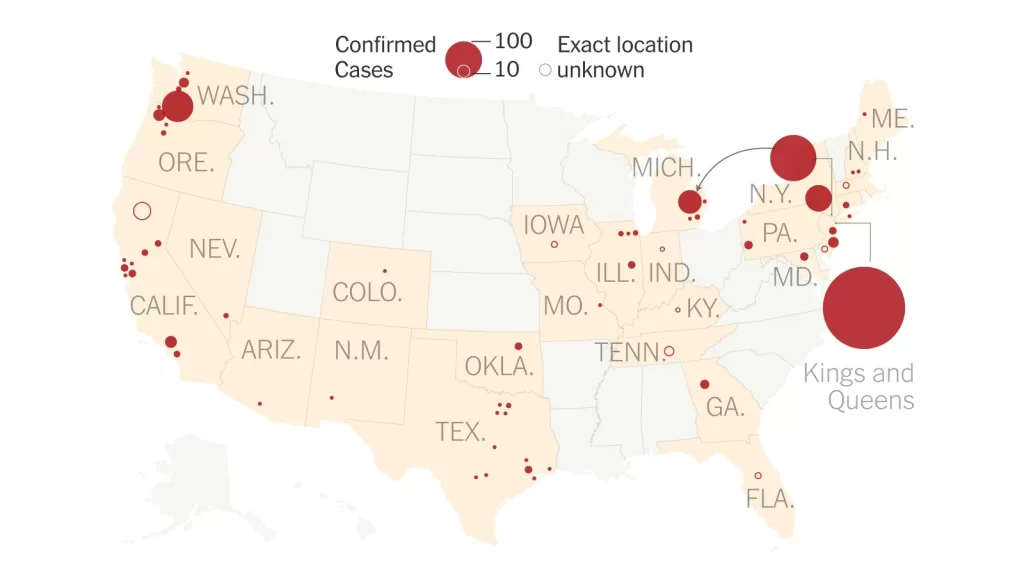
The recent U.S. measles outbreak has raised significant public health concerns as cases balloon across various states, particularly in Texas and New Mexico. With over 633 reported measles cases nationwide as of April 2025, including notable outbreaks in these two regions, health officials are emphasizing the urgent need for vaccination. This substantial increase and the associated risks highlight the impact of declining measles vaccination rates, which have fallen below the critical threshold necessary for herd immunity. Measles spread prevention strategies are now more essential than ever, especially given the interconnectedness of outbreaks in surrounding states like Oklahoma and Kansas. These alarming figures underscore the necessity for communities to prioritize measles vaccinations to protect public health.
The surge in measles infections in the United States mirrors a troubling trend of rising vaccine hesitancy and declining immunization rates. Notably affected areas include Texas and New Mexico, where localized epidemics have prompted health officials to take urgent action. Recent statistics indicate that unvaccinated individuals are the most affected, illustrating the critical role of effective immunization strategies in curtailing the virus’s transmission. Additionally, the outbreak’s implications extend beyond these states, with ripples being felt in neighboring regions like Oklahoma and Kansas, highlighting the need for comprehensive public health initiatives. It is imperative that communities prioritize vaccination efforts to mitigate the impact of these outbreaks and safeguard against future occurrences.
Understanding the Current U.S. Measles Outbreak
The U.S. is currently facing a concerning resurgence of measles, particularly identified through recent outbreaks in Texas and New Mexico. With over 633 reported cases nationwide as of early April 2025, public health officials have emphasized the importance of monitoring these outbreaks closely. The rapid spread of the virus, particularly among unvaccinated populations, highlights the urgent need for increased vaccination efforts and public awareness campaigns. Genetic links have been established between the cases in the neighboring states, indicating that unchecked measles cases can quickly spill over into surrounding communities.
Local health officials in Texas are actively tracking these outbreaks and have noted that the situation may persist for an extended period due to the high number of unvaccinated individuals. In areas like Gaines County, where vaccination rates are alarmingly low, this creates a ripe environment for the virus to proliferate. The related outbreaks that have affected states such as Oklahoma and Kansas further illustrate how critical it is to achieve herd immunity to prevent measles from spreading uncontrollably within vulnerable populations.
