Walking pneumonia, a mild yet highly contagious respiratory infection caused by the bacteria Mycoplasma pneumoniae, is seeing a concerning rise in cases, particularly among children. Many are unaware they’ve contracted this condition, as walking pneumonia symptoms often blend in with everyday ailments, making it difficult to diagnose early. Nonetheless, it can present with persistent cough, sore throat, and fatigue, prompting the need for walking pneumonia treatment, especially when symptoms worsen. Understanding the walking pneumonia causes is essential for prevention, particularly in children’s health, where the infection has spiked dramatically. With traditional measures like handwashing and vaccines being more critical than ever, being informed about walking pneumonia can help reduce its footprint in households.
Often referred to as atypical pneumonia, walking pneumonia is characterized by a less severe symptom profile compared to traditional pneumonia, making it easier for individuals to continue with daily activities despite being infected. It predominantly affects younger populations, particularly kids, who may experience unexpected respiratory symptoms due to the bacteria Mycoplasma pneumoniae. As respiratory infections continue to circulate widely, understanding the nuances of conditions like walking pneumonia becomes essential for effective treatment and management. Parents, in particular, should be vigilant about recognizing walking pneumonia symptoms to seek timely care and prevent spread within families. With common ailments and respiratory illnesses on the rise, keeping abreast of such infections can aid in safeguarding community health.
Understanding Walking Pneumonia: Causes and Symptoms
Walking pneumonia is primarily caused by the bacterium Mycoplasma pneumoniae, which is often responsible for mild respiratory infections. This condition, although not as severe as traditional pneumonia, can still lead to notable symptoms, including a persistent cough, sore throat, severe fatigue, and headaches. One of the challenges with walking pneumonia is that many individuals may not recognize they are infected, as their immune systems often combat the bacteria without severe effects. However, in some cases, particularly among children and those with weakened immune systems, the infection can exacerbate and lead to more serious conditions like severe pneumonia or even encephalitis.
Recognizing the symptoms of walking pneumonia is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. Symptoms often develop gradually and may include low-grade fever and a dry cough that does not resolve easily. Unlike traditional pneumonia, walking pneumonia does not usually present with significant nasal or sinus congestion, making it a bit tricky to identify. As such, health professionals recommend that patients who experience unresolved symptoms past a week seek medical evaluation, especially for those in vulnerable age groups like children, who are seeing an increase in diagnoses.
The Rising Incidence of Walking Pneumonia in Children
Recent data indicates a concerning rise in walking pneumonia cases among children, especially those between 2 to 17 years old. This spike has been attributed to various factors, including gaps in immunity resulting from reduced exposure to common pathogens during the Covid-19 pandemic. As children were sheltered from typical environmental germs, their immune systems did not build a sufficient defense against bacterial infections like Mycoplasma pneumoniae, leading to increased vulnerability. Statistics suggest that walking pneumonia cases in children aged 2-4 years rose substantially from 1.0% to 7.2%, highlighting an urgent need for awareness and preventive measures.
The contagious nature of walking pneumonia is another point of concern for families. Once infected, children can easily spread the bacteria to their siblings, parents, or classmates. Health experts emphasize that roughly 80% of children in the same household could contract the illness if one member is infected. Consequently, preventative strategies such as handwashing, social distancing during outbreaks, and the use of masks can significantly reduce transmission risks. Schools and daycares are particularly impacted, as these environments often act as breeding grounds for respiratory infections, making vigilance essential for maintaining health in these settings.
Effective Treatment Options for Walking Pneumonia
While walking pneumonia is categorized as mild compared to regular pneumonia, effective treatment is still vital to manage symptoms and prevent complications. The primary approach to treating walking pneumonia typically involves the administration of antibiotics, which target the Mycoplasma pneumoniae bacteria. These antibiotics can help eliminate the infection and reduce symptoms significantly within a few days. Additionally, over-the-counter cough suppressants and fever reducers may be recommended to alleviate symptoms and improve the patient’s comfort during recovery.
It’s important to note that despite the mild nature of walking pneumonia, patients should be monitored closely, especially children. Parents are advised to consult their pediatrician if symptoms worsen or do not improve after a week, as early intervention can prevent the escalation of the illness. A thorough evaluation can also rule out other potential respiratory issues and ensure that the treatment plan is tailored to the child’s specific needs. Overall, understanding and addressing walking pneumonia promptly can lead to better health outcomes for affected individuals.
