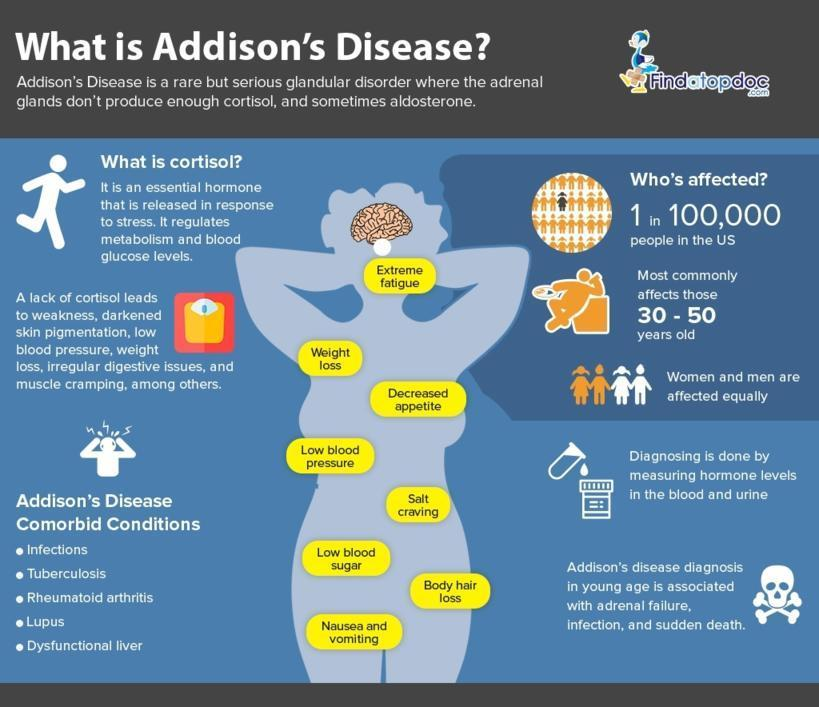
**Addison’s disease** is a serious endocrine disorder that arises when the adrenal glands fail to produce sufficient hormones, particularly cortisol and aldosterone. This condition can lead to various symptoms, significantly impacting a person’s quality of life. The **causes of Addison’s disease** often include autoimmune attacks on the adrenal glands, infections, and other underlying health issues. Recognizing the **symptoms of Addison’s disease** is crucial for timely intervention, as untreated cases can lead to life-threatening complications. In addition to human health, **Addison’s disease in dogs** also presents unique challenges, requiring careful **diagnosing Addison’s disease** in pets and appropriate **treatment for Addison’s disease** to ensure their well-being.
Addison’s disease, also referred to as primary adrenal insufficiency, is a condition characterized by inadequate hormone production from the adrenal glands. This disorder can stem from various factors, including autoimmune diseases, infections, or genetic predispositions, and it manifests through a range of symptoms such as fatigue, weight loss, and low blood pressure. The diagnosis of this adrenal insufficiency involves evaluating hormone levels and conducting specific tests. Effective management and treatment strategies are essential to support individuals and pets alike, ensuring they maintain a healthy lifestyle despite the challenges posed by this condition. Understanding the nuances of this endocrine disorder is vital for both human healthcare providers and veterinarians.
Understanding the Causes of Addison’s Disease
Addison’s disease is primarily caused by the autoimmune destruction of adrenal glands, leading to insufficient hormone production. This condition can be attributed to various factors, including genetic predisposition and environmental triggers. In some cases, infections such as tuberculosis or other diseases affecting the adrenal glands can also lead to adrenal insufficiency. Understanding these causes is crucial for early diagnosis and management.
Additionally, Addison’s disease can sometimes be secondary to other disorders affecting the pituitary gland, which regulates adrenal function. Conditions like pituitary tumors or adrenal tumors can disrupt hormonal balance, leading to symptoms of adrenal insufficiency. Recognizing these underlying causes is vital for effective treatment and prevention of complications associated with this disease.
Identifying Symptoms of Addison’s Disease
The symptoms of Addison’s disease often develop gradually and can be easily overlooked. Common symptoms include chronic fatigue, muscle weakness, and significant weight loss due to decreased appetite. Patients may also experience low blood pressure, which can result in dizziness or fainting spells, particularly during stressful situations. Skin changes, including hyperpigmentation, are also characteristic signs of this disorder.
Another critical symptom to note is the risk of an adrenal crisis, which can occur if Addison’s disease remains untreated. An adrenal crisis can lead to severe complications such as low blood sugar, shock, and even death if not addressed promptly. Therefore, recognizing these symptoms early on is crucial for initiating appropriate treatment and preventing life-threatening situations.
