Acute pancreatitis is a critical condition that can significantly disrupt an individual’s health and quality of life. Characterized by sudden and intense abdominal pain, this inflammatory disorder often arises due to various factors, including excessive alcohol consumption and gallstones. Recognizing the acute pancreatitis symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, and fever, is vital for prompt diagnosis and treatment. Effective management strategies, including dietary adjustments and therapeutic interventions, are crucial in addressing both the immediate effects and long-term implications of this condition. In this article, we will explore the causes, diagnosis, and treatment for acute pancreatitis, shedding light on recent developments that could improve patient outcomes.
Acute pancreatitis, also known as sudden pancreatic inflammation, is a severe health issue that can manifest with a variety of symptoms and complications. This condition often results from factors such as alcohol abuse or gallstone blockage, leading to inflammation of the pancreas. Understanding the underlying causes and recognizing the signs of this disease are essential for timely intervention and effective treatment. The management of acute pancreatic inflammation includes not only medical therapies but also dietary modifications to support recovery. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the diagnosis, symptoms, and innovative treatment strategies for managing this often-overlooked condition.
Understanding Acute Pancreatitis Symptoms
Acute pancreatitis symptoms can manifest suddenly and vary in intensity. The hallmark of this condition is intense abdominal pain, often felt in the upper abdomen and sometimes radiating to the back. Patients may describe the pain as a steady ache or sharp stabbing sensation. Accompanying symptoms often include nausea and vomiting, which can lead to dehydration and exacerbate the patient’s discomfort. Other signs such as fever and an increased heart rate may also indicate a systemic response to the inflammation in the pancreas.
In addition to the classic symptoms, some patients may experience more subtle signs that can go unnoticed. These ‘silent signs’ may include changes in appetite or digestion, which could signal the onset of more severe complications. It is crucial to recognize these symptoms early to seek prompt medical attention, as untreated acute pancreatitis can lead to further health deterioration, including organ failure.
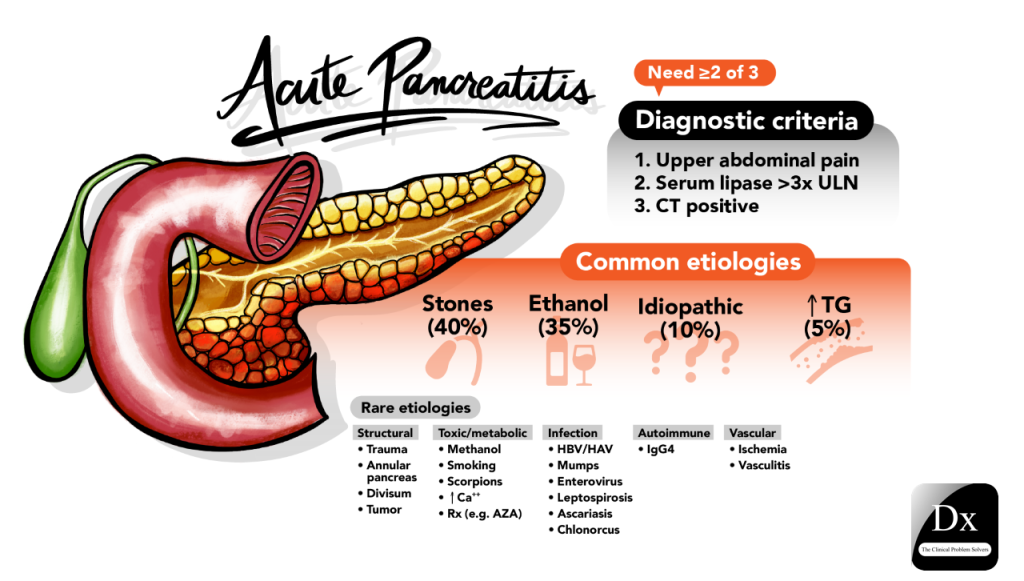
Causes and Risk Factors of Acute Pancreatitis
The causes of acute pancreatitis are multifactorial, with excessive alcohol consumption being a significant risk factor. Alcohol can irritate the pancreas, leading to inflammation and subsequent episodes of acute pancreatitis. Additionally, gallstones are another leading cause, as they can obstruct the pancreatic duct and trigger inflammation. Certain medications and abdominal injuries are also notable contributors to the onset of this condition, highlighting the importance of understanding and addressing these risk factors.
Identifying and managing these risk factors is essential for preventing acute pancreatitis. For instance, individuals at risk due to alcohol consumption should be encouraged to adopt healthier lifestyle choices and limit their intake. Furthermore, healthcare providers must remain vigilant in recognizing signs of gallstones or other underlying conditions that could precipitate acute pancreatic inflammation, ensuring timely intervention and patient education.