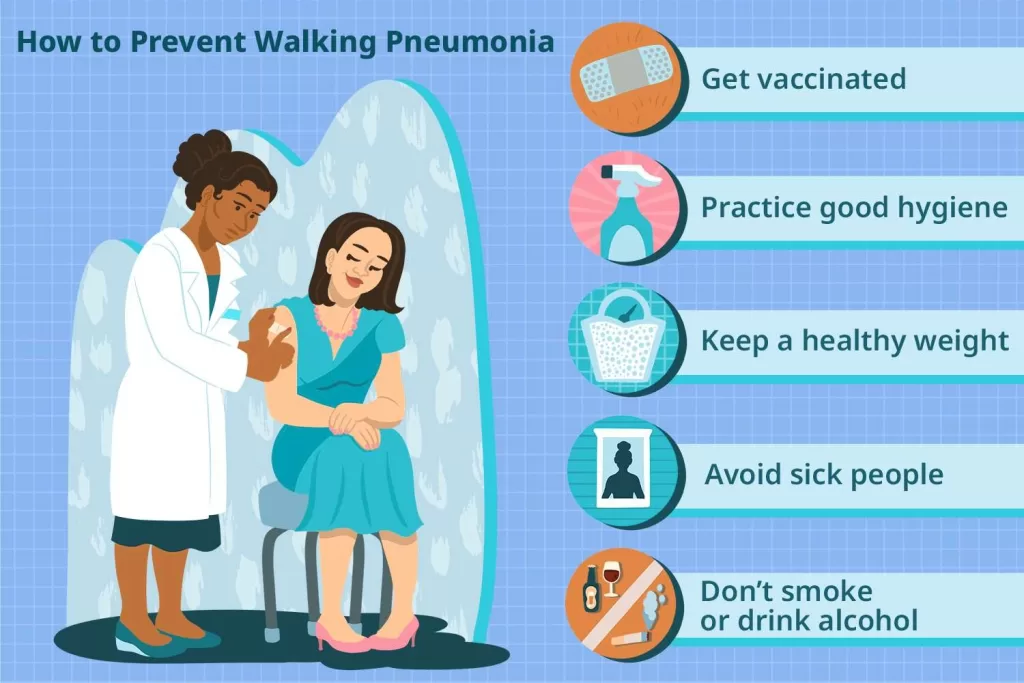
Preventing the Spread of Walking Pneumonia
Preventative measures play a crucial role in controlling the outbreak of walking pneumonia, particularly in communities with high populations of children. Encouraging proper hygiene practices, such as frequent handwashing with soap and water, is vital in reducing the transmission of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Families should also encourage children to avoid close contact with infected individuals to minimize the risk of spreading the infection. In addition, respiratory etiquette, like covering one’s mouth and nose while sneezing or coughing, can significantly contribute to preventing airborne transmission in crowded settings like schools and daycare centers.
Furthermore, maintaining overall health through regular vaccinations, healthy diets, and sufficient sleep can bolster the immune system and equip it to handle infections more effectively. Public health campaigns emphasizing vaccinations against respiratory viruses, including flu and Covid-19, are essential in building community resilience against opportunistic infections such as walking pneumonia. By adopting these strategies, families can help safeguard their children and mitigate the spread of respiratory infections in their communities.
The Role of Mycoplasma Pneumoniae in Respiratory Infections
Mycoplasma pneumoniae is a unique bacterium that significantly contributes to respiratory infections, especially walking pneumonia. This microorganism lacks a cell wall, which makes it resistant to many common antibiotics that target cell wall synthesis. As a result, treatment often requires specific antibiotics effective against this type of bacteria. Understanding the nature of Mycoplasma pneumoniae is essential for developing effective public health strategies to manage and treat respiratory infections, particularly in vulnerable populations such as children.
Given its role in the increasing incidence of walking pneumonia, healthcare providers emphasize the importance of awareness surrounding Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Many parents and caregivers may not be familiar with this bacterium and its association with mild yet highly contagious respiratory illnesses. Public health education can help families recognize the symptoms early and encourage prompt medical attention, ultimately leading to better health outcomes and decreased transmission rates within communities.
Differentiating Walking Pneumonia from Other Respiratory Illnesses
Distinguishing walking pneumonia from other respiratory conditions is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. Many individuals may confuse it with viral infections such as the common cold or the flu, which often present with nasal congestion and sinus symptoms that are less typical of walking pneumonia. Understanding these differences is key to preventing misdiagnosis and ensuring patients receive the appropriate care. Healthcare professionals often look for specific symptoms like a persistent dry cough, fatigue, and low-grade fever when assessing for walking pneumonia.
In a clinical setting, the diagnosis of walking pneumonia can involve testing methods similar to those for Covid-19, such as throat or nasal swab tests. This approach allows for a more accurate identification of Mycoplasma pneumoniae as the causative factor. Moreover, it is important for patients to communicate their symptoms effectively, as vague descriptions can lead to incorrect assessments. By improving the ability to differentiate walking pneumonia from other respiratory conditions, healthcare providers can enhance treatment strategies and reduce the risk of complications.
Impact of Seasonal Changes on Walking Pneumonia Cases
The incidence of walking pneumonia can often fluctuate with seasonal changes, as respiratory illnesses generally see spikes during the colder months. As people spend more time indoors, the likelihood of transmission increases, particularly in household settings. During these times, families are urged to remain vigilant about preventing the spread of infections, including walking pneumonia. Researchers note that certain times of the year, like late fall or early spring, may present higher risks for outbreaks, driven by factors such as increased indoor crowding and limited ventilation.