Addison’s Disease Symptoms in Dogs
Just like in humans, Addison’s disease can significantly affect dogs, leading to a variety of symptoms. Canine patients may present with gastrointestinal issues such as vomiting and diarrhea, which can cause dehydration and lethargy. Additionally, dogs with Addison’s disease often display a lack of energy and may become less active than usual, impacting their quality of life.
Stress intolerance is another major symptom in dogs with Addison’s disease. Unlike healthy dogs, those affected may struggle to cope with stress, leading to episodes of weakness or even collapse during stressful situations. Recognizing these symptoms in pets is essential for timely veterinary intervention and effective management of this condition.
Diagnosis and Treatment for Addison’s Disease
Diagnosing Addison’s disease involves a comprehensive approach, including blood tests and stimulation tests. The ACTH stimulation test is particularly important, as it assesses how well the adrenal glands respond to adrenocorticotropic hormone. Additionally, measuring cortisol and aldosterone levels through blood tests can confirm deficiencies, aiding in the diagnosis.
Once diagnosed, treatment for Addison’s disease primarily involves hormone replacement therapy. Patients typically receive medications such as hydrocortisone to maintain cortisol levels and fludrocortisone to help retain sodium and manage blood pressure. Regular monitoring and dosage adjustments are essential to ensure optimal management of the disease and prevent complications.
The Impact of Addison’s Disease on Overall Health
Addison’s disease can have wider implications for an individual’s overall health, particularly concerning co-occurring autoimmune disorders. Many patients with Addison’s disease may also experience conditions such as vitiligo, type 1 diabetes, or celiac disease. Understanding these associations is important for comprehensive patient care and management.
Moreover, the impact of Addison’s disease extends beyond physical health, affecting mental and emotional well-being. Individuals may experience anxiety or depression due to the chronic nature of the illness and the lifestyle adjustments required for effective management. Addressing these aspects through a holistic approach to treatment can significantly enhance the quality of life for those affected.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of Addison’s disease?
Addison’s disease is primarily caused by the autoimmune destruction of adrenal tissue, resulting in insufficient hormone production. Other causes include infections like tuberculosis and conditions affecting the pituitary gland, which may disrupt hormone regulation.
What are the common symptoms of Addison’s disease in humans?
Symptoms of Addison’s disease in humans often include fatigue, weight loss, low blood pressure, skin darkening, and in severe cases, adrenal crises characterized by extreme weakness and shock.
How is Addison’s disease diagnosed in dogs?
Diagnosing Addison’s disease in dogs typically involves blood tests to evaluate electrolyte levels and adrenal function, along with imaging studies to assess the adrenal glands’ condition.
What treatment options are available for Addison’s disease?
Treatment for Addison’s disease in both humans and dogs involves hormone replacement therapy. Humans may receive hydrocortisone and fludrocortisone, while dogs are treated with glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids to manage symptoms effectively.
Can Addison’s disease occur in pets, and what are its symptoms?
Yes, Addison’s disease can occur in dogs, presenting symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, lethargy, and stress intolerance. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing the condition in pets.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Overview of Addison’s Disease | A rare condition caused by adrenal glands’ inability to produce hormones like cortisol and aldosterone. |
| Causes | Autoimmune destruction, infections, and pituitary gland conditions. |
| Symptoms in Humans | Fatigue, weight loss, low blood pressure, skin changes, and potential adrenal crisis. |
| Symptoms in Dogs | Vomiting, diarrhea, lethargy, and stress intolerance. |
| Diagnosis in Humans | ACTH stimulation tests and blood tests for hormone levels. |
| Diagnosis in Dogs | Blood tests for electrolytes and imaging of adrenal glands. |
| Treatment in Humans | Hormone replacement therapy with hydrocortisone and fludrocortisone. |
| Treatment in Dogs | Hormone replacement therapy with glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids. |
| Impact of Addison’s Disease | Associated with other autoimmune disorders like vitiligo and type 1 diabetes. |
Summary
Addison’s disease is a serious condition that requires prompt recognition and treatment to improve health outcomes. This disease, characterized by the adrenal glands’ inability to produce sufficient hormones, can affect both humans and pets. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for managing the condition effectively. Early identification of symptoms, whether in people or animals, enables timely medical intervention, which can prevent complications and enhance quality of life. By maintaining awareness of Addison’s disease, individuals can take proactive measures to monitor and manage their health, ensuring better outcomes for themselves and their pets.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.