The Impact of Measles Cases in Texas and New Mexico
The Texas measles outbreak has tragically included hospitalizations and even fatalities among unvaccinated populations. Reports indicate that as of April 2025, at least 481 individuals in Texas have contracted the virus, with the majority being unvaccinated children. This alarming spike in measles cases not only underscores the risks associated with low vaccination rates but also raises vital public health questions regarding the safety and implementation of vaccine mandates. Recent studies have shown that vaccination rates directly correlate with outbreak severity, making it imperative for communities to prioritize vaccination education.
Similarly, New Mexico has declared an outbreak that reflects the interconnectedness of measles cases across state lines. Despite a higher overall vaccination rate in Lea County, the state still recorded several cases linked potentially to Texas’s ongoing outbreak. Public health officials are on high alert, recognizing that even modest fluctuations in vaccination rates can lead to significant spikes in reported measles cases. Effective public health policies that advocate for consistent vaccination across age groups are essential to halting this potentially devastating trend of rising infectivity.
Measles Vaccination Rates: A Community Concern
Vaccination rates play a pivotal role in controlling the spread of measles and preventing future outbreaks. In communities like Gaines County, Texas, where only 46 percent of kindergarten students have received the M.M.R. vaccine, public health experts warn that without action, these areas may continually face outbreaks. Local health campaigns need to address the misconceptions regarding vaccination and harness the importance of herd immunity, aiming for a vaccination threshold above 94 percent to protect the community as a whole.
Efforts to improve vaccination rates must also extend to informing adults about the benefits of measles immunization. In New Mexico, for example, while the vaccination rate among children and teens stands at a noteworthy 94 percent, adult vaccination remains significantly lower, with only 63 percent having received at least one dose of the vaccine. The disparity reflects a larger issue in public health outreach and may necessitate renewed strategies to engage adult populations in protective health practices, ensuring toda’s vaccination efforts not only benefit children but all community members.
Preventing Measles Spread: Strategies and Recommendations
As measles outbreaks continue to unfold across parts of the U.S., especially in Texas and New Mexico, experts have reiterated that prevention is essential to control the virus’s spread. Health authorities advocate for comprehensive vaccination strategies that emphasize the necessity of both doses of the M.M.R. vaccine for effective protection. By achieving a community-wide vaccination rate of at least 94 percent, we can significantly curb the risk of outbreaks, minimizing potential transmission among unvaccinated individuals and preventing cases linked to international travel.
Additionally, states must implement policies that ensure timely access to vaccinations and ongoing public health education campaigns. By enhancing community awareness of the high infectivity of measles, the seriousness of the disease, and the safety of vaccines, public health officials hope to encourage a cultural shift in the acceptance of vaccinations. This is particularly pertinent in areas with historically low vaccination rates, such as Gaines County, where community engagement is vital for fostering a healthier outlook and combating misinformation surrounding measles and vaccinations.
The Role of Public Health in Vaccination Education
Public health entities play an enormous role in shaping public perception and knowledge about vaccinations. As current outbreaks of measles are linked to a resurgence of vaccine hesitancy, education efforts must target misconceptions while providing factual information about measles vaccination benefits. Community outreach initiatives are pivotal in strengthening public confidence in vaccinations and reducing fears associated with vaccines, helping individuals understand the critical role vaccines play in safeguarding public health.
Furthermore, public health campaigns that include data about the measles outbreaks in Texas and New Mexico can amplify the urgency for vaccination compliance. By sharing personal stories of those affected and emphasizing the strikingly low vaccination rates in specific counties, these campaigns can humanize the statistics and resonate with the public’s emotional side. Emotional appeals can be a strong motivator for change, particularly when statistics demonstrate a direct connection between vaccination coverage and lowered incidence rates of infectious diseases like measles.
Conclusion: Importance of M.M.R. Vaccination
The current measles outbreaks in the U.S. highlight the critical importance of the M.M.R. vaccination in protecting communities against highly contagious diseases. With significant clusters of cases emerging in Texas and New Mexico, the call for increased vaccination efforts has never been clearer. Health experts stress that vaccinations not only prevent individual infections but also protect those unable to get vaccinated, such as infants and individuals with certain medical conditions.
