urinae endocarditis and how is it treated?
Aerococcus urinae endocarditis is a rare form of infective endocarditis caused by the gram-positive bacterium Aerococcus urinae. It can affect heart valves, particularly the tricuspid valve. Treatment typically involves a combination of antimicrobial therapy, often using intravenous ceftriaxone or penicillin G, and surgical interventions such as valve replacement, especially in complicated cases.
What are the symptoms of Aerococcus urinae endocarditis?
Symptoms of Aerococcus urinae endocarditis can include fatigue, shortness of breath (dyspnea), weakness, and rashes on the extremities, as well as other nonspecific symptoms. Patients may also experience recurrent falls, especially in elderly individuals or those with underlying health conditions.
How common is Aerococcus urinae endocarditis in clinical practice?
Aerococcus urinae endocarditis is a rarely reported condition, often overlooked due to the inadequate culture methods and challenges in identifying A. urinae in laboratory settings. Awareness and advanced microbiology techniques are essential for accurate diagnosis and effective management.
What is the significance of a tricuspid valve replacement in Aerococcus urinae endocarditis cases?
Tricuspid valve replacement is significant in cases of Aerococcus urinae endocarditis when there is severe damage to the valve due to infection. Surgical intervention not only helps remove the infected tissue but also facilitates recovery, especially when combined with appropriate antimicrobial therapy.
Why is antimicrobial therapy important in treating Aerococcus urinae endocarditis?
Antimicrobial therapy plays a crucial role in the management of Aerococcus urinae endocarditis as it targets the bacterial infection effectively. In many cases, initial treatment involves intravenous ceftriaxone, which is adjusted based on drug susceptibility testing, ensuring the selected antibiotic effectively combats the identified strain of A. urinae.
What has recent research revealed about Aerococcus urinae in endocarditis cases?
Recent research emphasizes the need for increased awareness of Aerococcus urinae as a potential pathogen in infective endocarditis cases. Studies highlight the risk factors associated with A. urinae infections and advocate for improved diagnostic methods to ensure timely and appropriate treatment.
How does a previous history of urinary tract infections relate to Aerococcus urinae endocarditis?
A previous history of urinary tract infections is a significant risk factor for developing Aerococcus urinae endocarditis. This bacterium is predominantly found in the urinary tract, and prior urinary disturbances can predispose individuals to subsequent cardiovascular infections affecting the heart valves.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Case Overview | A 61-year-old man in New York experienced recurrent Aerococcus urinae endocarditis affecting both native and bioprosthetic tricuspid valves. |
| Diagnosis | Identified through blood cultures and echocardiograms revealing large masses on valve leaflets. |
| Clinical Presentation | The patient presented symptoms including weakness, dyspnea, and painful lesions post-carnivore diet switch. He had a significant medical history and prior endocarditis diagnosis. |
| Treatment | Started on ceftriaxone, switched to penicillin G, followed by tricuspid valve replacement. |
| Outcome | The patient showed no residual symptoms after six weeks of treatment. |
| Discussion | A. urinae is often misidentified; increased awareness and improved diagnostics are needed for proper management. |
Summary
Aerococcus urinae endocarditis is a rare but serious condition that can recur in patients with pre-existing heart valve issues. In the highlighted case, a 61-year-old man successfully overcame a complex treatment journey involving antimicrobial therapy and surgical intervention. This case reveals the significance of accurate diagnosis and awareness regarding A. urinae, traditionally misidentified in clinical settings. Effective management strategies and further research into Aerococcus urinae endocarditis will enhance patient outcomes and treatment protocols.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.