Diagnosis and Imaging Techniques for Acute Pancreatitis
Diagnosing acute pancreatitis primarily involves a combination of clinical evaluation and imaging studies. Typically, a healthcare provider will begin with a thorough medical history and physical examination to assess symptoms. Following this, imaging techniques such as ultrasound are often utilized to visualize the pancreas and surrounding tissues. Ultrasound can help identify swelling and fluid accumulation but is not always definitive.
For a more comprehensive assessment, contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) scans are preferred due to their detailed imaging capabilities. CT scans provide critical insights into the pancreas’s structure and can reveal complications like necrosis or abscess formation. Accurate diagnosis is vital, as it informs the management plan, including necessary treatments and dietary modifications to support recovery.
Treatment Options for Acute Pancreatitis
The treatment for acute pancreatitis varies based on the severity of the condition. In mild cases, hospitalization may not be necessary, and patients can often manage symptoms at home with dietary adjustments and pain relief. However, severe cases typically require hospitalization, where patients may receive intravenous (IV) fluids, pain management, and nutritional support as needed. Fasting is commonly recommended initially to allow the pancreas to rest and recover.
Addressing the underlying causes is equally important in treatment. For instance, if gallstones are identified as a contributing factor, surgical intervention may be necessary. Additionally, patients should receive counseling on lifestyle changes, particularly regarding alcohol cessation, to prevent future episodes of acute pancreatitis. This multifaceted approach is crucial for effective treatment and long-term management.
Dietary Management and Lifestyle Changes for Acute Pancreatitis
Diet plays a crucial role in the management and prevention of acute pancreatitis. A low-fat diet is generally recommended to minimize stress on the pancreas, while a diet rich in carbohydrates and proteins can support recovery. Patients are advised to avoid high-fat foods, which can trigger inflammation and exacerbate symptoms. Nutritional support is carefully managed as patients stabilize, gradually reintroducing foods that are gentle on the digestive system.
In addition to dietary considerations, lifestyle changes are essential for preventing future episodes of acute pancreatitis. This includes promoting regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding alcohol consumption. Educating patients on the importance of these lifestyle modifications can significantly reduce their risk of recurrence and improve overall health outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common acute pancreatitis symptoms to look out for?
Common symptoms of acute pancreatitis include severe abdominal pain, often described as sharp or dull, nausea and vomiting, fever, increased heart rate, and a swollen abdomen. It’s crucial to recognize these symptoms early to seek prompt medical attention.
What are the primary causes of acute pancreatitis?
The primary causes of acute pancreatitis include excessive alcohol consumption, gallstones that block the pancreatic duct, certain medications that can irritate the pancreas, and abdominal injuries. Understanding these causes is vital for prevention and management.
How is acute pancreatitis diagnosed effectively?
Acute pancreatitis diagnosis typically involves imaging studies such as ultrasound and contrast-enhanced CT scans. These imaging techniques help assess the condition of the pancreas and surrounding tissues, providing crucial information for treatment planning.
What treatment options are available for managing acute pancreatitis?
Treatment for acute pancreatitis depends on severity and may include hospitalization, intravenous fluids, pain management, fasting to allow the pancreas to recover, and addressing underlying causes such as gallstones or alcohol cessation.
What dietary changes are recommended for someone recovering from acute pancreatitis?
A low-fat diet rich in carbohydrates and proteins is recommended for individuals recovering from acute pancreatitis. Patients should avoid high-fat foods to reduce stress on the pancreas and prevent future episodes.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Acute pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas causing severe abdominal pain and potential complications. |
| Recent Trends | Increasing cases among young adults, particularly linked to alcohol consumption. |
| Therapeutic Advances | Vitamin B12 is being researched as a potential treatment to reduce inflammation. |
| Emerging Strategies | Focus on mitochondrial homeostasis for managing cellular energy and pancreatic health. |
| Symptoms | Severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, increased heart rate, and swollen abdomen. |
| Causes | Excessive alcohol use, gallstones, certain medications, and abdominal injuries. |
| Diagnosis | Ultrasound and contrast-enhanced CT scans are used for diagnosis. |
| Treatment | Includes hospitalization, IV fluids, pain management, and dietary changes. |
| Dietary Management | A low-fat diet rich in proteins and carbohydrates is recommended for recovery. |
Summary
Acute pancreatitis is a serious condition that poses significant health risks, particularly among younger populations. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and the latest treatments is crucial for effective management. Recent trends indicate a rise in cases linked to lifestyle choices, such as alcohol consumption, while new research into Vitamin B12 and mitochondrial health presents promising avenues for future therapies. By raising awareness and promoting healthier lifestyles, we can combat the increasing incidence of acute pancreatitis and improve patient outcomes.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.