As measles vaccination rates decline, the threat posed by this preventable disease rises concurrently. For the sake of public health, parents, caregivers, and adults must prioritize their vaccinations and support policies that promote higher immunization rates. The fragility of the gains made since the measles elimination in 2000 serves as a stark reminder that vigilance is required, and through collective action, the U.S. can mitigate these outbreaks and safeguard against future risks.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the current measles cases in the U.S. related to the 2025 measles outbreak?
As of April 2025, there have been 633 reported measles cases across the United States, with 582 cases tied to outbreaks and 51 isolated cases, often linked to international travel. The ongoing measles outbreak emphasizes the need for increased vaccination rates to control the spread of the virus.
How is the Texas measles outbreak affecting neighboring states?
The Texas measles outbreak, which has infected at least 481 people, has extended its impact beyond Texas, affecting nearby states such as New Mexico, Oklahoma, and Kansas. Genetic links suggest that the outbreaks in these states are connected, highlighting the importance of vaccinations in preventing further spread.
What actions are being taken in New Mexico regarding the measles outbreak?
In response to the measles outbreak, New Mexico has reported 54 cases primarily in Lea County, which borders Texas. Officials have expressed concerns regarding the unvaccinated population and are urging residents to get vaccinated to prevent further cases associated with the ongoing outbreak.
What vaccination rates are required to control the U.S. measles outbreak?
To effectively prevent measles outbreaks, vaccination rates need to be 94% or higher. However, many regions, including Gaines County in Texas, are reporting lower rates, highlighting the urgent need to improve measles vaccination rates to control the outbreak.
How can measles spread be prevented during the ongoing U.S. measles outbreak?
Prevention of measles spread during the current outbreak involves increasing vaccination coverage. Health experts recommend that at least 94% of the population be vaccinated to effectively halt the spread of the virus. Additionally, public awareness campaigns about the importance of the M.M.R. vaccine are crucial in mitigating outbreaks.
What are the symptoms and complications associated with the measles virus during the U.S. outbreak?
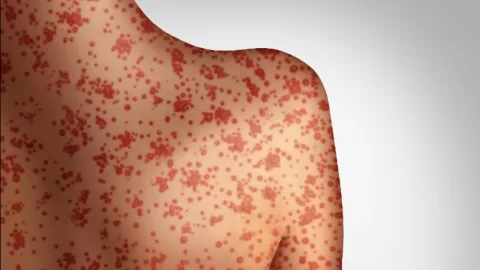
Measles is highly contagious and can lead to severe complications such as pneumonia, brain swelling, and long-term effects like blindness and intellectual disabilities. Symptoms typically resolve within a few weeks, but the risk of serious health issues emphasizes the need for vaccination during outbreaks.
What has contributed to the decline in measles vaccination rates in the U.S.?
Recent declines in measles vaccination rates in the U.S. can be attributed to vaccine hesitancy among certain communities, such as those in Gaines County, Texas, where a large Mennonite population prioritizes home remedies over vaccinations, resulting in lower immunization levels and increased outbreak risks.
What is the link between international travel and the U.S. measles outbreak?
Several isolated cases of measles in the U.S. are linked to international travel. Individuals returning from affected areas can carry the virus back, which has contributed to the current outbreak situation, emphasizing the need for thorough vaccination before traveling.
| State/County | Total Cases | Outbreak Status | Vaccination Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Texas (Gaines County) | 481 | Ongoing Outbreak | 82% (Kindergarten) |
| New Mexico (Lea County) | 54 | Related to Texas Outbreak | 94% (Children and Teens) |
| Kansas | 24 | Linked Cases | Not Specified |
| Oklahoma | 10 | Unspecified Locations | Not Specified |
| Ohio (Ashtabula County) | 10 | International Link | Not Specified |
| New Jersey (Bergen County) | 2 (Former Cases) | Resolved | Not Specified |
Summary
The U.S. measles outbreak has escalated significantly with Texas experiencing the most cases, particularly among unvaccinated individuals. As vaccination rates decline, especially in areas like Gaines County, the risk of outbreaks increases, highlighting the importance of the M.M.R. vaccine in controlling the spread of this highly contagious virus. Continued public awareness and vaccination efforts are crucial to preventing future outbreaks.
The content provided on this blog (e.g., symptom descriptions, health tips, or general advice) is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read on this website. If you believe you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately. Reliance on any information provided by this blog is solely at your own risk.