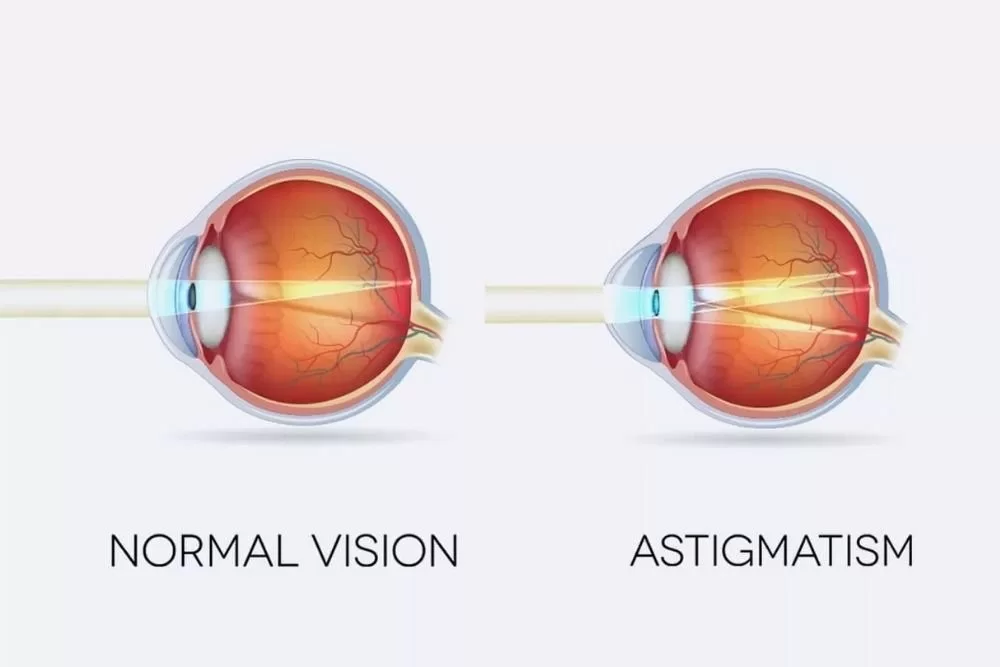
Understanding Astigmatism is crucial for anyone experiencing vision difficulties. This common refractive error occurs when the cornea or lens is irregularly shaped, leading to symptoms such as blurred vision, eyestrain, and headaches. Many individuals may not realize they have this condition until they undergo an astigmatism diagnosis, which can reveal the underlying causes of their vision problems. Fortunately, there are various astigmatism treatment options available, including astigmatism glasses and specialized contact lenses designed to improve visual clarity. By learning about astigmatism symptoms and available corrections, individuals can take proactive steps to enhance their eye health.
Astigmatism, often described as an irregular curvature of the eye, can cause significant challenges for those affected. This optical condition leads to distorted or blurred vision, making it difficult to focus on objects clearly. Alternative terms such as “refractive error” or “uneven corneal shape” are frequently used to describe this phenomenon. By understanding the mechanics of this eye condition, individuals can better appreciate the importance of regular eye examinations and the need for effective visual aids. With advancements in optical technology, options for managing astigmatism have expanded, providing relief and clearer vision for many.
Understanding Astigmatism: Causes and Effects
Astigmatism is primarily caused by the irregular shape of the cornea or lens, which prevents light from focusing properly on the retina. This condition can be inherited, or it may develop as a result of eye injury, surgery, or certain diseases. When light rays enter the eye, they do not converge at a single point but rather scatter, leading to blurred or distorted vision. Understanding the causes of astigmatism is crucial for effective management and treatment.
Moreover, astigmatism can be categorized into different types based on its severity and the nature of the curvature—regular or irregular. Regular astigmatism occurs when the cornea is more curved in one direction than the other, while irregular astigmatism indicates more complex distortions, often resulting from trauma or surgery. Recognizing these distinctions is essential for both patients and eye care professionals in determining the most appropriate course of treatment.
Common Symptoms of Astigmatism
Individuals with astigmatism often experience a range of symptoms that can significantly affect their day-to-day activities. The most common symptom is blurred vision, which can occur at all distances—close-up or far away. This blurriness can lead to difficulties in reading, driving, or even recognizing faces. Additionally, many people with astigmatism report experiencing eyestrain, particularly after prolonged periods of focusing on tasks such as reading or using digital devices.
Headaches are another frequent complaint among those suffering from astigmatism. The need to squint or strain to see clearly can contribute to recurring tension headaches, making it essential for individuals to seek proper diagnosis and treatment. Furthermore, difficulty with night vision is a notable symptom, as many astigmatic individuals find it particularly challenging to see in low-light conditions. This can be especially concerning for those who drive at night, underscoring the importance of addressing astigmatism.