Additionally, awareness around respiratory illnesses often peaks during flu season, prompting individuals to remain more observant regarding symptoms that may arise. Understanding the relationship between seasons and the incidence of walking pneumonia can help families prepare for potential outbreaks. By promoting public awareness campaigns, communities can educate members on recognizing symptoms early and seeking prompt care, ultimately reducing the burden of illness during peak respiratory infection seasons.
The Importance of Seeking Medical Attention for Walking Pneumonia
Despite the milder nature of walking pneumonia, recognizing the importance of seeking medical attention remains crucial. Many individuals may assume that their symptoms are manageable and do not require a doctor’s visit. However, lingering symptoms or worsening conditions over a week indicate potential complications that warrant professional evaluation. Medical check-ups can provide proper diagnosis and initiate timely treatment, helping to stave off more serious health issues related to the infection.
Moreover, education about walking pneumonia can empower patients and parents to take charge of their health. By understanding the symptoms and their significance, patients are more likely to respond appropriately to their condition. Encouraging discussions about respiratory health within families can foster an informed perspective regarding when to seek assistance. Ultimately, prioritizing health by recognizing when to consult a healthcare provider can dramatically improve outcomes for individuals affected by walking pneumonia.
Long-Term Effects of Walking Pneumonia on Respiratory Health
While walking pneumonia is generally considered mild, its potential long-term effects should not be overlooked. Some individuals may experience lingering respiratory issues following the initial infection, such as chronic cough or increased susceptibility to future respiratory infections. In children, the implications can be even more pronounced, with cases of severe pneumonia or asthma exacerbations occurring as a result of the infection. Thus, ongoing research into the long-term consequences of walking pneumonia is essential to understanding and addressing these health challenges.
Recognizing the importance of respiratory health in the aftermath of walking pneumonia can motivate patients to adopt healthier lifestyles. Engaging in regular physical activity, avoiding smoke exposure, and maintaining a balanced diet with appropriate nutrients can support lung health post-infection. Health professionals can play a critical role in guiding individuals on managing their respiratory health long after recovery, ensuring that previous infections do not hinder their overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common walking pneumonia symptoms to look for?
Common walking pneumonia symptoms include a persistent cough, mild fever, sore throat, tiredness, and headaches. Unlike traditional pneumonia, these symptoms are usually mild, which can lead many to overlook the infection.
What causes walking pneumonia and how is it transmitted?
Walking pneumonia is primarily caused by the bacterium Mycoplasma pneumoniae. It is highly contagious and spreads easily through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
How is walking pneumonia treated effectively?
Walking pneumonia can be treated effectively with antibiotics, which help combat the Mycoplasma pneumoniae bacteria. It’s important to consult a healthcare provider for appropriate treatment recommendations.
Is walking pneumonia common in children?
Yes, walking pneumonia is becoming more common in children, with increased infection rates noted. Children aged 2-4 years and 5-17 years are particularly vulnerable, as their immune systems may not be fully prepared for such infections.
What are the potential complications of walking pneumonia?
While walking pneumonia is usually mild, potential complications can include severe pneumonia, worsening of asthma, or even encephalitis. It is crucial to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen.
How does walking pneumonia differ from regular pneumonia?
Walking pneumonia is a milder form of pneumonia, often resulting in less severe symptoms than regular pneumonia. It typically does not cause significant nasal congestion, distinguishing it from viral respiratory infections.
How is walking pneumonia diagnosed?
Walking pneumonia can be diagnosed using a throat or nose swab, similar to tests for other respiratory infections. If symptoms linger for more than five to seven days, a doctor’s visit is advised to rule out walking pneumonia.
What are the preventative measures for walking pneumonia?
Preventative measures for walking pneumonia include regular hand washing, covering your mouth when coughing or sneezing, and reducing close contact with infected individuals, especially in family settings.
Can adults also get walking pneumonia, and what are the symptoms?
Yes, adults can get walking pneumonia. They typically experience milder symptoms such as a persistent cough and aches without significant nasal congestion, unlike more severe respiratory infections.
How has walking pneumonia incidence changed in recent years?
Recent data indicates a rise in walking pneumonia incidences, especially among children, with rates increasing significantly since the fall of 2024, likely due to immunity gaps from reduced exposure during the COVID-19 pandemic.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Increase in Cases | Walking pneumonia cases are rising, particularly in children. |
| Definition | A mild respiratory infection caused by the bacteria Mycoplasma pneumoniae. |
| Symptoms | Common symptoms include cough, sore throat, fatigue, and headache. Severe cases can lead to complications. |
| Diagnosis | Diagnosis can be done via a nose or throat swab. |
| Transmission | Highly contagious; spreads easily within families. |
| Treatment | Treatable with antibiotics; traditional preventative measures apply. |
Summary
Walking pneumonia is becoming an increasing concern, particularly for children where cases have notably risen. This mild respiratory infection, caused by the Mycoplasma pneumoniae bacteria, often leads to subtle symptoms that can worsen if left untreated. Parents should be vigilant for signs and seek medical advice if symptoms persist, as the infection is quite contagious and can spread rapidly among young children. Taking precautionary health measures, such as regular hand washing and proper coughing etiquette, is essential in curbing the spread of walking pneumonia.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.