Astigmatism Diagnosis: What to Expect
Diagnosing astigmatism involves a series of eye tests conducted by an eye care professional. The process usually begins with a visual acuity test, where patients read letters from an eye chart to determine how well they can see at various distances. If astigmatism is suspected, further tests such as keratometry and refraction tests are performed to measure the curvature of the cornea and assess the precise prescription needed for corrective lenses.
During the keratometry test, a keratometer is used to measure the surface curvature of the cornea, providing important data on the degree of astigmatism. Meanwhile, the refraction test helps determine the specific lenses that will improve the patient’s vision. These comprehensive assessments are critical in creating an accurate diagnosis and formulating an effective treatment plan tailored to the individual’s needs.
Astigmatism Treatment Options: From Glasses to Surgery
Once diagnosed, various treatment options are available to correct astigmatism and improve vision clarity. The most common solution involves the use of corrective lenses, including glasses or contact lenses. Prescription glasses are specifically designed to counteract the uneven curvature of the cornea, providing a clearer visual experience. For those who prefer contacts, toric lenses are available, designed with different optical powers to address the specific needs of astigmatism.
In more severe cases, surgical options may be considered to reshape the cornea, with procedures such as LASIK or PRK proving effective for many patients. These surgeries aim to provide long-term correction of astigmatism, reducing or eliminating the need for glasses or contacts. However, candidates for these procedures must undergo thorough evaluations to ensure they are suitable for surgical intervention, highlighting the importance of consultation with an experienced eye care provider.
Living with Astigmatism: Tips for Management
Managing astigmatism effectively involves adopting certain lifestyle habits that can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall eye health. Regular eye exams are crucial, as they allow for the monitoring of vision changes and timely adjustments to prescriptions. Eye care professionals recommend scheduling these check-ups at least once a year, especially for individuals with worsening symptoms.
In addition to routine eye care, protecting your eyes from harmful UV rays by wearing sunglasses is essential, particularly when spending time outdoors. Staying hydrated also plays a significant role in eye health, as proper hydration can help maintain moisture in the eyes. Lastly, taking breaks during extended periods of screen time can reduce eyestrain, making daily activities more comfortable for individuals living with astigmatism.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of astigmatism?
Common astigmatism symptoms include blurry or distorted vision at various distances, eyestrain, frequent headaches, and difficulty seeing at night. Individuals may experience discomfort, especially during tasks that require focused vision, such as reading or using a computer.
What are the causes of astigmatism?
Astigmatism is primarily caused by an irregular shape of the cornea or lens in the eye, leading to uneven bending of light. This can be due to genetics, injury, or conditions affecting the eye. Understanding the causes of astigmatism is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment.
How is astigmatism diagnosed?
Astigmatism diagnosis typically involves several tests, including visual acuity tests, keratometer measurements to gauge corneal curvature, and refraction tests using a phoropter. These assessments help eye care professionals determine the extent and nature of the astigmatism.
What are the treatment options for astigmatism?
Astigmatism treatment options include corrective lenses such as prescription glasses or toric contact lenses specifically designed for astigmatism. In more severe cases, surgical options like LASIK or PRK may be considered to reshape the cornea for improved vision.
Can astigmatism be corrected with glasses?
Yes, astigmatism can be effectively corrected with glasses. Astigmatism glasses are specially prescribed with lenses that compensate for the uneven curvature of the cornea, helping to improve vision clarity and reduce symptoms such as eyestrain and headaches.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition of Astigmatism | Astigmatism is a refractive error caused by an irregular shape of the cornea or lens, leading to blurred or distorted vision. |
| Common Symptoms | 1. Blurry Vision 2. Eyestrain 3. Headaches 4. Difficulty with Night Vision |
| Diagnosis Methods | Visual acuity tests, keratometry, and refraction tests are used to diagnose astigmatism. |
| Treatment Options | 1. Corrective Lenses (glasses/contact lenses) 2. Specialty contact lenses (toric lenses) 3. Surgical options (LASIK, PRK) |
| Management Tips | Regular eye exams, sun protection, hydration, and rest can help manage astigmatism effectively. |
Summary
Understanding Astigmatism is crucial for anyone experiencing vision issues related to this common refractive error. Astigmatism occurs due to an irregular shape of the cornea or lens, leading to blurred and distorted vision. Recognizing the symptoms such as blurry vision, eyestrain, headaches, and difficulty seeing at night allows individuals to seek timely diagnosis and treatment. With advancements in corrective lenses and surgical options, effective management is within reach. Engaging with eye care professionals and adhering to recommended management strategies can significantly enhance the quality of life for those living with astigmatism.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.





Hair Cuts
It抯 actually a great and helpful piece of info. I am happy that you just shared this useful information with us. Please stay us up to date like this. Thanks for sharing.